Dry Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]

Important points about the Dry Tropical Climate:
- What is? The dry tropical climate is located in the regions of the planet located between the tropics, whose main characteristics are high temperatures and practically total absence of changes in the seasons. It is an intermediate climate between the humid tropical and the desert.
- Where it is located? It is located exactly between 15º and 25º latitude, both north and south of the Earth. This type of climate develops in arid regions, such as the Sahara and the Sahel in Africa, as well as in the Australian desert.
- How is the flora? The flora is scarce in the arid zones of the dry tropical climate. There are thickets, grasslands, cardonales, izotales, succulent and xerophytic plants, such as cacti and nopales.
- How is the wildlife? A varied fauna with a predominance of big cats, such as jaguars and pumas, as well as monkeys, armadillos, deer, tapirs and many species of insects, birds, fish and reptiles.
- How long is the day and night? The days and nights are 12 hours, without variations throughout the year.
- Can human beings live in this climate? It has a presence on almost all continents, except in the Antarctic region. Interestingly, it is one of the largest climates on the planet, occupying 14% of the total. Countries with a tropical climate are among the 30 best places to live.
What is dry tropical climate?
 The dry tropical climate is located in the regions of the planet located between the tropics, whose main characteristics are high temperatures and practically total absence of changes in the seasons.
The dry tropical climate is located in the regions of the planet located between the tropics, whose main characteristics are high temperatures and practically total absence of changes in the seasons.
It is an intermediate climate between the humid tropical and the desert. In fact, its appearance has been studied just when there is an extension in the duration of the dry season of the humid tropical climate, which can last more than six months.
It is considered dry simply because rainfall is scarce throughout the year. When it rains the duration is short, although torrential rains can be unleashed.
That is why it cannot be considered in any way that in the dry tropical climate there is a winter period, because the cold is not relevant, rather it is almost non-existent. What there is is a prevailing heat in the environment that can become as unbearable as that produced in the desert climate.
But it has a big difference: it is found at higher altitudes at different latitudes, since it is born with the help of continental tropical air masses, which generate dry air and a lot of heat.
Eventually, the so-called Intertropical Convergence zone also originates, because in this area of the planet the so-called tropical anticyclones located above a continent, not the sea, are produced. Consequently, these anticyclones produce a dominant action zone of dry and hot climates.
Where is the dry tropical climate located geographically?
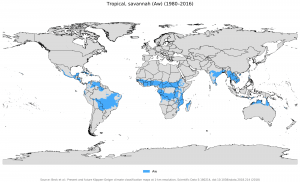 It is located exactly between 15º and 25º latitude, both north and south of the Earth.
It is located exactly between 15º and 25º latitude, both north and south of the Earth.
Its appearance has been studied just when there is an extension in the duration of the dry season of the humid tropical climate.
This type of climate develops in rather arid regions such as the Sahara and the Sahel in Africa, as well as in the Australian desert. Also less extensive regions of South Africa, Mexico and South America, are governed by the dry tropical climate.
What characteristics does the dry tropical climate have?
 It happens in the middle of great conditions of high insolation, since there is low humidity coming from the air masses. That is why there is greater solar exposure on the earth’s surface.
It happens in the middle of great conditions of high insolation, since there is low humidity coming from the air masses. That is why there is greater solar exposure on the earth’s surface.
The air is dry and at night the temperature drops sharply, because the greenhouse effect that cools the atmosphere does not take place.
The rains are scarce, so much so that less than 250 mm per year, or a little more, can hardly be quantified.
Temperatures, as has already been said, are warm during most of the year, around 27ºC, although there are wide ranges between 10ºC and 18ºC, between the warmest and coldest months.
Sometimes, the amplitude is much greater and reaches 30ºC in the summer or dry season, which usually lasts more than six months. Likewise, an aridity prevails in the environment for most of the year, with the occurrence of strong winds and a suffocating heat that prevents the proliferation of a copious vegetal layer.
What flora predominates in the dry tropical climate?
 The vegetation that makes up the predominant landscape of this climate is savannah, but the thorny steppe also rules in the higher regions.
The vegetation that makes up the predominant landscape of this climate is savannah, but the thorny steppe also rules in the higher regions.
The flora is really scarce in the arid zones of the dry tropical climate and they appear from the thickets, grasslands, cardonales and izotales.
Succulent plants, which retain water, and xerophytic, thorny plants, such as cacti and nopales, are present in the landscape.
The soils are poor, practically infertile and saline. The plants tolerant to this habitat are precisely of the halophilic type. However, there is the presence of mighty rivers that generate times of floods and descents throughout the year.
A clear example is the behavior of the Nile River in Africa, which varies during the alternation of the rainy and dry seasons. In short, the landscape is very different, rather contrary to that of the humid tropical climate, with dense forests and jungles, with dense vegetation.
What fauna does the dry tropical climate have?
 A varied fauna with a predominance of big cats such as jaguars and pumas, as well as monkeys, armadillos, deer, tapirs and many species of insects, birds, fish and reptiles make up wonderful habitats.
A varied fauna with a predominance of big cats such as jaguars and pumas, as well as monkeys, armadillos, deer, tapirs and many species of insects, birds, fish and reptiles make up wonderful habitats.
Snakes, lizards, squirrels, vultures, spiders, scorpions and coyotes have adapted splendidly to this climate.
These species have gained great resistance to the aridity of the landscape, so much so that many animals live at night to protect themselves from strong daytime insolation and environmental dryness.
Many animals also appeal to aestivation, a prolonged sleep of strategic value that allows them to stop the process of metabolic activity, there is no growth to save energy and not to perish due to the unbearable high daytime temperatures.
Both turtles, earthworms, alligators, crocodiles, snails and many reptiles use this survival mechanism successfully. The same is applied by amphibians and lungfish called Dipnoos.
How long is the day and night in the dry tropical climate?
 Most tropical regions with climates of this type do not usually have all four seasons but rather a rainy and a dry period.
Most tropical regions with climates of this type do not usually have all four seasons but rather a rainy and a dry period.
With days and nights of 12 hours duration each, without variations throughout the years.
Can humans live in the dry tropical climate?
 Countries with a dry tropical climate tend to have temperatures above 18ºC most of the year, with the presence of a rather dry environment and scarce rainfall.
Countries with a dry tropical climate tend to have temperatures above 18ºC most of the year, with the presence of a rather dry environment and scarce rainfall.
It has a presence on almost all continents, except in the Antarctic region. Interestingly, it is one of the largest climates on the planet, occupying 14% of the total.
Countries with a tropical climate are among the 30 best places to live, since a good climate favors the living conditions of all living beings, especially human beings, who better develop many productive and leisure activities in warm climates, with the benefits that tropical climates lavish.
Precisely the climates of the tropics are the most sought after on the planet. Hence, life in countries located in the imaginary strip parallel to the equator, known as the intertropical strip, does not have the 4 seasons of the year, but rather a dry period and a rainy period of greater or lesser intensity.
Although there are varied tropical climates, in all life it develops in a pleasant way. Among these spectacular forests and savannahs, with endemic flora and fauna, we have: Mexico, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Dominican Republic, Costa Rica, Trinidad and Tobago, Aruba, among others from the American continent.
Also all of the Australian desert and the Sahara in Africa, Arabia, Iran and small regions of South Africa have a dry tropical climate.
Bibliographic references
- The tropical dry forest at risk: conflicts between agricultural use, tourism development and provision of ecosystem services on the coast of Jalisco, Mexico, A Castillo, C Godínez, N Schroeder, C Galicia… – Interciencia, 2009 – ve.scielo.org
- Floristic composition of the dry tropical forest of the «Los Besotes» sanctuary and phenology of dominant tree species (Valledupar, Cesar, Colombia), ML Berdugo-Lattke, JO Rangel-Ch – Forest Colombia, 2015 – redalyc.org
- Productive and reproductive behavior of Holstein cows in semi – dry tropical climate, SRM Martha – 1992 – repository.cucba.udg.mx
- Evaluation of the regrowth capacity of two tree species in the dry tropical forest in Nandarola, South Pacific, CE Silva, OD Salgado, B González Rivas – La Calera, 2008 – repository.una.edu.ni
- Chronology of the regeneration of the dry tropical forest in Santa Rosa, Guanacaste, Costa Rica: II. Vegetation in relation to the soil, JA Leiva, OJ Rocha, R Mata… – … of Tropical Biology, 2009 – scielo.sa.cr
- Effect of management on soil aggregation in a dry tropical ecosystem, S Martínez-Trinidad, H Cotler… – Terra…, 2008 – scielo.org.mx
Maybe you are also interested in:
- Koppen climate classification: [Concept, Characteristics and Types of Climates]
- Alpine Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Arid Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- High Mountain Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Climate of Argentina: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Australia Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- California Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Climate of Europe: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Tundra Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Equatorial Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Cold Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Cold Weather: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Mediterranean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Ocean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Polar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subpolar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subtropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subhumid Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Humid Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]

![Photo of Prune a Dimorfoteca: [Importance, Time, Tools, Considerations and Steps]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/prune-a-dimorfoteca-importance-time-tools-considerations-and-steps-390x220.jpg)


