Home Gardens | How to make a garden at home step by step

Do you want an easy guide to know how to make a garden? Today we will summarize everything you need to know to create a garden at home step by step.
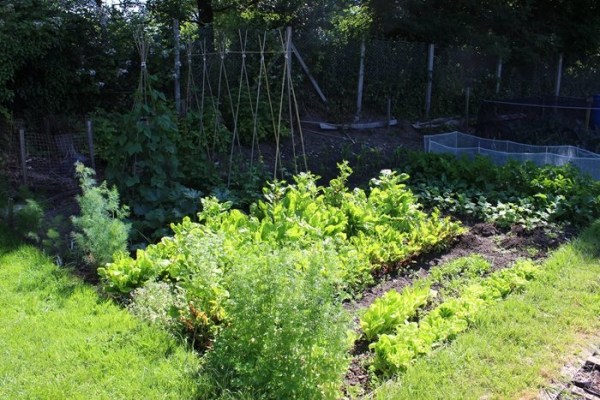

I will also leave you the links to other articles with useful and expanded information on the different aspects to consider in order to learn how to make a home garden.
How to make a garden at home step by step
Next we will see what are the steps to create a family garden from scratch. The first of all will be to plan the garden: the space, the crops, the irrigation… and then we can start with the planting and other tasks to make a home garden.
1. Decide the type of garden
If you have a garden, you can install your garden directly on the ground or on raised beds like these:

If you don’t have that much space or you prefer not to bend down to work in the garden, you can put cultivation tables on the terrace or on the roof, or even install a garden in the patio, a planter in the windows or in any other place… There are many the options when choosing the cultivation containers to make a garden (find some ideas by typing the word «containers» in the search engine on the top right)
2. Choose the crops
There are many possibilities, not just the typical vegetables and greens. In fact, if you include flowers, aromatic herbs, red fruit hedges or even “green manures” in your garden, you can have many benefits, such as pest and disease control. We saw it in the post What plants to grow in the garden, so take a look if you want more ideas on how to make a garden and what to grow in it.
When choosing, in addition to thinking about our tastes, it may be smart to think about less common plants on the market (and therefore more expensive). I leave a list that I have taken from the book «Sustainable urban garden» (Pérez and Vázquez, 2013):
- Plants that are easy to grow and relatively more expensive on the market: Swiss chard, broccoli, zucchini, Brussels sprouts, spinach, berries, broad beans, beans, turnips, leeks, beets or sugar snap peas.
- Other easy-to-grow garden plants are, for example: garlic, onions, lettuce, radishes, Swiss chard, aromatic plants or herbs, and carrots.
3. Choose and plan irrigation
It is very important to plan irrigation in the orchard. This is, for example, placing the plants according to the water they need, grouping those that need more watering and those that need less. That is in the case that we have an automatic irrigation, since if it is a manual irrigation we will water ourselves according to the needs of each one.
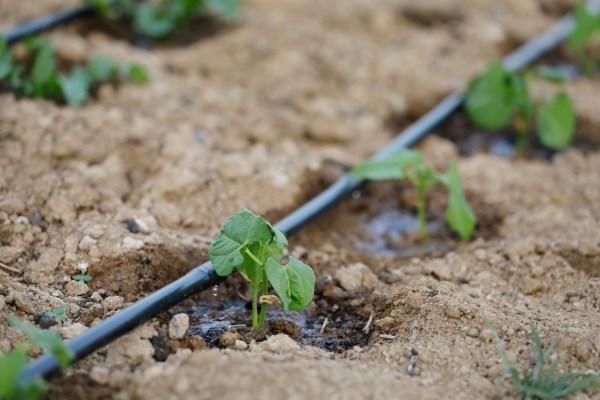

We must also choose the type of irrigation based on the available water, the type of garden (in pots, on terraces, on cultivation tables) and the time we have to dedicate ourselves to the work of our garden.
In the post 6 types of irrigation for your garden or orchard you can see the main methods. I always recommend micro-irrigation systems with a programmer, such as drip, micro-sprinkler or exuding tape, since they save a lot of water and are more comfortable and less “slaves” when it comes to watering.
4. Decide on crop placement
One of the keys to how to make a good garden is to choose the placement of crops appropriately. To do this, several things must be taken into account, such as the correct distance between plants, or the existence of compatibilities and incompatibilities between the different species.
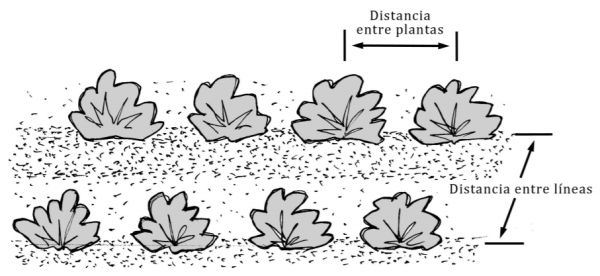
For example, pepper plants should be spaced 30-50cm apart, however carrots can be 10cm apart. The separation between the plants will depend on the type of crop (More information on this in the post Planting distances: What distance to leave between the plants in the garden.
It is also very important to know the beneficial and harmful associations of some plants with others, in order to put the plants «that get along well» together and avoid putting the ones that are incompatible next to each other.

From year to year, it uses the crop rotation technique, that is, if one year we have put fruit vegetables such as tomatoes or peppers on a terrace, which are quite demanding plants, the following year we will put other plants with less requirements, such as lettuce, or species that enrich the soil such as legumes.
5. Prepare the ground: substrate and fertilizer
If you are going to mount the garden directly on the ground, it is very important to plow or remove the soil with a hoe or, more superficially, with a rake before implanting the crops. This is done to remove weeds and fluff up the soil. If, on the other hand, you have a garden in pots or cultivation tables, you will have to buy substrate for the containers. In this video, Álvaro told us some tips about substrates:
You also have to fertilize so that the plants have the necessary nutrients and that they can grow well and give good harvests. There are many ways to fertilize the garden, in this link I leave you some ideas of organic and natural fertilizers or fertilizers for the garden at home. One of the most complete is compost, which can also be made at home by reusing dry leaves, cut grass, pruning debris or organic kitchen scraps.
6. Sowing and planting
Normally, especially for those who are starting to grow gardens, it is better to first make some seedbeds or seedlings instead of sowing directly in the final land. You can buy them or use recycled containers like I did:

In this way, the seeds will germinate more easily and we will be able to better control and care for each little plant. In the post How to make a seedbed in the garden we saw the keys to go step by step with the sowing of seeds for the garden.
A few weeks after the germination of the seeds (depending on the plant in question) you should carefully remove the seedlings from the seedbeds (with the «root ball» or soil that surrounds the roots), make a small hole in the ground or final container and introduce the seedlings. Afterwards, “plantation irrigation” is very important. Álvaro gives us some advice about the transplant in this video:
7. Prevention of pests and diseases and «Integrated control»
This is an essential aspect for the success of the crops. If you want an organic garden free of artificial substances, the most important thing is to prevent pests and diseases to avoid the use of chemical insecticides and fungicides.
To do this, you can use biostimulants for healthier and stronger plants, padding or mulching for the garden or grow plants together with vegetables that, with their smell, repel pests and diseases, such as basil, marigolds and other flowering plants.

In the case of organic farming, » integrated pest control » is essential, a set of techniques that mix prevention with various ecological methods against pests and diseases, such as insect traps, preparations or natural remedies based on extracts of plants, or the use of beneficial insects or «natural enemies of pests».
8. Cultivation work
Weeding crops is a very beneficial task for most vegetables and garden vegetables. Weeding consists of removing the soil with a small rake or hoe. For some cultivation tasks like this, there are basic tools that cannot be missing in your garden (find out what they are by typing the word “tools” in the blog search engine, at the top right).
Another task that is recommended in some horticultural species is pruning. Pruning tomato plants, pepper plants, or zucchini is very good to have better harvests. With pruning, better quality and larger fruits are usually obtained. (If you want some tips on this we also have some blog posts on pruning different plants).

The last task of cultivation is the harvest. The harvest must be harvested at the optimal moment of maturation, which depends on each type of plant. There are some vegetables from which you will get even more than one harvest in each season, and others that can even last you several years, such as the aromatic ones. Use the appropriate pruning shears and instruments and cut the vegetable without damaging the rest of the plant.
The way of harvesting is different for each type of vegetables, so take a look at our crop sheets if you want information about a specific plant.
How to make an organic garden
We have already seen throughout the post some keys to organic farming (such as integrated fighting), but if you want more information on how to make an organic garden, I recommend that you take a look at the entry « How to make an organic and sustainable garden «, where you will find more ideas to replace the use of chemical fertilizers and insecticides with other ecological methods.
References
- Brechelt, A., 2004. Ecological soil management. Agriculture and Environment Foundation (FAMA), Dominican Republic.
- González López, M. et al., 2007. Ecological Program for Gardens and School Gardens. Advisory Guide for its implementation. Ministry of Education, Government of Cantabria (Spain).
- Goites, E., 2008. Crop Manual for the Family Organic Garden. INTA (National Institute of Agricultural Technology). Argentinian republic
- Ecologists in Action, 2009. Small manual of cultivation on rooftops. Ed.: Ecologists in Action of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Social Work of the Caja de Canarias.




