My plants are rotting. What happens and how to fix it?

Hello farmers! Sometimes, we go to the garden and… bad news, our plants rot ! Therefore, the objective of today’s article will be to learn to identify what are the causes of this rot and know how we should act.

Rotten fruits Who is to blame?
There are different causes that can cause rot. It can be caused by fungi, bacteria, or a lack of some type of nutrient. Of all of them, I will focus on those that are most common and important, following the following scheme:
1. BACTERIA
- Soft rot of fruits
2. FUNGI
- anthracnose
- botrytis
- Mildew
3. LACK OF NUTRIENTS
- Blossom end rot: Calcium deficiency
Soft rot of fruits
On this occasion, vegetables rot due to a disease caused by the bacterium Pectobacterium carotovorum and affects a large number of species. Infection occurs when the bacteria enter through wounds or natural openings in the plant.

The main symptoms are:
- Soft, watery depressions appear on the fruit.
- The epidermis (outer part of the fruit) becomes wrinkled.
- On the stems sometimes appear dark spots.
- They can give off bad odours.
Prevention and control methods:
- Avoid sprinkler irrigation, as they favor dispersion.
- Disinfect implements and tools.
- Promote aeration by using wide planting frames.
- Carry out crop rotation.
Black spots on tomatoes: anthracnose
Anthracnose is a disease caused by a fungus of the genus Colletotrichum sp. Normally, it occurs in summer and the most affected orchard crops are tomatoes, beans, peppers and strawberries.
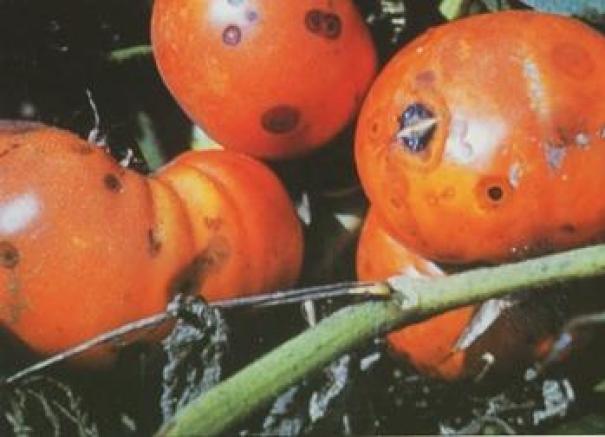

Among the most common symptoms are:
- Water-soaked, circular spots on ripe fruit.
- They darken and deepen as the fungus spreads.
Prevention methods:
- Plant in soils with good drainage to prevent water accumulation.
- Perform crop rotation every 3 or 4 years.
- Clean crops of weeds.
- Red thyme application.
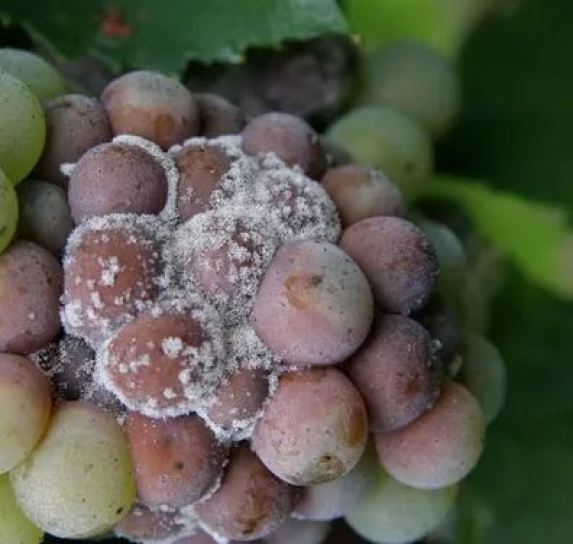
Botrytis or gray rot
If your plants are rotting and you see a whitish color… There is no doubt, it is the Botrytis sp fungus.
It mainly affects strawberries, tomatoes, lettuce, vines, cucumbers and aubergines. Surely you have all seen it when you leave strawberries at home for several days. To propagate it needs high humidity, little ventilation and mild temperatures.

The main symptoms are:
- Gray and whitish rots on the fruit.
- The fruits soften and lose color.
Prevention methods:
- Remove the fruits and part of the affected plant.
- Do not leave infected plant debris nearby.
- Ecological treatments such as: horsetail, potassium soap, red thyme, etc.
Brown spots: mildew
Another fungus that can cause rot in your plants is Mildew. It affects a wide group of plants, highlighting the vine and the Solanaceae (tomato, aubergine, pepper or potato). Other crops damaged by this fungus are strawberries, cucumber, melon, beet, spinach or chard.
This fungus takes advantage of plant wounds or leaf stomata to enter. You can infect them through irrigation water. It requires medium temperature (approximately 20ºC) and high humidity (which is why it usually appears after the rains).
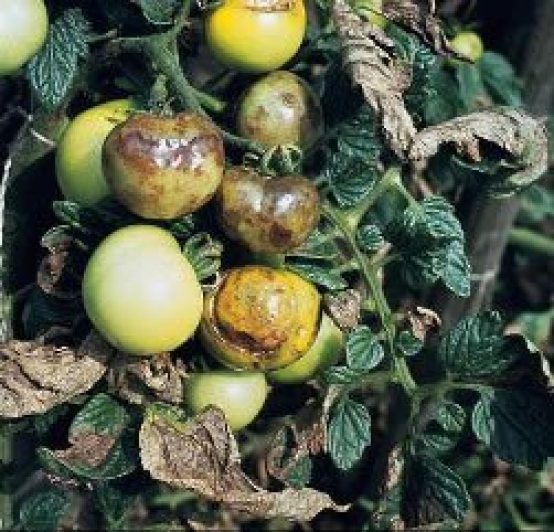

Most common symptoms:
- Stains on the fruits with a greasy appearance of different shades, which later turn brown and wither.
- The stems also blacken.
Prevention methods:
- Do not water from above.
- Good ventilation.
- Remove weeds.
APICAL ROT: Hotalizas with rotten tip
This type of rot mainly affects tomatoes and peppers. It is due to a lack of calcium and/or water stress in the plant, which causes the death of the apical cells of the fruit and the consequent loss of color. It mainly manifests itself in summer.
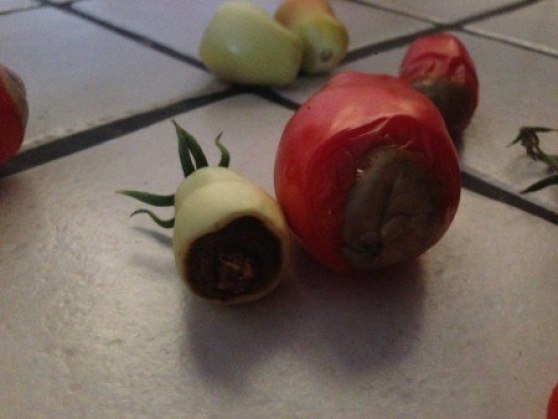

Symptoms:
- Sunken, dark, black spots appear at the lower end of the fruit.
- The rest of the fruit ripens normally.
Prevention and control methods:
- Calcium application via foliar or through irrigation.
- Affected fruit should be removed.
I leave you here a video about the rotten ass of the tomato and a very original solution: apply pieces of eggshell. It is a very simple and totally effective method, so if you have problems with a lack of calcium, do not hesitate to apply it.
Finally, I also leave you the link of an article where we explain different ecological remedies to put an end to diseases caused by fungi: « Prevention and ecological treatments for fungi in the garden »
References
- Sutton, JC (1995).9 Evaluation of micro-organisms for biocontrol: Botrytis cinerea and strawberry, a case study. Advances in Plant Pathology. Academic Press. 11, 173-190.
- Singhalage ID, Seneviratne G, Madawala HMSP, Wijepala PC (2018).Profitability of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) production with biofilmed biofertilizer application. Scientia Horticulturae. 243, 411-413.
- Blancard, D. (2012).The Tomato Plant and its Culture. Tomato Diseases (Second Edition). Academic Press,17-34.
- G. KALLOO. (1993).Tomato: Lycopersicon esculentum Miller. Editor(s): G. KALLOO, BO BERGH. Genetic Improvement of Vegetable Crops, Pergamon, 645-666.
This is all for today, I hope that if your plants rot you will be able to make a good diagnosis of the cause. In any case, any doubt, experience, photos or methods that you want to tell us about can be done in the comments. This is how we all learn!
Have a nice day!


![Photo of Ambulia: [Care, Characteristics, Cultivation, Substrate and Pests]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/características-de-la-ambulia-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of [7] Varieties of Potatoes and their Characteristics](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/7-varieties-of-potatoes-and-their-characteristics-390x220.jpg)