Orange Tree Diseases: [Characteristics, Types, Detection and Treatment]

What are the diseases of the orange tree and how can we detect them?
 The diseases of the orange tree originate fundamentally from poor management of the crop, excess irrigation and bad subscribers, among others.
The diseases of the orange tree originate fundamentally from poor management of the crop, excess irrigation and bad subscribers, among others.
Like most citrus plants, the orange tree can be affected by injuries caused by fungi or bacteria.
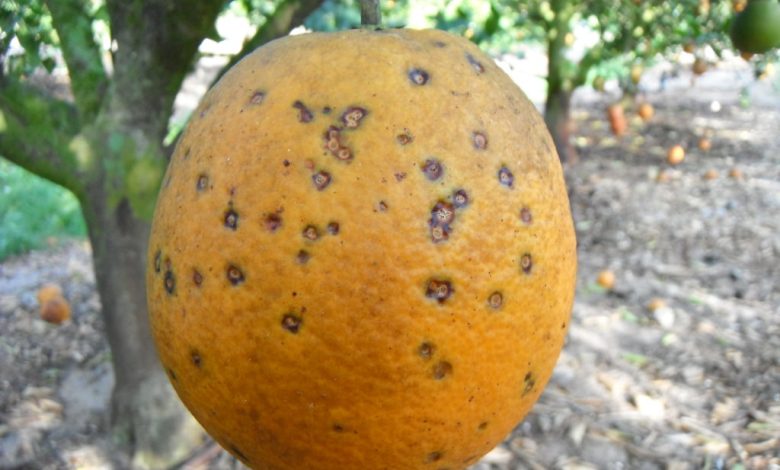
Among the diseases that attack the orange tree are: the black spot of citrus fruits, which injure ripe fruits and «temporones» and very rarely green fruits and leaves.
It is characterized by a variety of spots that often make it difficult to detect.The orange tree is also attacked by greasy spot that appears as spots on both sides of the leaves that change from blackish brown to a greasy appearance.
In the case of the orange tree, there are three diseases transmitted by fungi of the Phytophthora species, trunk rot or trunk gummosis; root rot and fruit rot.
These diseases rot the roots, but also affect the aerial part including the trunk, branches, leaves and fruits.
Description of orange tree diseases
Among the diseases that usually attack the orange tree, as one of the most important citrus fruits for human consumption, we have:
citrus black spot
 It is a disease known as black mottle and mainly affects the external quality of the orange tree.
It is a disease known as black mottle and mainly affects the external quality of the orange tree.
Caused by the fungus Guignardia citricarpa, it is a disease that has caused significant damage in orange-producing regions, and other citrus varieties in Australia and South Africa.
greasy stain
It is a disease caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella citri that affects plants in production causing their intense and premature defoliation during spring.
Trunk rot or gummosis of the orange tree
 It is a disease that occurs in the root of the mandarin and spreads throughout the base of the trunk, forming cracks.
It is a disease that occurs in the root of the mandarin and spreads throughout the base of the trunk, forming cracks.
When this disease is observed in an advanced state, the trunk, branches and sometimes the fruits fill or transpire gummosis, which is why it is known by that name.
root rot
 As its name indicates, this disease directly affects the roots, rotting them and, on many occasions, causing the death of the plant.
As its name indicates, this disease directly affects the roots, rotting them and, on many occasions, causing the death of the plant.
The use of susceptible rootstocks in heavy and waterlogged soils favors this disease.Currently, the spread of tolerant rootstocks has reduced the incidence of orange root rot.
fruit rot
It is also known as brown rot, brown rot or watery fruit.It is a disease that affects all types of citrus crops and in wet and rainy periods it is common to see rotten fruit.
How to identify and eliminate orange tree diseases?
Among the citrus fruits, the orange tree enjoys great favoritism in the daily diet, hence the need to identify very well the type of disease that the plant has and use ecological and preventive treatments before chemical ones.
citrus black spot
 The symptoms of the disease in the orange tree appear as small pink depressed punctuations, similar to the «pitting» caused by the cold on the surface of the fruits.
The symptoms of the disease in the orange tree appear as small pink depressed punctuations, similar to the «pitting» caused by the cold on the surface of the fruits.
The appearance of these symptoms usually continues even after the fruit is harvested. It causes significant damage to late orange trees such as Valencia, late and grapefruit.
The main source of inoculum is constituted by the litter located under the affected plants.However, once the disease is established, the use of preventive and curative fungicides is recommended.
greasy stain
It is identified by the spots that appear on both sides of the leaves, they are translucent yellowish in color that change to blackish brown with a greasy appearance.
To control this disease, spraying (between March and May) of copper oxychloride or copper sulfate (50% metallic copper) at 2‰, carbendazim (50%) at 0.75‰ or benomyl (50%) at 0.6 %.
Trunk rot or gummosis of the orange tree
It is observed on the plant as a dark spot in the shape of a triangle on the part of the trunk.As a preventive treatment of the disease, it is recommended to control the risks, scraping the affected surface to apply a solution based on liquid fungicides with copper content.
Another solution can also be used, such as applying potassium permanganate and Bordeaux paste on the polished and dry surface of the affected surface.
root rot
 Since this disease affects only the underground part of the plant, its diagnosis is more difficult.
Since this disease affects only the underground part of the plant, its diagnosis is more difficult.
The aerial symptoms described for “foot rot” are not characteristic and can be confused with nutritional deficiencies, soil waterlogging, and other diseases.
Preventive control is recommended through the use of copper-based or systemic fungicides such as fosetyl-Aluminium, which can be applied in localized treatments, and metalaxyl.
fruit rot
 The first symptoms of this disease appear a few days after infection, as a moist-looking spot on the fruit that spreads with a brown coloration.
The first symptoms of this disease appear a few days after infection, as a moist-looking spot on the fruit that spreads with a brown coloration.
This disease is favored by plant injuries caused by poor praxis during pruning.
It is recommended to be very attentive to the appearance of this disease, especially during rainy periods, especially in the varieties of the early type.
To combat the disease through chemical procedures, cupric products such as fosetyl-aluminum are recommended, placed in the lower part of the orange tree’s crown, days before harvest.
Bibliography and references
- Mcbride S., R. French, G. Shuster, and K. Ong. Citrus Disease Guide. Department of Agriculture of the State of Texas, US. 2010. PDF.
- González, S. Luis R., Cirilo Catalino Tullo A. Technical guide for citrus crops. Technological Parks Project, San Lorenzo Paraguay; FCA, UNA, 2019. PDF.
digital database
- Map.gob.es Registration of phytosanitary products. Reproduced from: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/agricultura/temas/sanidad-vegetal/productos-fitosanitarios/registro/productos/forexi.asp?e=0&plagEfecto=6&culUso=0102020101000000&ambUti=01&solEsp=
- Agromatic.es. Diseases and pests of the orange tree. Reproduced from: https://www.agromatica.es/plagas-del-naranjo/
- hidalgo.agrilife.org. Quick guide to citrus fruit identification Reproduced from: https://hidalgo.agrilife.org/files/2012/01/Guia-rapida-de-identificacion2.pdf.
- Inta.gob.ar. Fungal diseases and their control. Reproduced from: https://hidalgo.agrilife.org/files/2012/01/Guia-rapida-de-identificacion2.pdf.




![Photo of Prune the Poinsettia: [Importance, Time, Tools, Considerations and Steps]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/prune-the-poinsettia-importance-time-tools-considerations-and-steps-390x220.jpg)