Climate of Europe: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
Important points about the Climate of Europe:
- What is? Europe’s climate is the product of a great confluence of factors that are generated by its geographical location.
- Where it is located? The climate of Europe is established throughout the entire continent, including the small islands that surround it, such as Ibiza and Formentera in Spain.
- What flora predominates? The predominant flora in this area are roses, dandelions, poppies, daffodils and tulips. The trees tend to be of the deciduous type.
- What fauna predominates? Bears, cats, fish, insects, birds and many other mammals and reptiles make up the great family of European fauna.
- How long is the day and night? The longest day lasts about 15 hours, while the night is adjusted to 7 hours, corresponding to summer.
- Can humans live in this climate? Logically, life is possible in the climate of Europe, since all the countries that are within this continent are more or less populated.
 Europe is a continent that has a great climatic variety, all of them being predominantly temperate.
Europe is a continent that has a great climatic variety, all of them being predominantly temperate.
With its location in the northern hemisphere and a set of elements that influence climate development, it is well worth studying what happens there.
These climatic variations bring with them the presence of many types of flora and fauna species that enrich the biological value of the area.
From the characteristics of the environment, to human life in the climate of Europe, it will be the subject of study of the next lines. If you are interested, do not miss a single detail.
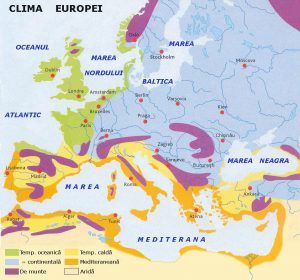
What is the climate of Europe?
Europe’s climate is the product of a great confluence of factors that are generated by its geographical location. Here are items like:
- The polar air masses that occur at both the oceanic and continental levels.
- Tropical air masses that are generated at sea level with a low incidence of continental type.
- The continental extensions product of its communication with the Asian continent.
- The type of relief that exists in each zone and that is one of the most influential elements in the matter of low temperatures.
Where is Europe’s climate located geographically?
The climate of Europe is established throughout the entire continent, including the small islands that surround it, such as Ibiza and Formentera in Spain.
Europe is distributed from 30º to 70º north latitude, occupying about 10.18 million square kilometers of extension.
Within its geography there are 48 countries, each with its own climatic diversity. For example, the bone- chilling cold in Siberia, Russia, is nothing like the warm wind that blows across the Greek islands year-round.
This does not exempt that within the countries themselves there are climatic variations of their own. For example, the variation between the Canary Islands and the Pyrenees.
What characteristics does the climate of Europe have?
Despite the diversity of climates that exist, it is possible to establish a set of characteristics typical of the climate of Europe:
- Temperatures: they have an average that ranges from 18º to 20º C, descending below 0º C in some areas of the north and other spaces where there are frosts in winter. Summer temperatures are not so high unless there is the presence of so-called «heat waves» that could place thermometers above 35º C.
- Winds: they are influenced by the set of air masses that operate from the oceans and from the continents, especially in the part of Eurasia.
- Precipitation: the usual thing is that the rainy season is generated between spring and summer, even arriving some rains in autumn. However, winters tend to be dry.
- Types of climate: depending on the area in which the climate is being studied, it is possible to note the presence of the Mediterranean climate, the humid continental climate, the dry climate of the mid-latitudes, the climate of the boreal forests, the climate of mountain, west coast maritime climate and tundra climate.
What flora predominates in the climate of Europe?
 The flora of Europe is rich and varied, finding species of all kinds throughout its territory.
The flora of Europe is rich and varied, finding species of all kinds throughout its territory.
These are distributed in habitats such as temperate forests and other reservoirs that have been influenced, in some way, by man.
The predominant flora in this area are roses, dandelions, poppies, daffodils and tulips.
The trees tend to be of the deciduous type where the coldest winters are generated and remain evergreen where they are mild. In addition, it is possible to work in agriculture and get good harvests of fruits, legumes and vegetables of almost all types.
Even so, species that were once common in Europe are today severely threatened, which is why more and more conservation strategies for natural habitats are being considered.
What fauna predominates in the climate of Europe?
 The fauna is also rich and varied, being possible to observe species characteristic of the coldest environments and other colorful ones popular in the tropics.
The fauna is also rich and varied, being possible to observe species characteristic of the coldest environments and other colorful ones popular in the tropics.
Bears, cats, fish, insects, birds and many other mammals and reptiles make up this great family of European fauna.
Due to the highly variable conditions that exist in certain parts of Europe, there are species adapted to the hibernation process during the winter.
Migration is also a frequent practice, especially in birds, which head south in search of more favorable conditions to reproduce. When the winter passes, these species return to their natural habitat and continue their daily lives.
How long is the day and night in Europe’s climate?
 The duration of these daily events responds to the arrival of the solstices throughout the year, making the nights last longer in winter and the days longer in summer.
The duration of these daily events responds to the arrival of the solstices throughout the year, making the nights last longer in winter and the days longer in summer.
On average, the nights lengthen until they occupy a maximum of 15 hours, and then begin to descend.
On the contrary, the longest day lasts about 15 hours, while the night is adjusted to 7 hours, corresponding to summer.
Can humans live in Europe’s climate?
 Logically, life is possible in the climate of Europe, since all the countries that are within this continent are more or less populated.
Logically, life is possible in the climate of Europe, since all the countries that are within this continent are more or less populated.
Man has managed to adapt to each of the conditions that the seasons bring with them, including the study and work with plants for the provision of food.
Europe’s climate is highly variable and heterogeneous due to its position in the world and the way in which the sun’s rays are projected on its territory.
And if we consider the progress and development of each of its countries, it is more than clear that it is a pleasant climate for human, animal and plant life.
Bibliographic references
- Climatic fluctuations and historical change: The climate in Central Europe since the sixteenth century and its significance for the development of population and agriculture, C Pfister – Geo Critique: critical notebooks of human geography, 1989 – raco.cat
- Review of» The Little Ice Age. How Climate Affected European History. 1300-1850″ by Brian Fagan, RJ Marce – Historical Signs, 2012 – redalyc.org
- Glaciers and Climate revisited: alpine glaciers and history of the European climate, ES Cañadas – Geographical Research Notebooks, 2004 – publications.unirioja.es
- INFLUENCE OF EL NIÑO ON THE CLIMATE OF WESTERN EUROPE IN SUMMER, MM DÍEZ, BR FONSECA, J LÓPEZ – aeclim.org
- Climate change and climate risks in Spain, J Olcina – 2009 – rua.ua.es
- Climate and landscape of the Hispanic Peninsula, F Hernández-Pacheco – Arbor, 1954 – search.proquest.com
- REPERCUSSIONS OF CLIMATE ON EUROPEAN TOURISM, AF Rodelgo – ucm.es
Maybe you are also interested in:
- Koppen climate classification: [Concept, Characteristics and Types of Climates]
- Alpine Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Arid Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- High Mountain Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Climate of Argentina: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Australia Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- California Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Tundra Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Equatorial Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Cold Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Cold Weather: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Mediterranean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Ocean Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Polar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subpolar Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subtropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Subhumid Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Temperate Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Humid Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]
- Dry Tropical Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]

![Photo of Vriesea: [Characteristics, Cultivation, Care and Disadvantages]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/vriesea-characteristics-cultivation-care-and-disadvantages-390x220.jpg)


