Home remedies against garden pests and diseases

Today we will see how to make home remedies for sick or pest plants. Natural preparations to eliminate pests and fungi are made with plants, so they are organic remedies suitable for organic farming.
What are natural preparations for the control of pests and diseases
Natural preparations are insecticides and antifungals made from plant extracts.
In organic or ecological agriculture, phytosanitary treatments or chemical insecticides are not allowed to eliminate pests and diseases, so home remedies made with plants are a good alternative and one of the most common methods of integrated fight against pests and diseases.

The “ integrated fight ” is the combination of different ecological methods to eliminate pests and diseases from the orchard. The use of home remedies or natural preparations made with plants is one of them. Apart from these, there are other ecological methods such as insect traps, the use of natural enemies or biological control, etc.
Plants to make Home Remedies against Pests and Diseases
If you want to cultivate a chemical-free organic garden, you should use home remedies made with plants or organic preparations against pests and diseases.
Next we will see three plants with which you can make home remedies for pests and diseases and how to make natural preparations.
1. Natural remedies with horsetail
Horsetail or Equisetum is one of the most effective plants against fungi in the garden. Ecological home remedies made from this plant can be used in order to prevent fungi or fight against diseases caused by them.

Horsetail natural preparations are also useful for repelling snails and slugs and for fighting other common pests in the garden, such as aphids and spider mites.
How to make home remedies with horsetail
Next we will see how to make two natural remedies with horsetail to prevent fungi in the soil and on plants:
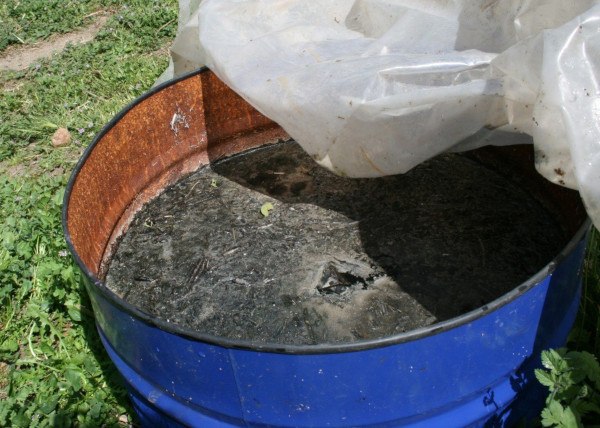
Horsetail slurry: Boil approximately 1 kg of fresh horsetail, or 500 grams if dried, in 10 liters of water for half an hour. Then filter it and let it rest for a few days, until an unpleasant smell appears. Dilute by adding 100 liters of water (1:10 ratio) and store for application (maximum storage: 2 weeks).
Horsetail decoction: Boil 50 grams of dried horsetail (or twice as much if fresh) in 5 liters of water for one hour. Let stand, strain and use diluted to 20%.
How to apply horsetail preparations in the orchard
You can apply them on the ground to prevent them from passing to the plants, and also in the areas of your vegetables where fungi have appeared on other occasions:
- In autumn and winter (when we haven’t planted anything yet): periodically treat the soil with the decoction or slurry, spraying it on it. Use about 30-40 liters per hectare. In an orchard of 20 square meters, for example, this would be equivalent to 60-80 ml of the preparation in the entire orchard.
- Before sowing/transplanting or just sowing/transplanting: disinfect the seedbeds and the substrate (the “earth”) by spraying the decoction, or the mixture of it and an infusion of tansy (a plant that is also used to make home remedies organic) in a 2:1 ratio (2/3 horsetail and 1/3 tansy).
- During cultivation: preventively spray crops every 10-15 days. If the fungi have appeared on the plants in the garden, it will be necessary to act quickly and spray with the decoction or with the slurry for 4 to 8 days in a row until the attack subsides a bit. Then do it once or twice a week throughout the crop so that it does not appear again. In wet periods there is no problem with applying the solutions to the leaves, but it is not convenient to do it when the weather is hot and dry (if so, apply only to the soil and stems).
2. Nettle slurry against pests and fungi
Nettle is a plant widely used in natural remedies against pests. This plant helps plants grow stronger and more vigorous, collaborating in the prevention of diseases caused by fungi and also helping to eliminate them. Nettle is very effective against fungi that normally develop at low humidity, such as Oidium. Also, like Equisetum, it helps in the fight against aphids and spider mites.

Nettle slurry: 1 kg of fresh nettles (or 250 grams of dried nettles) + 10 liters of water. Let macerate for about 10 days and stir every two or three. Once this time has passed, remove the film that has formed on the surface of the liquid and you can filter it and store it in jars to use it when you need it. When you are going to spray it on the soil or on crops, you must dilute it in water (in a 1:20 ratio). If you do not have time or space to make this preparation, you can buy the extract directly, which is prepared to be diluted in water and applied.
This natural preparation must be applied at the beginning of the crop by spraying the soil and/or the plants with the slurry or a mixture of it and the horsetail decoction. This will help the plants in the garden grow healthier.
To eliminate aphid and red spider pests with nettle slurry, spray the preparation on the branches and leaves and alternate this method with other methods such as traps or natural enemies.
3. Home remedies with garlic to eliminate pests and diseases
Garlic is bactericidal and fungicidal, so preparations made from it will help prevent and treat diseases caused by fungi and bacteria. It is also effective in repelling worms, aphids and mites.

Garlic alcohol: beat or blend four or five cloves of garlic with half a liter of alcohol and half a liter of water for three minutes. Then strain the mixture and store in a covered jar in the fridge to chill (the effect is greater when the mixture is cold).
Garlic infusion: soak 6-8 cloves of garlic in a liter of water for 24 hours. Then boil the water with the garlic for 20 minutes over low heat and allow to cool.
Apply the garlic preparations in the soil and spray on the stems of the affected plants.
There are other plants to make home remedies or natural preparations against pests and diseases, such as chamomile or onion, and substances such as Neem oil, or pyrethrum, which are natural products that also come from plant extracts.
References
- Ledezma, E. & Apitz-Castro, R., 2006. Ajoene, the main active compound derived from garlic (Allium sativum), a new antifungal agent. Ibero-American Journal of Mycology, vol. 23 (2), p. 75-80.
- Pino, O. et al., 2013. Plant secondary metabolites as alternatives in pest management. Plant Protection Magazine, vol. 28 (2), p. 95-108.
- Ali, P. et al., 2014. Bioactive Molecules of Herbal Extracts with Anti-Infective and Wound Healing Properties. Microbiology for Surgical Infections. Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment, p. 205-220.
- Chávez, AR & Aquino Jara, AS, 2014. Control of soil fungi Rhizoctonia sp., Fusarium sp. and Sclerotium sp. with plant extracts. Agricultural Research, vol. 14 (1), p. 17-23.
- Muy-Rangel, MD et al., 2018. In vitro antifungal activity of garlic essential oil (Allium sativum L.) against Alternaria tenuissima. Mexican Journal of Phytopathology, vol. 36 (1), p. 162-171.