Guano: [Fertilizer, Benefits, Nutrients and How to Prepare It]
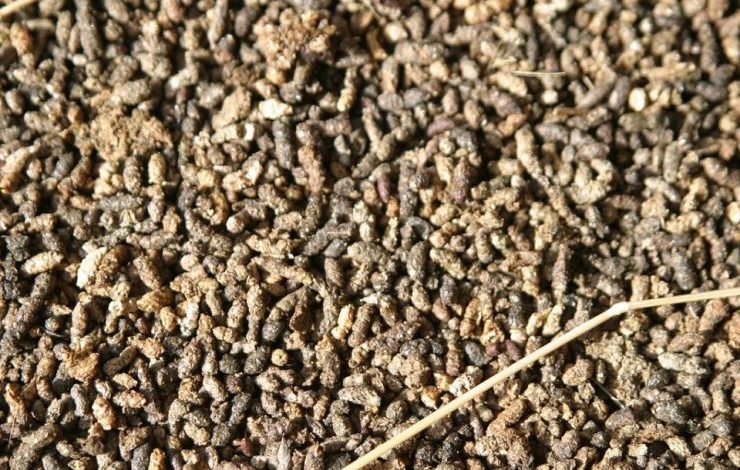

Guano (from Quechua: wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds and bats.
As a manure, guano is a very effective fertilizer due to its exceptionally high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium—nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also sought, to a lesser extent, for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials.
What is guano?
 The term «Guano» is formed from natural mineral deposits consisting of excrement, eggshells and carcasses of dead seabirds found in climatic regions with almost no rain and hot and dry climate, and the corresponding fertilizers.
The term «Guano» is formed from natural mineral deposits consisting of excrement, eggshells and carcasses of dead seabirds found in climatic regions with almost no rain and hot and dry climate, and the corresponding fertilizers.
Guanos are classified according to age, genesis, geographic origin, and chemical composition.
The main types are nitrogen and phosphate guanos. Phosphate guanos require a calcareous subsoil for their development, while nitrogen guanos form only in the special climatic conditions of the tropical high-pressure belt of the subtropical rim with coastal deserts.
Nutrients provided by guano
 Bat guano normally has a 10-3-1 ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
Bat guano normally has a 10-3-1 ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
The high nitrogen content helps plant leaves turn greener within a few days. It also helps that guano slowly releases these nutrients, over several months.
Phosphorus helps promote seed setting and flowering, while potassium helps the plant move water and nutrients more efficiently.
soil improvement
Bat and bird guano contain microbes that benefit the texture of your garden soil.
It also has the potential to enrich the soil and improve its drainage properties. In addition, it helps to make dense soils lighter and holds loose soils together.
Also, guano is not easily washed out of the soil, so it benefits plants much longer than inorganic fertilizers that are displaced or washed away after a single day of rain.
microbes
 Bat guano supplies more than just nutrients; it also carries microorganisms that help break down dried stool.
Bat guano supplies more than just nutrients; it also carries microorganisms that help break down dried stool.
These microbes help break down other organic materials in the soil, such as compost, and turn them into nutrients for plants. This can help improve the density of the soil, creating a texture that retains moisture and encourages plant roots without becoming overly saturated.
fungicide and insecticide
Bat guano tends to act as a fungicide in the soil, breaking down fungi along with other organic materials.
This helps keep plants healthy and disease free. It can also control nematodes, a nasty bug that can destroy your plants. Bat guano application early in the season can help keep the nematode population from exploding.
 Vitaterra Guano Ecological Fertilizer for Garden 3 kg, 16130
Vitaterra Guano Ecological Fertilizer for Garden 3 kg, 16130
- It nourishes the plant naturally
- Valid for organic farming
- High in Potassium
View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-30 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
How to use guano on your plants
When using the powder or pellet form of bat guano, simply sprinkle around the base of your plants and water liberally.
You can also mix 2-3 teaspoons of guano in 3-4 liters of water and pour it over your plants. Bat guano tea can be used as a foliar spray or poured onto plant roots.
Collect about 300 grams of guano in cheese cloth and soak it in 4 liters of water for at least three days, then use said water to fertilize your plants.
You can pour it into the ground immediately before planting. This ensures that the soil in your garden or orchard is sufficiently prepared to provide the beneficial nutrients for your crops.
Why is guano so effective as a fertilizer?
Guano is important from an ecological point of view due to its role in terms of the nutrients it provides.
Cave ecosystems, in particular, often rely entirely on bats to provide them with nutrients through their guano, which supports bacteria, fungi, invertebrates and vertebrates.
The loss of bats from a cave can lead to the extinction of species that depend on their guano. Guano also plays a role in cave formation, as its high acidity leads to erosion.
Did you know…?Tip: Make sure you always read the instructions on the fertilizer label before using it.
Also, if your plants show any signs of decline, immediately stop using the guano fertilizer. You don’t want to burn your plants with an overabundance of guano.
Where to use the guano
Sprinkle guano powder around the base of your growing plant and water considerably well. You can also make guano tea and sprinkle it on the leaves of your plant to protect it from fungal diseases.
 Vitaterra Guano Ecological Fertilizer for Garden 3 kg, 16130
Vitaterra Guano Ecological Fertilizer for Garden 3 kg, 16130
- It nourishes the plant naturally
- Valid for organic farming
- High in Potassium
View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-30 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
What types of guano can we find?
bird guano
Bird guano has high levels of nutrients such as nitrate and ammonium. By mass, it is 8-21% nitrogen; the nitrogen content is about 80% uric acid, 10% protein, 7% ammonia, and 0.5% nitrate.
Some of the most common chemical elements in bird guano are phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium. It can react with island bedrock such as basalt to form true phosphate minerals, including taranacite and leukophosphite .
bat guano
 When freshly excreted, insectivorous bat guano consists of fine particles of insect exoskeleton, which are composed largely of chitin. Elements found in high concentrations include carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
When freshly excreted, insectivorous bat guano consists of fine particles of insect exoskeleton, which are composed largely of chitin. Elements found in high concentrations include carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
Due to the action of bacteria and fungi, fresh guano decomposes rapidly, and generally loses its organic matter more quickly. Organic matter does not usually persist in a cave guano deposit at depths greater than a few centimeters.
Fresh guano contains about 2.4 to 7 times more carbon than nitrogen; the carbon to nitrogen ratio decreases or remains similar as older guano is sampled.
 CULIVERS Ecological Fertilizer with Guano of 25 kg. Universal Fertilizer of 100% Organic and Natural Origin for Orchard and Garden. High NPK concentration.
CULIVERS Ecological Fertilizer with Guano of 25 kg. Universal Fertilizer of 100% Organic and Natural Origin for Orchard and Garden. High NPK concentration.
- Increased fruit caliber, higher harvest yield.
- Stimulates natural defenses.
- Ecological organic fertilizer with a high concentration of NPK
- 100% Natural and Harmless product for animals and plants.
€39.75 View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-30 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
Fresh guano has a pH of 5.1-7.3, making it neutral or somewhat acidic. However, as it ages, guano becomes strongly acidic, reaching pH levels of 2.7-4.1.
Like bird guano, the acidic properties of guano and cave limestone can interact to create phosphate minerals such as whiteite, taranakite, variscite, spheniscite, montgomeryite, and leukophosphite. Other minerals found in guano are quartz, graphite, gypsum, bassanite, and mica.
insectivorous or sanguivorous bat
 The composition of guano varies among bat species with different diets.
The composition of guano varies among bat species with different diets.
Comparing guano from insectivores (Mexican free-tailed bats), frugivores (Rodrigues flying foxes), and sanguivores (common vampire bats), a 2007 study found that the three did not differ significantly in proportions of organic matter or carbon in the dry matter.
Sangivores had high carbon in organic matter, sangivores and insectivores had high nitrogen in organic and dry matter, and insectivores and frugivores had high phosphorus. Frugivores had the highest carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, while sangivores had the highest nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio and carbon-to-phosphorus ratio.
history of guano
 The guano trade in the 19th century played a key role in the development of modern, input-intensive agriculture, but its demand began to decline after the discovery of the Haber-Bosch process of nitrogen fixation led to the production of synthetic fertilizers.
The guano trade in the 19th century played a key role in the development of modern, input-intensive agriculture, but its demand began to decline after the discovery of the Haber-Bosch process of nitrogen fixation led to the production of synthetic fertilizers.
The demand for guano stimulated human colonization of remote bird islands in many parts of the world, leading to some of the earliest examples of American colonialism and the expansion of the British Empire.
The guano extraction process led to ecological degradation due to the loss of millions of seabirds. Unsustainable guano mining in caves alters their shape, causing bats to leave the roost.
Discount!  GUANOKALONG Granules – POT 1 KG
GUANOKALONG Granules – POT 1 KG
- cannabis
€15.00 −€1.95 €13.05 View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-30 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
Guano mining also involved the mistreatment and enslavement of workers such as Chinese immigrants, Native Hawaiians, and the African diaspora.
The most important nitrogenous guano is Peru-Guano, which has been used for more than 2000 years as an agricultural fertilizer in Peru.
In Europe, the application of guano as a fertilizer emerged in the 1840s as a «guano boom» and lasted until the early 20th century, when guano was replaced by industrially manufactured fertilizers. Only a small amount is still exported to Europe as an additive to organic/mineral fertilisers, more for image than effect.
Did you know…?The guano trade was very dangerous.
If a clipper ship, the fastest way to travel in the mid-19th century, headed from the east coast of America to Peru, it would first have to navigate the dangerous waters off Cape Horn.
To navigate dangerous seas, ships used charts and other navigational tools.
However, there was also danger on the islands from which the guano was extracted. The workers, most of them Chinese servants, extracted the guano, which was backbreaking and dangerous work. Since the guano dust filled the air with ammonia, miners and sailors alike were vulnerable to the poisonous and asphyxiating gases.
Bibliography and references
- Bat guano ecosystems, TL Poulson – Bulletin of the National Speleological Society, 1972 – ww.caves.org
- Ecological imperialism and the global metabolic fracture. Unequal exchange and the guano/nitrate trade, B Clark, JB Foster – Theomai, 2012 – redalyc.org
- Chicken guano compost in the composition of substrates for the production of floral seedlings, LA Barbaro, MA Karlanian, PF Rizzo, NI Riera.
- Book: Fertilizers and fertilization, A Finck – 1988.
- Composition of guano produced by frugivorous, sanguivorous, and insectivorous bats, K Emerson, AM Roark – Acta chiropterologica, 2007 – ingentaconnect.com
- Effect of nitrogen fertilization and guano from the island on onion cultivation (Allium cepa L). Canaan 2750 masl. Ayacucho.


![Photo of Pests and Diseases of Peonies: [Detection, Causes and Solutions]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/pests-and-diseases-of-peonies-detection-causes-and-solutions-390x220.png)
![Photo of Peat: [Characteristics, Utility, Obtaining and Application]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/peat-characteristics-utility-obtaining-and-application-390x220.png)