Cold Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
Important points about Cold Weather:
- What is? The cold climate, as its name indicates, is one that is subject to predominantly cold temperatures throughout the year.
- Where it is located? The cold climate is located on the coldest areas of the planet that are the poles, the Arctic and the Antarctic.
- What flora predominates? The flora found within the cold climate is very limited due to the adverse conditions that develop in these places. Lichens, certain grasses and mosses are counted.
- What fauna predominates? One of the most characteristic species of fauna of the cold climate is the polar bear. Birds are not frequent, nor are land mammals or insects.
- How long is the day and night? Winter brings with it lower temperatures and also longer nights. In this period the time of darkness can last for days.
- Can human beings live in this climate? Cold climate zones are not conspicuous for human life because there are no suitable conditions.
 Cold weather is established in those areas where temperatures are permanently below 0º C.
Cold weather is established in those areas where temperatures are permanently below 0º C.
They are spaces that stand out for being dry, sometimes with cold and icy winds that make life difficult for all kinds.
That does not exempt that there are certain species of flora and fauna that have managed to adapt, and even humans in very small numbers. But this topic has much more information to highlight and here you will have the answers you are looking for about cold weather and everything that develops in it.
What is cold weather?
 The cold climate, as its name indicates, is one that is subject to predominantly cold temperatures throughout the year.
The cold climate, as its name indicates, is one that is subject to predominantly cold temperatures throughout the year.
Precipitation is unusual, while winds are generated with great force. It is a climate that occurs because the sun’s rays penetrate obliquely, so they produce little heat.
Where is cold weather located geographically?
 The cold climate is located on the coldest areas of the planet that are the poles, the Arctic and the Antarctic.
The cold climate is located on the coldest areas of the planet that are the poles, the Arctic and the Antarctic.
There are other spaces that are not located within these three areas of the world but that, due to their altitude, reach similar temperature conditions.
For this reason, it is also common to talk about cold weather in these areas, betting on the corresponding subdivision. These cold climate zones are:
- The tundras that predominate in the northern part of Europe, America and Asia.
- The highest mountains that due to their relief tend to have very low temperatures throughout the year. For example, the Andes and the Himalayas.
- The southern zone of America which are the closest points to the pole in this area. For example, Patagonia.
All these spaces are located between 65º and 90º latitude, both in the northern hemisphere and in the southern hemisphere.
What characteristics does cold weather have?
There are many factors that characterize the cold climate and that make it so different from other types of known climates. Here they are counted:
- Air masses: it is influenced by the air masses that come from the coldest areas of the planet: the polar, arctic and antarctic. These are strong and are produced by the changes that occur in the atmospheric pressure of these places.
- Temperatures: they are always very low, in most cases being below 0º C and, in certain spaces, they can reach up to -50º C inclusive.
- Precipitation: it is reduced throughout the year, which causes a dry climate to prevail. This is another of the compelling reasons that very few animal and plant species can survive in cold weather. When precipitation does occur, it is most likely in the form of snow.
- Types: depending on the area where they are located and the characteristics of the environment, the cold climate can be divided into tundra climate, polar climate and mountain climate.
What flora predominates in cold weather?
 The flora found within the cold climate is very limited due to the adverse conditions that develop in these places.
The flora found within the cold climate is very limited due to the adverse conditions that develop in these places.
Lichens, certain grasses and mosses are counted as the main representatives of the plant world.
Flowering plants are rare, but there is a variety that produces very small flowers known as Antarctic carnation.
When temperatures are extremely low and the ground is frozen, all possibility of flora growth is eliminated.
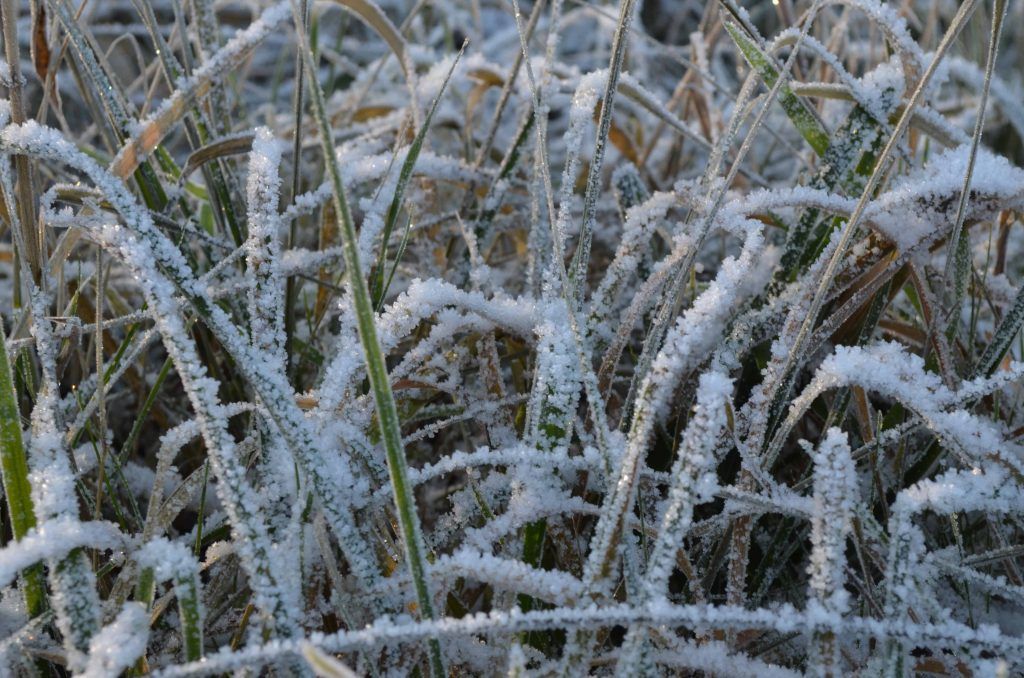

What fauna predominates in the cold climate?
One of the most characteristic species of fauna of the cold climate is the polar bear, which is covered with fur and filled with subcutaneous fat that helps keep it warm internally.
Other species that seem to have adapted very well to cold temperatures are the aquatic ones, since some variety can be found.
The main reason is that cold weather areas have a high amount of plankton, which encourages mollusks, mammals and fish to live there.
Birds are not frequent, nor are land mammals and insects. However, in the summer time it is possible to see some that arrive by migration.

How long is the day and night in cold weather?
 Winter is a time of year that brings with it the lowest temperatures and also the longest nights. In this period the time of darkness can last for days.
Winter is a time of year that brings with it the lowest temperatures and also the longest nights. In this period the time of darkness can last for days.
In the case of summer, the opposite happens, temperatures rise very little and lighting lasts for several days.
Can humans live in cold weather?

 Areas with (extreme) cold weather are not conspicuous for human life because the appropriate conditions do not exist.
Areas with (extreme) cold weather are not conspicuous for human life because the appropriate conditions do not exist.
They are spaces that require a lot of logistics for shelter and keeping at a healthy temperature for the body (which prefers warmth).
In addition, it does not allow planting and animal life is very reduced, since what exists is prepared for adaptation issues with very special characteristics.
This minimizes the chances of getting food, both for animals and for humans. Even so, there are indigenous settlements in the Arctic polar zone, which take advantage of the minimal resources that exist in their environment to survive.
It is also common for there to be small settlements of researchers who go to these places to carry out studies of a diverse nature.
The cold climate is inhospitable due to the conditions it supposes for the life of any species. However, it is important to safeguard the ecosystems of planet Earth.
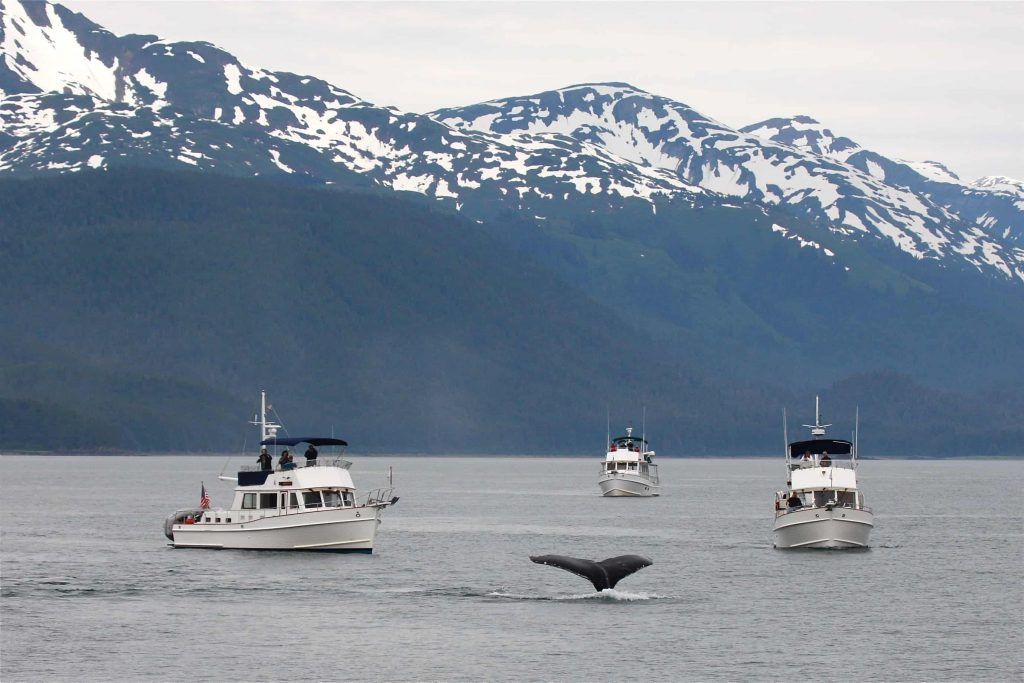

Global warming is causing considerable damage to these areas that are beginning to lose the density of ice that once existed. The human activities that are carried out in its vicinity have brought pollution problems in the waters, harming said ecosystem.
Although we do not live there, it is essential to heed the call for help that the planet makes us to remain a good place to live for everyone.

Bibliographic references
- Cold climate pastures and forages, PE Vicuña – 1985 – repository.sena.edu.co
- Cold climate mammals in the prehistoric sites of the Basque Country, J Altuna – Munibe, 1966 – aranzadi.eus
- Cold weather weeds, J Cardenas, O Franco, CE Romero Maldonado… – 1970 – sidalc.net
- Moderate cold climate fruit trees, Á Tamayo, JA Bernal, M Londoño – 2001 – sidalc.net
- Certified Organic Production of Cold Climate Vegetables, MR Pinto – 2003 – books.google.com
- The cold climate accumulations of the Sierra de Albarracín, JLP Monné, MVL Tena, MS Fabre… – … of the relief of the Sierra de …, 2010 – hoyos.org.es
Maybe you are also interested in:
- Koppen climate classification: [Concept, Characteristics and Types of Climates]
- Alpine Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Arid Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- High Mountain Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Climate of Argentina: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Australia Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- California Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Climate of Europe: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Tundra Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Equatorial Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Cold Weather: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Mediterranean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Ocean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Polar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subpolar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subtropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subhumid Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Humid Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Dry Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]


![Photo of Aconite: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/aconito_1618355790-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of How to Plant Ruda in Your Garden: [Complete Guide + Step by Step]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/how-to-plant-ruda-in-your-garden-complete-guide-step-by-step-390x220.jpg)