5 Organic fertilizers for the garden: Properties and application

Hello Agroguerters! Today we are going to talk about organic fertilizers or fertilizers. Depending on the type of plant, it will require more of one type of nutrient than others. Fertilization can be made according to the specific lack of nutrients, but as on many occasions, it is known what specific deficit it has, it is paid in such a way that all kinds of nutrients are provided.

The essential nutritional elements are N (Nitrogen), which is what makes the plant grow quickly; Phosphorus (P), helps the proper development of stems, leaves and fruits; and finally Potassium (K), which is essential for the development of seeds and fruits. In addition to these, which are the ones that plants take in large quantities, many others are needed, such as calcium, sulfur, magnesium, manganese, iron, etc.
These are the 5 most used organic fertilizers:
Eggshell
It’s surprising to use eggshell for fertilization, but you can. The reason is its high calcium content. Calcium is a very important element for plants, especially for fruit trees. Since its bark accumulates high contents of this element.

In our garden we can use it in different ways or by crushing the shell of an egg and spreading it over the substrate; or without crushing it, burying the pieces of shell a little. The use of this fertilizer should not be abused, since the pH of the soil can increase and this does not benefit because, as we always say, the pH has to be close to neutral.
Coffee
On previous occasions we have already talked about the great benefits that coffee brings to our garden, as manure or fertilizer is one of them because it is very rich in Nitrogen. It can be added in various ways to the substrate; either infused or boiled in water or else another option is to add the ground grains, either in small pieces or powder, to the substrate. You can leave it on top or stir it lightly to mix it.
home compost
The most common is to make the compost in a large container (composter), and in layers, in the first one, which is the deepest, we must put a layer of about 15 cm high of dry material, such as wood, leaves or dry branches., on top of this we can already put the layer of fresh organic material also of another 15 cm, such as pruning remains or vegetable remains from the kitchen, we must take advantage of all the remains of organic matter that we can. You can also add another layer on top from the ground, so that there is more richness of nutrients and microorganisms.
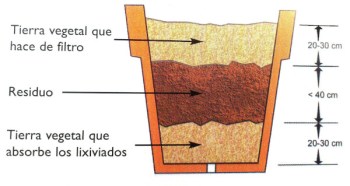
This should be left to stand with moisture for about 3 months. It is very complete in nutrients and very cheap to make, you just have to be patient until it is finished, and place it in a strategic place to avoid bad smells.
ashes
These are generally obtained from the remains of dry burned wood or firewood. They provide a high content of phosphorus and potassium, on the other hand, excessive use can increase the pH of the substrate, that is, it becomes basic. To add it to our crop, it is best to mix it with the substrate, this can be done superficially.
Earthworm humus

This fertilizer is one of the most recommended due to its numerous advantages, such as the improvement in water retention in the soil or substrate, the high nutrient content that it provides, especially Nitrogen and Calcium. Worm humus, you can buy it or even make it yourself, it can be done in different ways, it is what is known as vermiculture.
One recommendation is that, contrary to what one might think, fertilization should be avoided during flowering times, during the ripening of the fruit, because these are times when the plant is at its maximum functional activity, and a very large as providing large amounts of fertilizer could be harmful, the plant not responding normally.
On the other hand, something that greatly benefits the maintenance of soil fertility if what we have is a garden on a piece of land, is crop rotation.
The subscriber is not only important to nourish the plants, but also to improve the soil, in sandy soils it greatly improves its structure as well as helping to retain water, avoiding dryness. In clay soils it also benefits a lot, since it improves its aeration.
References
- Margulis, L., Chapman, M. (2009). Chapter Five – KINGDOM PLANTAE. Editor(s): Lynn Margulis, Michael J Chapman, Kingdoms and Domains (Fourth Edition). Academic Press. 411-462.
- Ali, P., Chen, Y., Sargsyan, E. (2014). Chapter 12 – Bioactive Molecules of Herbal Extracts with Anti-Infective and Wound Healing Properties, Editor(s): Kateryna Kon, Mahendra Rai. Microbiology for Surgical Infections. Academic Press. Pages 205-220.
- I. Yamaguchi, J. Cohen, A. Culler, A. Quint, J. Slovin, M. Nakajima, S. Yamaguchi, H. Sakakibara, T. Kuroha, N. Hirai, Yokota, T. (2010).Plant Hormones.Editor(s): Hung-Wen (Ben) Liu, Lew Mander. Comprehensive Natural Products II. Elsevier. 9-125.
Agrohuerters, apart from having seen these ecological fertilizers, we have also reviewed their advantages. You already know that you have to use it in moderation and when the plants need it. In the flowerpot they are usually used less frequently, because as the plants are contained in such a small container, there are not as many losses as in the soil. Until next time!

![Photo of Mulch Fly: [Detection, Steps to follow and Products to use]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/mulch-fly-detection-steps-to-follow-and-products-to-use-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Camellia Cuttings: [Concept, Period, Rooting and Planting]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/camellia-cuttings-concept-period-rooting-and-planting-300x220.jpg)

