Bordeaux Broth: [Origin, Characteristics, Uses, Preparation and Application]

How does Bordeaux broth originate?
 The origin of the Bordeaux wine is attributed to an invention of the vintners of the Bordeaux region, France, to scare away those who passed by the edges -bordelaise-, of the vineyards and uprooted the clusters.
The origin of the Bordeaux wine is attributed to an invention of the vintners of the Bordeaux region, France, to scare away those who passed by the edges -bordelaise-, of the vineyards and uprooted the clusters.
French grape growers observed that the lines of vines treated with this product remained healthier than the rest of the plants.
They thus discovered the effects of the product on fungi, bacteria and mites. Its diffusion is attributed to the French phytopathologist Alexis Millard who used it for the first time in 1882 to control crop pests.
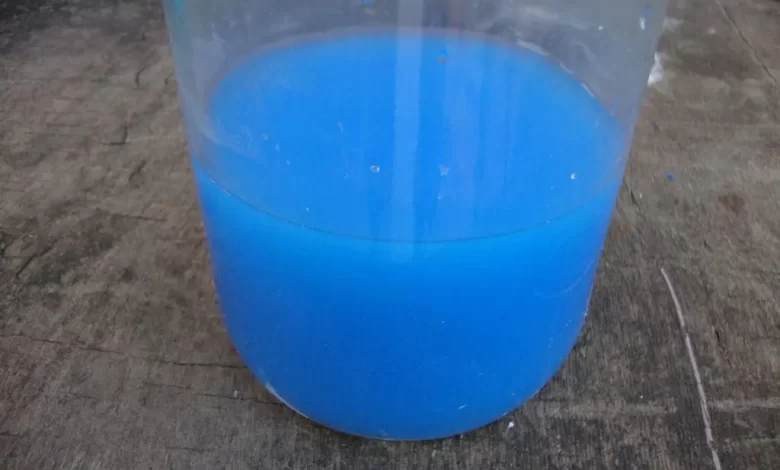
The manufacture is based on a process of neutralization of a solution of copper sulfate with lime. It can be made by hand, although it can currently be purchased on the market in 1, 4 and 20 liter presentations.
What is Bordeaux broth?
 It is a fungicide based on lime and copper sulfate (cuprocalcium), very effective and used for pest control in organic or ecological crops.
It is a fungicide based on lime and copper sulfate (cuprocalcium), very effective and used for pest control in organic or ecological crops.
The Bordeaux mixture has a wide field of action against a large number of diseases caused by fungi.
It is highly valued as it is a low cost fungicide, easy to prepare and its ingredients can be easily purchased in the market.
What is Bordeaux broth used for?
Bordeaux mixture is used as an agent for the «prevention» and also to combat diseases caused by fungi in the stems, leaves and fruits of crops.
How to prepare the Bordeaux broth step by step?
Depending on the amount of Bordeaux mixture to be prepared, a certain amount of Ingredients will be used and the most important thing is that personal protection, such as masks and gloves, must be used during preparation.
Ingredients
Among the necessary ingredients, for example, for 100 liters are:
- 1 kilogram of hydrated lime or quicklime.
- 1 kilogram of copper sulfate.
- 100 liters of warm water around 60º C to favor the solubility of the ingredients.
- Wooden paddles used to stir the solution.
- Plastic bucket of 100 liters and another of 20 liters or plastic tanks where to prepare the broth.
Preparation
- Prepare the solution with copper sulfate and then add the hydrated lime, it is recommended to follow this order because otherwise it can produce toxic gases. This process is carried out, moving with the paddle until solubility is achieved.
- Check the degree of oxidation (corrosion) by introducing iron objects that can be nails or a machete. Excess acidity will oxidize the metals, which means that more lime must be added until the iron does not rust.
- Do not use the Bordeaux mixture for more than 24 hours, once it has been prepared, in order for it to have the specific effect required.
- Among the limitations of the Bordeaux mixture are that it should not be mixed with other products because it can be dangerous; Use skillfully as it can clog the nozzle of sprinkler hoses.
How and when is the Bordeaux mixture applied?
 The Bordeaux mixture is applied through the sprinkling process, either on trees or herbaceous plants with the aim of preventing the appearance of diseases or to stop their spread.
The Bordeaux mixture is applied through the sprinkling process, either on trees or herbaceous plants with the aim of preventing the appearance of diseases or to stop their spread.
The application of the product must be carried out as follows:
A mixture based on 50% solution and 50% water will be applied to “nursery” seedlings, and in “field” plantations, Bordeaux mixture will be used at 100% of the product concentration (pure).
Its application in fruit trees must be done when it is still without leaves and with buds swollen for budding. Never apply to fruit trees with leaves. It is very important that the right mixture is made to be applied and try to use everything immediately after having prepared it.
What pests and diseases does Bordeaux mixture combat?
 The new pests and diseases that appear in the environment and that attack plants force us to search for more and better ways to combat them, from which the Bordeaux mixture arises.
The new pests and diseases that appear in the environment and that attack plants force us to search for more and better ways to combat them, from which the Bordeaux mixture arises.
These techniques must provide harmony to the environment, easy preparation and low costs, which makes the Bordeaux mixture an excellent alternative.
Bordeaux mixture is applied to repel diseases caused by fungi that attack most horticultural items, including: La Roya; Anthracnose; Chicken eye; Coffee iron stain; Phytophthora; downy mildew; Monilia and Alternaria, among other fungi.
What is Bordeaux paste?
 Bordeaux paste is a more concentrated and thick Bordeaux broth. It is made with the same ingredients as the broth: copper sulfate and lime.
Bordeaux paste is a more concentrated and thick Bordeaux broth. It is made with the same ingredients as the broth: copper sulfate and lime.
Its use is to disinfect cuts on trees that have been pruned or that have undergone surgery because many tissues were rotten or injured, as is the case with citrus gummosis.
Bordeaux paste can also be used to brush trunks, thicker branches and the base of many roots that are exposed above ground, in order to prevent future diseases.
It is an excellent fungicide to be used in coffee cultivation after pruning and socas (drastic pruning that coffee plantations undergo for their renewal).
How to make Bordeaux paste?
The preparation of the Bordeaux paste is the same procedure used to prepare the original 1% Bordeaux mixture.
Hence, 1 kg of copper sulfate, 2 kg of quicklime and 12 liters of water must be mixed in a bucket. Stir well to create a dense but manageable paste. Bordeaux paste can be stored for a maximum of three days.
Bibliography and references
- Centa.gob.sv. Bordeaux broth. Technical Guide No 5. National Center for Agricultural and Forestry Technology. Reproduced from: http://www.centa.gob.sv/sidia/inicio.html
- Estoesagricultura.com. (2019, November 3). Bordeaux broth. Reproduced from: https://estoesagricultura.com/caldo-bordeles/
- Inta.gob.ar. Bordeaux broth. Secretariat of Agroindustry- Argentina. Reproduced from: https://inta.gob.ar/sites/default/files/inta_cartilla_practica_3_caldo_bordeles.pdf