Nitrogen in the Orchard: [Concept, Benefits, Advantages and Disadvantages]

 Nitrogen is one of the three macronutrients that are of major importance in crop development.
Nitrogen is one of the three macronutrients that are of major importance in crop development.
Its absorption can be carried out by plants from the ground, thanks to the fact that it is commonly obtained after the mineralization of the decomposing remains.
However, these amounts are not enough to meet the demand that plants usually have and that is why it must be added by fertilization.
An excess or deficit of nitrogen in crops can be harmful to the health of the plants and that is why all the data in this regard must be known.
What is nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a chemical element with a high presence in the environment. In fact, in the soil it can be found in two forms: mineral and organic.
The mineral form is what plants have the ability to absorb to fulfill their vital processes of growth and development.
This means that its supply must be done through formations such as nitrate or ammonium.
Inside the tissues, plants need the presence of nitrogen to carry out basic processes such as photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
Why is nitrogen important?
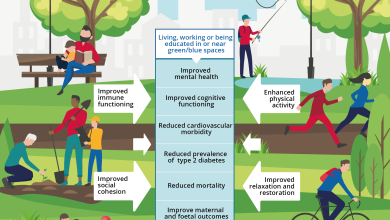
Nitrogen, the most abundant element in our atmosphere, is crucial for life.
Nitrogen is found in soils and plants, in the water we drink, and in the air we breathe.
It is also essential for life: a key component of DNA, which determines our genetics, is essential for plant growth, and therefore necessary for the food we grow.
But as with everything, balance is key: too little nitrogen and the plants won’t thrive, leading to poor crop yields; But too much nitrogen can be toxic to plants, and it can also harm our environment.
Plants that do not have enough nitrogen turn yellow and do not grow well and may have smaller flowers and fruit. Farmers can add nitrogen fertilizer to grow better crops, but too much can harm plants and animals and pollute our aquatic systems.
Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle – how nitrogen moves from the atmosphere to the land, through soils, and back into the atmosphere in a never-ending cycle – can help us grow healthy crops and protect our environment.
What factors influence crop response to nitrogen fertilization?
Because nitrogen is found in the environment, it is much easier for plants to appropriate it from the soil.
For this to happen, it is necessary that the environment and the soil meet a series of conditions that favor the processes of nitrogen transformation.
Some of these conditions are:
- That the average environmental temperature is warm, located in a range between 20 and 35º C.
- That the soil is able to remain moist for a good period of time, but without waterlogging.
- Let the soil be aerated.
What is the nitrogen content in the soil?
The calculation of the nitrogen that can be present in the soil is variable because it depends a lot on its conditions.
When you have good quality soil in an area with cold temperatures, there could be a minimum of 10 kg of nitrogen per hectare.
In the case of sandy soils and those located in hot climates, this amount can amount to up to 60 kg of nitrogen per hectare.
This taking into account that the soils have sufficient organic matter, being acceptable between 1% and 2% of it.
What benefits can a soil rich in nitrogen have?
When progress is made in planting crops in soils rich in nitrogen, these species thrive healthier and this is evident in their structure.
- First of all, nitrogen is essential for growth, as it operates in the creation of chlorophyll and also in photosynthesis.
- On the other hand, nitrogen is present in the structure of many proteins (which it also helps to synthesize) and enzymes .
- It has an important role in cell division , which is why it helps to obtain new species of good quality.
- It plays a determining role in the formation, structure and length of the roots .
- Finally, it is a nutrient that plays a leading role in carrying out the different metabolic processes of the plant.
What disadvantages does an excess of nitrogen have?
The application of very high levels of nitrogen to crops will cause complications in the development of plants that will be evidenced by:
- Growth alterations, since they will look much larger than they should based on their species. One would then speak of an exaggerated growth.
- Cell multiplication will also be much more significant, leading to a greater number of shoots and branches being produced.
- The plant will not be able to develop properly because it will appear younger than it really is, with few woody parts, very immature and even lignified.
- Increased chances of being attacked by pests and diseases.
- Although there will be cell multiplication, the harvests will be in a lower number than expected.
What crops benefit most from the presence of nitrogen in the soil?
 All crops need the presence of nitrogen as a base for their correct development.
All crops need the presence of nitrogen as a base for their correct development.
In some cases, consumption is not as high as in others and that is why the requirements of each species must be met.
Nitrogen is especially essential in leafy vegetables, such as spinach, celery or lettuce.
In fact, thanks to the fact that this is so, human beings have access to the consumption of nitrate naturally.
However, in species such as tomatoes or aubergines, this need is considerably reduced.
How do we detect deficiency or lack of nitrogen in our crops?
The symptoms of plants that have nitrogen deficiency are very evident, since it is one of the most important components of vitality.
- In the first instance, growth is impaired, noticing the same much smaller than they should be according to planting time.
- On the foliage, the impact is also pronounced and easily visible, with older leaves developing paleness . However, this is a condition that will quickly take over the entire structure of the plant, turning it yellow and leading to defoliation .
- The main reason is that nitrogen is not performing the required and mandatory function to help in the production of chlorophyll.
- There are also plant species whose most obvious impact is on the stem, which turns slightly purple.
- The good news is that there are homemade fertilizers with a very high nitrogen content that can be used to alleviate these conditions.
- Among the main ones are organic matter such as cattle manure and compost.
- It is important to take into account that the nutritional conditions of all plants are not the same.
- In addition, it is necessary to consider the contributions that plants obtain from other sources, such as the soil itself and water.
If all this is taken into account, there are high chances of obtaining healthy and prosperous crops.
What elements can we recycle and that can provide nitrogen to our plants?
grass debris
 When composted, grass contains about 3% nitrogen by weight.
When composted, grass contains about 3% nitrogen by weight.
the coffee beans
Used fresh or composted, coffee beans contain around 5% nitrogen by weight.
Manure
Rabbit, cow, horse, goat, sheep and chicken manure are VERY high in nitrogen and can be anywhere from 4% to 9% nitrogen by weight.
Guano also provides a large amount of nitrogen.
human urine
As gross as it sounds, human urine is an extremely reliable form of nitrogen, and it also contains other beneficial trace elements that aid plant growth. Urine may contain approximately 5% nitrogen by weight.
Urine should be diluted 5 parts water to 1 part urine to prevent burning.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a repeating cycle of processes during which nitrogen moves through living and nonliving things: the atmosphere, soil, water, plants, animals, and bacteria. Bacteria can cause the decomposition, or breakdown, of organic material in soils.
 In order to move through the different parts of the cycle, nitrogen must change form.
In order to move through the different parts of the cycle, nitrogen must change form.
In the atmosphere, nitrogen exists as a gas (N2), but in soils it exists as nitrogen oxide, NO, and nitrogen dioxide, NO2, and when used as a fertilizer, it can be found in other forms, such as ammonia, NH3., which can be further processed into a different fertilizer, ammonium nitrate, or NH4NO3.
There are five stages in the nitrogen cycle, and we will now discuss each of them separately: fixation or volatilization, mineralization, nitrification, immobilization, and denitrification. In this image, soil microbes convert nitrogen gas (N2) into what is called volatile ammonia (NH3), so the fixation process is called volatilization.
When a mineral or chemical (such as nitrate or NO3) runs out of the soil or other soil material and seeps into the surrounding area. This is when certain forms of nitrogen (such as nitrate or NO3) dissolve in water and leach out of the ground, potentially polluting waterways.
How do plants store nitrogen?
Ammonium ions are taken up by the plant through ammonia transporters.
Nitrate is taken up by various nitrate transporters that use a proton gradient to drive nitrate transport. Nitrogen is transported from root to shoot through the xylem in the form of nitrate, dissolved ammonia, and amino acids.