What fungi affect plants ?: The most harmful fungi

Hello to all gardeners! How are you? Today we are going to talk about the most harmful fungi for the garden. Although we have already mentioned it on other occasions, the term plague and disease are not the same. When we talk about our plants having a plague , we mean that a group of arthropods (mites, insects, crustaceans, …), nematodes or other types of animals are causing damage to our crops. However, when we use the term disease , we refer to the fact that it is fungi, bacteria or viruses that are affecting our plants.

On this occasion, we will focus on fungi , which are a group of microorganisms capable of causing diseases in the orchard or garden.
The most harmful fungi for plants
There are many types of fungi , some may affect the roots (genus Rhizoctonia ), seeds and seedlings (genus Pythium and Phythoptora ), the leaves, the fruit, to the stem or vascular vessels.
However, the most harmful and common fungi to see in our orchards and gardens are the following:
Powdery mildew: ash, bad white or white mold
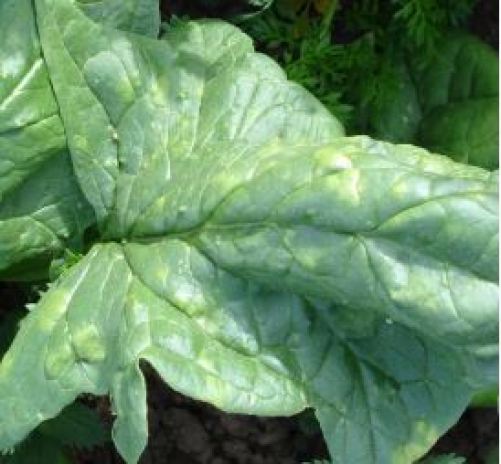
- Species affected: Powdery mildew can affect a wide variety of crops, but without a doubt, it is one of the most damaging fungi on the vine . It is very common in cucurbits: pumpkin, zucchini, cucumber, melon or watermelon . In addition, it can be found in tomato , potato, chard, spinach or beans.
- Description and symptoms: It appears in the form of white spots and turns into a grayish-white powder. Thanks to that white powder, it is one of the easiest fungi to detect. It normally develops in the upper part of the leaves, although it can also spread through the stem or the fruits. Its presence makes photosynthesis difficult. If we don’t control it well, the leaves turn yellow and can dry out.
- Propagation conditions: Humidity and warm temperatures are the ideal conditions for powdery mildew to appear in our garden.

For those of you who have a garden, this fungus also usually affects the leaves of rose bushes.
In the following link you can read how to eliminate hatred from plants.
Mildew
- Affected species: Mildew affects a wide group of plants, highlighting the vine and nightshade (tomato, eggplant , pepper or potato). Other crops damaged by this fungus are strawberries, cucumber, melon, beets, spinach or chard.
- Description and symptoms: It produces greasy-looking spots of different shades on the edges of the leaves or on the fruits, which later turn brown and wither.
- Propagation conditions: This fungus takes advantage of plant wounds or leaf stomata to enter. You can infect them through irrigation water. It requires medium temperature (approximately 20ºC) and high humidity (that is why it usually appears after the rains).
Rust on plant leaves
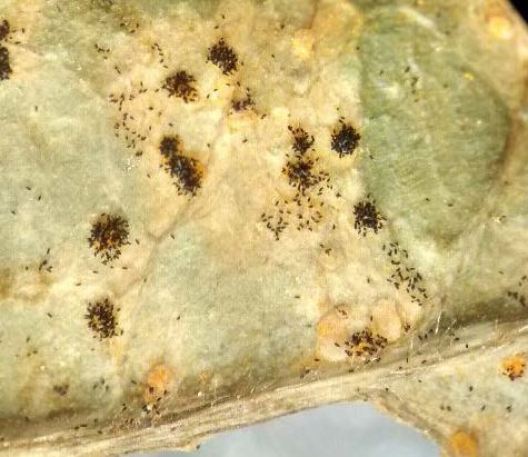
- Species affected: Rust can affect rosebush, garlic, onion, leek, arugula, legumes, asparagus and others.
- Description and symptoms: Orange bumps appear on the underside of the leaves and small yellow spots on the upper surface.
- Propagation conditions: Needs mild temperatures and very high humidity. It can appear after long periods of abundant rains.

Botrytis or gray rot
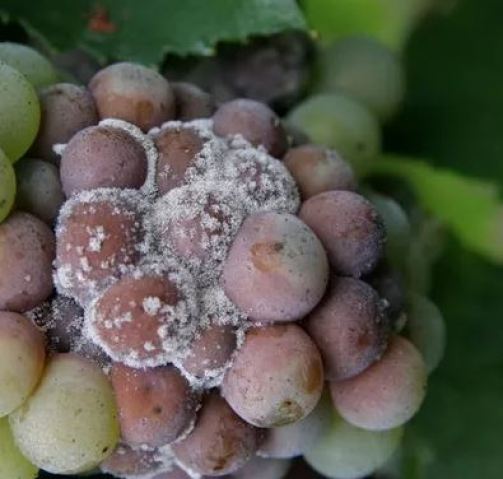
- Species affected: Botrytis mainly affects strawberry, tomato, lettuce, vine, cucumber and eggplant.
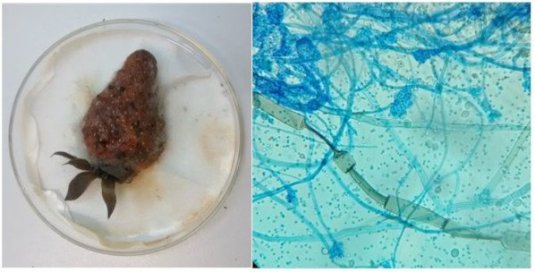
- Description and symptoms: This fungus causes gray rot and the plant tissue appears as if it is rotten. Very common to see if we leave the strawberries for a while in our house.
- Propagation conditions: The Botrytis genus needs high humidity, little ventilation, and mild temperatures to spread.

If anyone is curious to see what this fungus looks like under the microscope , I leave you some photos of a practice I did in the laboratory with a Botrytis infected strawberry :
Marssonina or Black Spot: one of the most harmful fungi in the rose bush
- Species affected: it mainly affects rose bushes and, sometimes, begonias or geraniums.
- Description and symptoms: rounded black spots appear on the leaves, which spread and can cause defoliation. The best way to eliminate it is to remove the affected leaves and destroy them.
- Propagation conditions: Requires mild temperatures and the presence of water. It is spread by splashes of rain.

How to control fungi in the garden?
For today, knowing how to identify them is worth us. But if you want more information on how to control garden fungi in the following link, Lucía explains how to prevent and treat garden fungi in an ecological way .




