Laurel diseases

Gardening – What Are Bay Leaf Diseases?

Gardening – plant diseases – Symptoms of white sickness
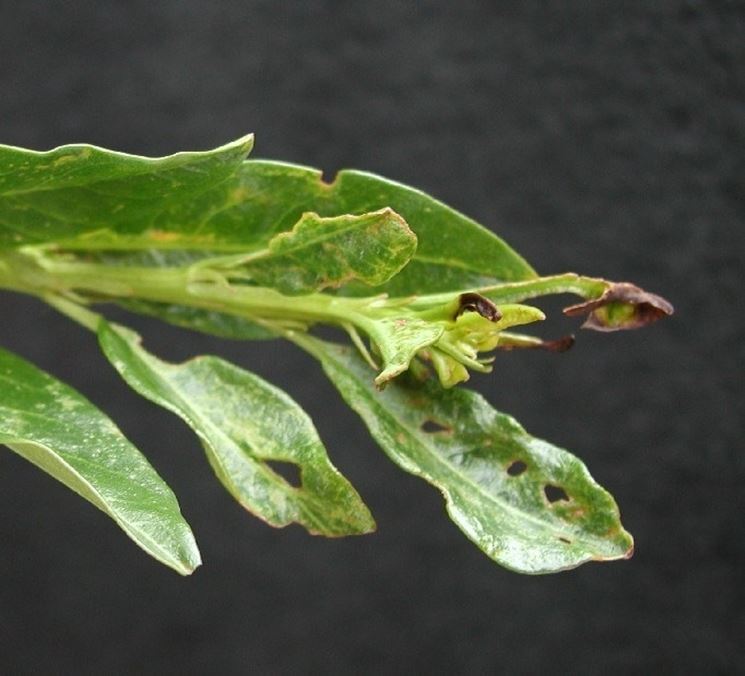

Laurel diseases can have the following symptoms; White powder coating typical of powdery mildew infections that initially grows on the leaf surface. After some time the underlying tissues rot, turning brown and die. Usually as a result of powdery mildew infections, the brown tissue then falls off, often leaving irregular holes in the leaves and shredded edges very similar to the damage done by insects.While fungi and bacteria, more precisely the leaf pathogens called Stigmine and Eupropolella cause spots browns on the leaves. The centers of the spots finally fall off, leaving irregular holes in the leaves that resemble damage from hunting pellets. The bacterium Pseudomonas Syringae in turn causes lesions impregnated with
Gardening – Control over laurel plant diseases
Laurel disease control can be done with non-chemical control systems, however, to prevent infections by natural means, when conditions allow, it can be of little use. The plants usually are born with the problem already inside them and are genetically predisposed to fight it by themselves through the birth of new foliage, so it is advisable to let the plant grow before intervening. of affected leaves to encourage healthy growth. But be careful to prune the plant too much, because this operation if not done well could aggravate the problem. Feeding the plant well can be useful, but usually the laurel is sturdy enough to make this superfluous.
Laurel diseases: Gardening – Biology and spread of laurel plant diseases

For the treatment of laurel diseases, several factors must be taken into account. The pathogenic powdery mildew Podoasphaera pannosa for example also attacks roses and some varieties of peaches, while the Podosphaera tridactyla fungus is found on numerous species of the genus Prunus. As with other types of white disease, this fungus initially grows on the surface of the leaves, feeding on the tissues without killing them, thus spreading the spores that spread the infection into the air. Later the leaves die and later the infection will leave the plant, this makes the plants more robust such as bay leaf among the main carriers of the fungus which often survives even through the winter. You will need this information to understand how the disease spreads and what type of action to take to resolve the problem.




