Kiwi Pests and Diseases: [Detection, Causes and Solutions]

 Kiwi is a climbing plant that produces one of the most exquisite fruits that are marketed worldwide.
Kiwi is a climbing plant that produces one of the most exquisite fruits that are marketed worldwide.
With a soft and sweet pulp, this subtropical climate fruit is becoming increasingly popular.
Knowing all the epidemiological aspects that revolve around your environment will help you to enjoy more and more numerous and higher quality productions.
Hence, it is such a good plan that you enjoy first-hand information on this subject and it is just what we provide you below.
Gray mold
 Gray mold, gray rot or botrytis is a very common disease in kiwi, whose origin is conferred by the presence of a fungus from the botrytis family.
Gray mold, gray rot or botrytis is a very common disease in kiwi, whose origin is conferred by the presence of a fungus from the botrytis family.
Although its most common action occurs after harvesting them , if the environmental conditions are favorable, it can also attack on the plant .
In some rare cases, the harmful action of the fungus can manifest itself on the flowers . Among the conditions that are favorable to reproduce, are the high temperatures and constant humidity of the environment.
To detect if a crop has been affected, you have to look at the structure of the fruit , which usually shows spots and a very soft texture. In more advanced cases, the fungus is perfectly visible to the human eye, showing itself as a kind of cotton on the outside of the fruit.
The prevention of this disease will go through keeping the plant in a ventilated area, not fertilizing with decomposing matter and taking care of humidity. The use of botricidal chemical products is also highly recommended during the flowering stages and prior to harvest.
Neck rot
 Also known as root and crown rot, it is a disease caused by fungi that lodge in the lower part of plants.
Also known as root and crown rot, it is a disease caused by fungi that lodge in the lower part of plants.
Its ideal setting to live is loaded with humidity, which is why it usually manifests itself in areas with puddles and poor drainage.
The action of the fungus can remain at rest for years in certain types of land , manifesting itself when the conditions are appropriate. This is, above all, after a long period of rain that could trigger a complex outbreak capable of leading the plant to death in a short time.
In not so aggressive cases, what tends to happen is that the fruits are small and that they ripen much earlier than they should. To detect if the plant is being affected, it is best to scrape part of the bark from the trunk and assess the internal state.
In case this is the disease, what will be observed is a reddish brown color, instead of the typical white of healthy plants. Damages will be avoided by applying preventive fungicides at the beginning of spring , since after the disease appears it is very difficult to eradicate.
Bacterial cancer
 Although bacterial cancer is not so common within kiwi plantations, it does present a super aggressive work system.
Although bacterial cancer is not so common within kiwi plantations, it does present a super aggressive work system.
The disease is produced by different types of bacteria, being capable of attacking both yellow and green kiwis.
Another important detail is that it usually manifests in young plants more frequently, in children under 6 years of age.
Among the frequent causes that accompany the attack of this disease are:
- Plants that are subjected to fertilizations with high levels of nitrogen and calcium. As well as organic fertilizers such as guano .
- Plantations that are made in soils that are not very profitable for the characteristics demanded by kiwi, such as good drainage or poor in nutrients.
When it comes to detecting whether a culture is being attacked by bacterial cancer, it will be possible to notice symptoms such as orange exudations . Damage to the bark of the trunk and branches also usually appears, manifesting in brown or black colors that are easily detectable.
The necrotic spots on the leaves also soon appear and this will bring about a drop outbreaks after eventually affect the rest of the plant. Treatments will include pruning affected parts , isolating diseased plants, and burning infected tissues as a last resort.
Red spider
 The spider mite is a pest that consumes the sap of plants , reducing its vitality and it is possible that in kiwi it will find a good home.
The spider mite is a pest that consumes the sap of plants , reducing its vitality and it is possible that in kiwi it will find a good home.
Its action occurs on the back of the leaves and after suctioning, the points where the incision is made turn yellowish.
This becomes an ideal setting for the disease known as necrosis to attack. If detected early, the spider mite will not lead to crop loss. However, when its attack spreads, the plant can die.
The good news is that certain natural products, such as nettle slurry, can help eliminate the pest without causing damage to the crop.
Fruit moths
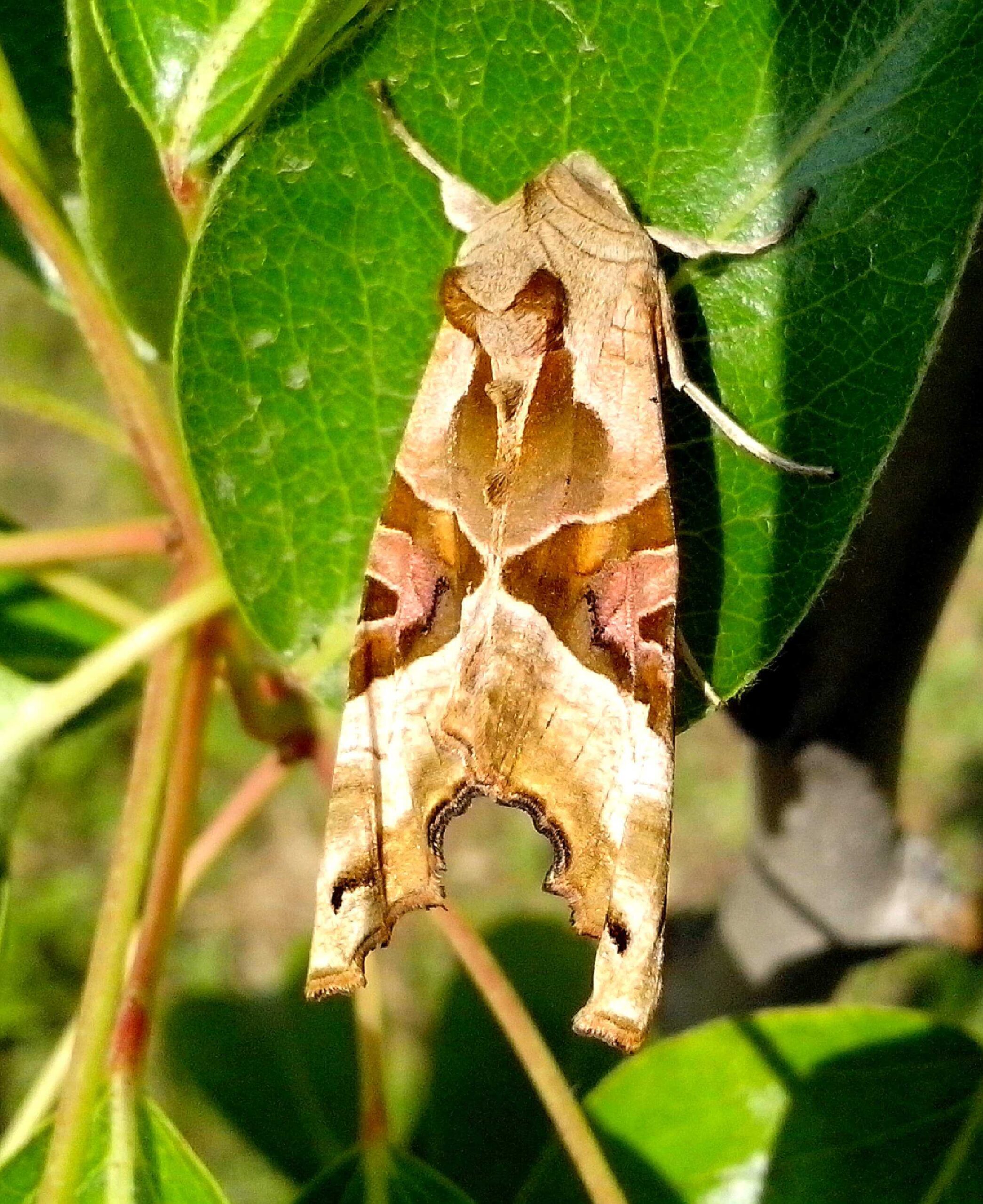 In the world there are many types of moths and those of the fruit are considered a pest when they become capable of abundantly attacking crops.
In the world there are many types of moths and those of the fruit are considered a pest when they become capable of abundantly attacking crops.
There are several types, which makes it easy to recognize what type of fruit you have a predilection for. Its shape is like a small butterfly .
Some fruit moths feed on the holes they make in the fruits themselves, for example in the case of apples.
In other cases, their diet is based on buttons and flowers, causing the fruiting process to be affected. The biggest problem that the adult moth has is that they have the ability to move from one place to another by flying, which could affect an entire plantation .
To avoid its appearance, it is very important that the plants are well nourished, applying the fertilizations that correspond to each case. In addition to that, well-planned and executed pruning is ideal for maintaining the good health of fruit trees of all kinds.
In case a corrective treatment is needed, there are specialized products that affect moths in different areas of your body. Its correct application will help to eliminate all traces and to continue with a quality and abundant harvest.

![Photo of Carnation Cuttings in Water: [Concept, Time, Rooting and Sowing]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Que-significa-plantar-por-esquejes-6-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Oleander Pruning: [Proper Period and Technique]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/oleander-pruning-proper-period-and-technique-390x220.jpg)