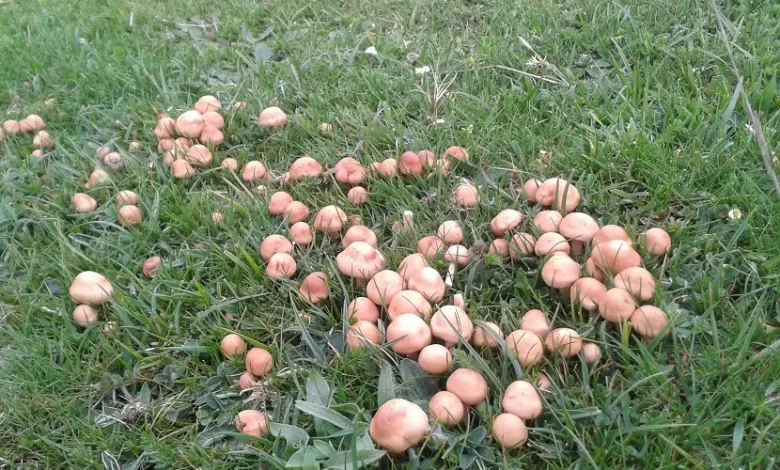
Senderuelas: [Care, Planting, Types, Irrigation, Substrate and More!]

Important points when sowing Senderuelas
 When? Spring and autumn are the times of proliferation of senderuelas, but in temperate zones of the globe they can be seen several times a year.
When? Spring and autumn are the times of proliferation of senderuelas, but in temperate zones of the globe they can be seen several times a year.- Where? They abound in grasslands, meadows, gardens, roadsides and even in the dunes of coastal regions.
- How do we prepare the land? In the garden, a good substrate with peat and organic matter must be composed, it will be more than enough for mushrooms to grow.
- How do we sow? In the garden, several species available in mushroom growing kits can always be grown, with seeds and mycelia that will colonize the entire substrate fed with compost, peat and oak soil.
- How do we pay? There are many combinations, but in the garden an excellent substrate is one that combines organic matter and peat.
- When are they harvested? Like most wild mushrooms, they are abundantly available for harvesting in autumn, when humidity rises.
- Ideal temperature? They love cool temperatures, in spring meadows, with estimates at 3-17ºC, approximately.
- How do we water? The substrate must always be moistened, up to 70%.
- Diseases and pests? They can contract viruses, be a victim of bacteria and other fungi and some of the pests that attack the most are: flies, mosquitoes, mites, snails and slugs. Diptera, or flies and mosquitoes.
What are Senderuelas?
 Senderuelas are mushrooms that come from a fungus known by the scientific name of Marasmius oreades, belonging to the Agaricales order of the Fungi kingdom.
Senderuelas are mushrooms that come from a fungus known by the scientific name of Marasmius oreades, belonging to the Agaricales order of the Fungi kingdom.
Typically European, it has managed to expand throughout the world, with a good presence in the American continent (north) and in Australia (east).
According to the geographical origin, it acquires many names. For example, in the region of Cantabria, Spain, it is called Seta de Carrillo, in Segovia they are Senderinas, Pucheretes or Pucheruelos. In France, they are known as Mousseron or Faux mousseron. In Mexico, Nanacate or nanácatl.
They are also recognized as nymphs, carreres, carrerilla mushroom, ring mushroom, worms, grids, sendejuelas, rubber bands, among others.
Appearance and types of senderuelas
Hat
They exhibit a hood or hat that has an approximate diameter between 2 to 6 cm, with an elliptical shape and in the center, when it matures, a kind of distinctive mamelon is formed.
sheets
Inside the hat there are separations in perfect sheets of cream or hazelnut color. They are spaced, numerous and go from the trunk to the edge of the hat.
The foot
The foot or rod is strong, elongated and bulbous. It doesn’t break easily. Withstands torsion. It is also not edible.
Color
The color of the senderuela lightens in the rainy season, but they are mostly a dark cream tone, like that of hazelnuts.
spore
 It is white.
It is white.
Characteristic smell
The easiest way to recognize it and avoid confusion with other species of meadow mushrooms such as cliyocybe or collibia, is its penetrating smell of bitter almonds or amaretto, the world famous Italian liqueur.
exquisite taste
Its sweet almond flavor makes it popular in international cuisine. Although its meat is not very generous, many mushrooms are gathered and dehydrated beforehand, to add it to various dishes, from soups, stir-fries, salads, tortillas, meat, fish and pasta.
trehalose
This sweetish flavor is produced thanks to a type of sugar called trehalose, which makes the mushroom revive when it comes into contact with water after it has been dehydrated for preservation and use in the kitchen.
Trehalose also promotes cell reproduction and spore formation, so that the reproductive cycle continues over and over again.
Where should we plant the senderuela?
 These wonderful senderuelas multiply throughout Europe and North America, but it is also very feasible that they can reproduce easily in temperate climates after the appearance of the rains.
These wonderful senderuelas multiply throughout Europe and North America, but it is also very feasible that they can reproduce easily in temperate climates after the appearance of the rains.
They can be seen in green meadows, pastures, gardens, roadsides and even in the dunes of coastal areas, in short, they are very likely to multiply several times a year in seasonal regions and those hot or temperate places.
But it does not grow or reproduce in intricate or wooded areas. They can form paths along the entire mycelium, several meters. That is why they are also named as seta de reperilla or senderuela.
When do we grow senderuelas?
The senderuelas have the peculiarity of growing spontaneously in what is known as a circle of witches, because several sprout that are usually grouped in a circle, during spring and autumn, but in the temperate regions of the planet they are usually seen all year round, as long as the conditions of ambient humidity are appropriate.
Its popular name is given by the mark it leaves on the grass as it develops, because the area changes color thanks to the substances that are released from the senderuela mycelium.
The proliferation of witches’ circles in the summer can be maintained as long as they are moderate temperatures and rainy days.
Its sweet almond flavor makes it popular in world cuisine. Although its meat is not very generous, many mushrooms are gathered and dehydrated beforehand, to add it to various dishes.
How do we prepare the land?
 In the garden, a good substrate with organic matter mixed with peat will be ideal for mushrooms to grow, as soon as spring or autumn arrives, which is when this variety reproduces more widely, although it can also do so on rainy summer days with moderate temperature.
In the garden, a good substrate with organic matter mixed with peat will be ideal for mushrooms to grow, as soon as spring or autumn arrives, which is when this variety reproduces more widely, although it can also do so on rainy summer days with moderate temperature.
An excellent substrate for mushrooms can be prepared with the following ingredients, as long as they are lignicolous fungi, which decompose wood and are capable of transforming organic matter into inorganic.
- 4 parts sawdust from large-leaved trees.
- Chips and plaster in a proportion of 3%.
- 1 part wheat or rice bran.
The substrate must be moistened, up to 60 to 70%.
It is advisable to consult a specialist to obtain the most recommended substrate for the variety you wish to grow in your garden or garden.
How to grow mushrooms in the garden, step by step?
To grow mushrooms in the garden of the macrolepiota type, the following materials must be obtained first of all:
 Compost (straw in sufficient quantity).
Compost (straw in sufficient quantity).- Oak grove land.
- Hoe.
- Rake.
- Peat.
- Mushroom growing kit of the variety you prefer to get at your trusted store.
- Large bucket or basin with water.
Follow these instructions, step by step:
- A good place in the garden, with well-drained soil (preferably under a tree with abundant foliage), should be selected to grow our mushrooms.
- Dig a hole about one square meter.
- Pour the peat to the bottom of the hole and then add the oak soil.
- Spread mycelium, or mushroom seeds, all over the site and put another layer of peat moss on top.
- Mix everything with the help of a rake and then put gardening peat on top, to rake again until the ground is covered.
- A thin layer of the original garden soil is placed.
- After a few weeks, the mycelium (vegetative apparatus of the plant) colonizes the entire substrate. When the mycelium is developed, in less time the carpophages that give way to the mushrooms will form.
This presentation of mycelium is available on the market.
How to sow the most common mushroom; Pleurotus ostreatus
If you want to cultivate the most popular or common mushroom, the so-called Pleurotus ostreatus, the following instructions must be followed, step by step:
- Sterilize with the help of hot water, sawdust, straw and cobs, among others, for approximately 2 hours at 70ºC. The substrate must undergo a careful sterilization process, because it is essential to eliminate harmful agents such as parasites, pathogens, competitors and seeds, following a good heat treatment.
- Then wash everything with cold water, repeating the operation about 3 times.
- This substrate continues to drain, then it is finished cooling to a temperature of between 20-25ºC, mixing it with 3% of mycelium.
- The mixture should be stored in a plastic bag with holes and put in a dark place, at an average temperature of 20-23ºC.
- As soon as you notice the formation of a whitish mass, then you should take it to a cool place, with an ambient temperature of 15ºC.
- In case the ambient humidity is low, water with water every day, without exception.
Other species that are usually grown at home are the oyster mushroom, poplar mushroom, shiitake, thistle mushroom and mushrooms.
But without a doubt, the most reliable method to grow them is to buy a bag prepared by a specialist, which will need a ventilated space, with good environmental humidity, without direct sunlight.
You can make a kind of cave in a semi-shaded corner of your garden and lay the sack on a bed of straw.
What care do senderuelas need?
 The best care for mushrooms grown at home goes through the environment that we must create for them.
The best care for mushrooms grown at home goes through the environment that we must create for them.
It is highly recommended to place them in places like these, to favor their reproduction:
- Cereal straw such as rye, wheat. Oats and barley suck up a lot of water and are less recommended.
- stumps.
- Cut logs.
- Corn cobs, vegetable scraps, dried sunflower, hay, cardboard, paper,
- I usually.
It is absolutely essential that the substrate is decontaminated with the help of the heat treatment technique.
Autumn is the best time to grow many varieties, because the ambient humidity increases and the rains help the whole process to flow much better.
In addition, it is required to have good control over the following variables:
Food
The best substrate that is achieved, if it is prepared by a specialist, will be much better
Temperature
There are mushrooms that support more heat and others prefer cold, lower temperatures. But between 10ºC to 24ºC is an acceptable range, depending on the variety.
Oxygen
Sufficient ventilation, good looseness of the substrate.
health check
It is important to save you competitors, pests and diseases.
What pests and diseases does it have?
 Generally speaking, mushrooms also contract diseases and are attacked by pests.
Generally speaking, mushrooms also contract diseases and are attacked by pests.
The most common diseases are bacteria, viruses and fungi, which can destroy them in a short time and with the impossibility of avoiding it.
That is why it is essential to sterilize everything or be very careful to remove a fungus or a strange mushroom from the culture bag, because when its spores spread it will be very late, but the truth is that it is somewhat unlikely that a variety of poisonous type sneaks into the crop.
The pests that attack the most are the following:
- Mites.
- Diptera, or flies and mosquitoes.
- Snails and slugs.
- Springtails or very small insects that jump and have no wings.
To combat them, specialized information must first be requested from a trusted mycologist, in order to apply the correct insecticide at the appropriate dose and frequency.