Sulfur in Plants: [Use, Advantages, Excesses and Deficiencies]
 Sulfur is part of the secondary nutrients that are recognized in crops by the amount they need to be healthy.
Sulfur is part of the secondary nutrients that are recognized in crops by the amount they need to be healthy.
However, on many occasions this condition is confused with the situation of whether they are more or less important.
It is a fact that being part of the family of the most relevant micronutrients, with calcium and magnesium, it is an essential element.
And we can notice this because a sulfur deficit could be detrimental to the absorption and functioning of other nutrients.
If you had not thought before about the relevance of sulfur for your crops, pay attention because here we will tell you everything.
What is sulfur?
Sulfur is denoted within the chemical elements with the symbol S and at the level of crops it represents one of the three secondary nutrients.
Its importance is associated with keeping plants with a good growth rate, while contributing to their optimal health.
For plants to be able to absorb it from the soil, sulfur must be present in the form of sulfate, manifesting as SO4.
Obtaining this form is relatively simple in the environment because sulfur is very easy to dissolve, although losses can also be generated.
What factors influence crop response to sulfur fertilization?
- Sulfur comes from the decomposition of organic matter in the soil. For this reason, one of the factors that directly influence the correct levels of this element for fertilization is organic matter.
- This means that soils with a high organic matter content will have more available sulfur.
- However, this form is not suitable for plants to absorb, since, as we have already seen, they need the form of sulfates.
- What does happen is that the sulfur from the organic matter goes through a progressive decomposition process that, some time later, will give rise to sulfates.
- Another element that is closely related to the soil’s capacity for sulfur fertilization is pH.
- As in most cases, a soil with a high pH will have less available sulfur.
- Finally, the texture is related to the fact that soils with more clay content will have more sulfur than sandy ones.
- In general, this is due to the level of filtration that each one has, since the sulfur tends to be lost through a process known as leaching.
What is the sulfur content in the soil?
The total amount of sulfur in the soil is variable depending on the factors described above.
This percentage can occupy from 0.005% to 0.04%.
The best way to validate the exact point is through a soil study.
What benefits can a soil rich in sulfur have?
- Soils rich in sulfur make it easier for plants to obtain the amount of element they need for the constitution of their proteins.
- This is because sulfur is an essential part of them, as well as in the formation and functioning of different hormones.
- Another part in which sulfur intervenes, and which is decisive, has to do with the formation of some oils.
- Sulfur also plays a leading role in the proper development of chlorophyll and is present in some reactions at the cellular level.
What disadvantages does an excess of sulfur have?
The main problem that occurs when there is an excess of sulfur has to do with its high competitiveness with nitrogen.
This means that high levels of sulfur can lead to the plant not absorbing and distributing nitrogen well, so there will be a deficit of it.
What crops benefit most from the presence of sulfur in the soil?
- Sulfur is necessary for the development and health of all plant species.
- However, its presence is essential in crops such as garlic and onion.
- In them, they are part of the volatile compounds that they need for their constitution.
- Cereals are another of the crops that greatly benefit from soils rich in sulfur because the level of flour in their composition increases.
- As it also helps develop oils, crops that have to do with oilseeds need it a lot .
- In the case of vegetables, sulfur helps the crops to be much more uniform in size and texture.
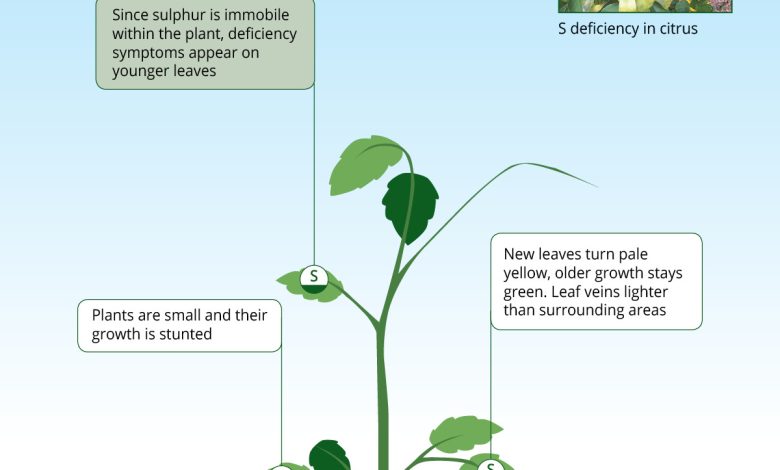
How do we detect deficiency or lack of sulfur in our crops?
Sulfur is closely linked to nitrogen as both are involved in similar processes.
In fact, sulfur helps the plant to better absorb nitrogen.
This results in the lack of sulfur manifesting itself with symptoms very similar to those that would occur if the deficit were nitrogen.
The first thing is the chlorosis that progressively goes through the entire structure of the plant, from the youngest leaves to the oldest.
The reason is that the sulfur mobility pattern is relatively slow, but at the same time it helps to show a uniform appearance throughout the plant.
One way to separate nitrogen chlorosis from sulfur chlorosis is to note where it begins:
- Nitrogen deficiency chlorosis begins with the lowest or oldest leaves.
- Sulfur deficiency chlorosis occurs on the youngest leaves.
Enjoying a soil with a good amount of organic matter leads to it being rich in all kinds of nutrients, especially sulfur because it depends on it.
In any case, when in doubt about the amount of sulfur available, it is best to carry out a soil study.
This will make it possible to define if an extra supply of sulfur is needed or if the levels available are more than enough.
It is even the best measure to take when you notice that something with the plant is not going as well as it should.


![Photo of How to Plant Water Lilies: Important Points + Pictures + [9 Steps]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/how-to-plant-water-lilies-important-points-pictures-9-steps-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Nymph Care: [Earth, Moisture, Pruning and Problems]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/5186DMQFYgL._SL500_-390x220.jpg)
