Aquaponics or farming with fish. What is it, how does it work and advantages
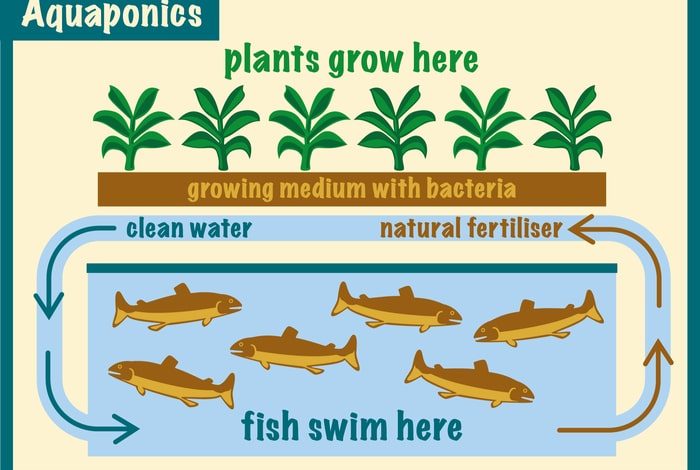
Aquaponics is a sustainable system for the simultaneous production of plants and fish that combines traditional aquaculture (breeding of aquatic animals) with hydroponic cultivation (cultivation of plants without substrate but in water with dissolved nutrients) in a symbiotic environment in which the plants they benefit from the fish and vice versa.
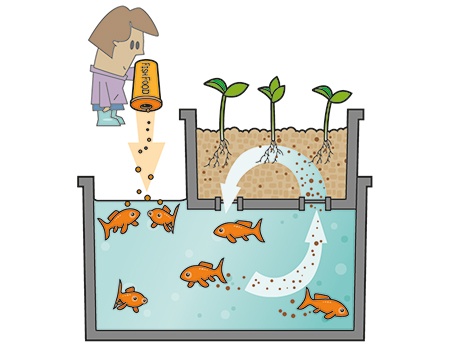
What is aquaponics?
As we have said before, aquaponics has two fundamental parts: aquaculture, to raise aquatic animals, and hydroponics, to grow plants.
Aquatic waste resulting from fish farming accumulates in the water due to the use of closed recirculation systems implemented in most aquaculture systems. Effluent-rich waters and in high concentrations can be toxic to aquatic animals; however, they are a source of essential nutrients for plant growth.

Components of an aquaponic system
Aquaponics systems are normally grouped into different components or subsystems. Typical components include:
- Breeding tank: where the fish grow and feed.
- Solids Removal – A unit to remove uneaten food, detached biofilm, and fine sediment.
- Bio-filter: the place where nitrifying bacteria grow and convert ammonia into nitrates, so that they can be assimilated by plants.
- Hydroponic Subsystems – The part of the system where plants grow by absorbing nutrients from the water.
- Sump – The lowest point in the system where water flows and is pumped back to the rearing tanks.
Aquaponics Basics
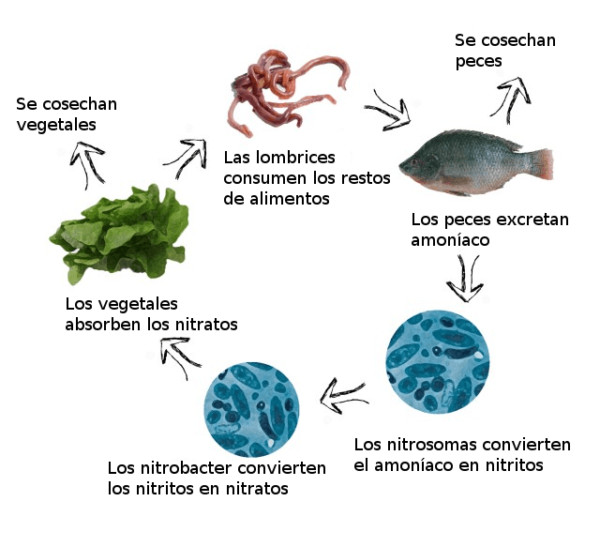
Nitrification
Nitrification is the aerobic conversion of ammonia to nitrates. It is one of the most important functions in an aquaponics system, as it reduces the toxicity of the water to fish, and allows the resulting nitrate compounds to be removed by plants and used for nutrition. Fish constantly release ammonia into the water as a product of their metabolism, but most of it must be filtered out as high concentrations of ammonia can kill fish. Aquaponics takes advantage of the ability of some bacteria to convert it into other nitrogenous components. In this case we distinguish two types of bacteria:
- Nitrosomonas – bacterium that converts ammonia to nitrites
- Nitrobacteria – bacteria that convert nitrites to nitrates.
In the aquaponic system, the bacteria responsible for this process form a biofilm on all solid surfaces that are in constant contact with water. The submerged roots of vegetables have a large surface area, allowing many bacteria to accumulate on them. The care of these colonies of bacteria is important to regulate the complete assimilation of nitrogen. Since the nitrification process acidifies the water, it is necessary to add non-sodium bases, such as potassium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide, to neutralize the pH of the water.
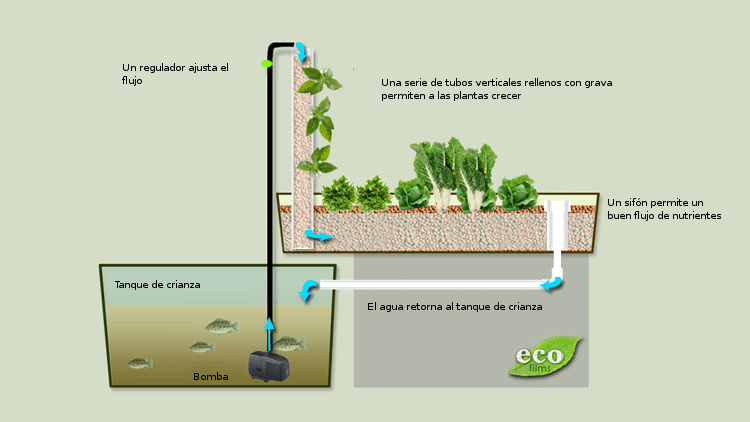
Elements of an aquaponics system
An aquaponic system is made up of two subsystems:
- The cultivation of plants in hydroponics or hydroponic subsystem.
- Fish farming in attached fish tanks, or aquaculture subsystem.
hydroponic subsystems
The plants are grown in the same way as in conventional hydroponic systems, with their roots immersed in the nutrient-packed water. This allows them to filter ammonia that is toxic to aquatic animals and its metabolites. After the water has passed through the hydroponic subsystem, it is cleaned and oxygenated, and can return to the aquaculture vessels, forming a continuous cycle.
Most green leafy vegetables, such as lettuce, spinach, or Swiss chard, grow well in hydroponic subsystems. Other vegetable species that grow well in an aquaponics system include: beans, radishes, strawberries, onions, and herbs.
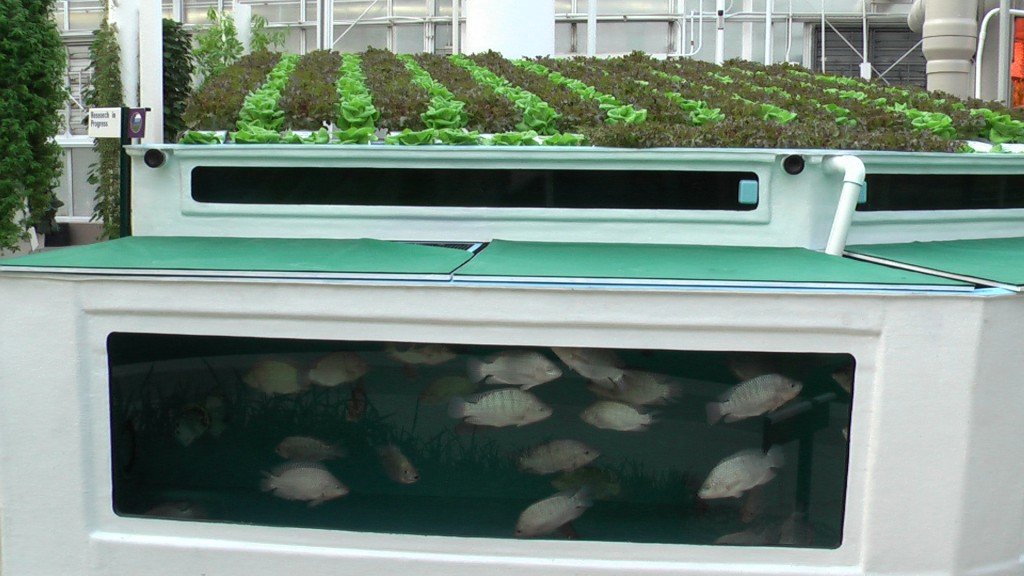
Freshwater fish are the most commonly farmed aquatic animals using aquaponics, although crayfish and prawns can also be farmed. In practice, tilapia is the most popular fish in food projects, although barramundi, silver perch, tandanus catfish (siluriformes) or jade perch are also used. For temperate climates, when there is no need to maintain water temperature, Lepomis macrochirus (bluegill) and catfish are good choices for a home system. Koi and crucian carp (or goldfish) can also be farmed if the fish are not for human consumption.
How to grow plants with fish
Aquaponic systems generally do not discharge or exchange water under normal operations, so they recirculate and reuse water very effectively. The system relies on the relationship between animals and plants to maintain a stable aquatic environment with minimal fluctuation in oxygen levels and a nutrient environment. Water is added only to make up for loss due to plant uptake and transpiration, evaporation of surface water, or removal of biomass as solid waste from the system. As a result, aquaponics uses approximately 2% of the water that a conventional farmrequired to irrigate the same vegetable production. This enables aquaponic crop and fish production in areas where water or fertile land is scarce.
The three main inputs to the system are: water, feed given to the aquatic animals, and the electricity to pump the water between the aquaculture subsystems and the hydroponics systems.

Advantages and disadvantages of aquaponics
The advantages of aquaponic systems are:
- Reuse of water, presenting an advantage for those areas where its availability is scarce.
- Organic plant fertilization with natural fish emulsion.
- The disposal of solid waste resulting from intensive aquaculture.
- The reduction of arable land needed for crop production.
- The general reduction of the footprint caused to the environment by the production of vegetables and animal husbandry.
- The reduction of pathogens that frequently plague aquaculture production systems.
Some possible disadvantages of aquaponics are:
- The initial cost of the installation.
- The large number of ways the system can be configured tends to lead to equally varied results.
- Some aquaponic installations rely heavily on man- made power, technological solutions, and environmental control to achieve optimal recirculation and water and tank temperatures. Although if a system is designed with energy conservation in mind, using alternative energy and a reduced number of pumps instead of using gravity, it can be very efficient in terms of energy utilization.
This is all. I hope you have found this topic of aquaponic crops interesting. Until next time Agrohuerters!



![Photo of Prune the Lady of the Night: [Importance, Time, Tools, Considerations and Steps]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Podar-Dama-de-Noche-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Weevils (Otiorhynchus spp.): [Characteristics, Detection, Effects and Treatment]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/weevils-otiorhynchus-spp-characteristics-detection-effects-and-treatment-390x220.jpg)