Bacillus thuringiensis and biological control: alternative to insecticides
Hello to all agrohuerters! As you know, there are multiple ways to control plant pests and diseases in an ecological way, always trying to make these methods as least harmful as possible to the environment. In today’s article we are going to talk to you about biological control, specifically about a bacterium known as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) and how this bacterium can help us in the garden to eliminate pests and diseases. In this way, we will have more information when choosing a product for our plants and we will know what we are buying.

What is Bacillus thuringiensis?
We are sorry to tell you that there is no simpler common name to call this bacterium, so we will have to get used to its Latin name…
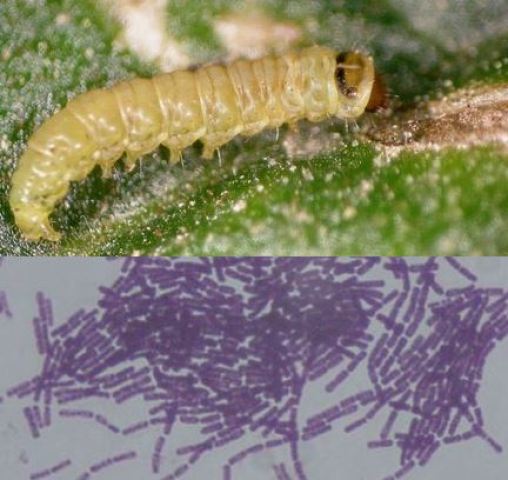
Bacillus thuringiensis is a type of entomopathogenic bacteria, that is, it can cause infectious diseases in insects. It is a bacterium classified as «Gram positive», which means that they have a specific cell envelope compared to other bacteria known as «Gram negative». In addition, it is present in the soil. Therefore, it is necessary to take good care of the microbiological content of our soils, through compost or other techniques.
It was discovered for the first time in Japan in 1902. In the 1960s, in the United States, it was the first approved microorganism in the world as a bioinsecticide. And, currently, it is one of the most widely used biological control products.

Advantages of using Bacillus Thuringiensis
The fact that Bacillus thuringiensis is one of the most used biological pest control products in Organic Farming is no coincidence.
This bacterium has several advantages over other products such as the ones we mention below:
- It is a very specific product. Therefore, it respects the beneficial fauna present in the orchard and is not harmful to the environment.
- It is not toxic to humans.
- Very effective against different caterpillars.
- The prices are not very high.
How does Bacillus Thuringiensis work?
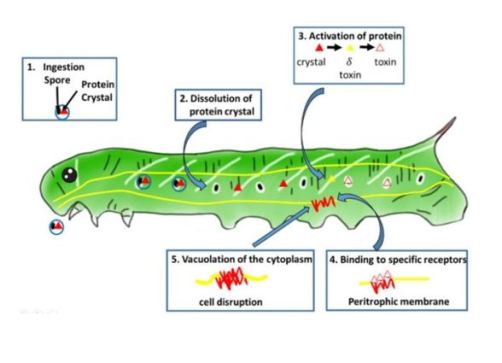
The particular way of acting of this bioinsecticide is based on the moment of sporulation (production of spores) of the bacteria, that is, at the moment of their reproduction (asexual). By sporulating, they produce a kind of protein crystals known as «delta-endotoxins». These toxins are activated once they are ingested by the insect and «hook» in the intestine. Specifically, they cause a rupture of the cell membrane of the cells of the intestine and the subsequent death of the insect between 24 and 48 hours later.
Pest treatment with Bacillus thuringiensis
As we have said before, one of the advantages of this biological control insecticide or bioinsecticide is its effective use against various pests present in fruit trees, vines, vegetables, conifers, oaks, etc.
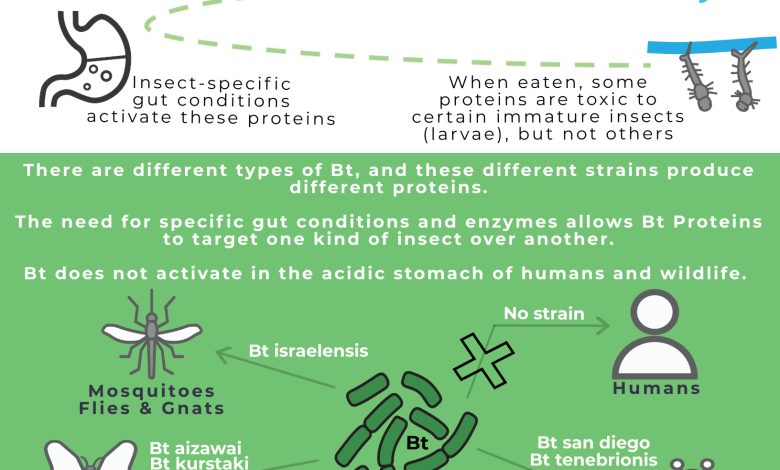
In biological control product stores you can find some where it is written “biological insecticide – Bacillus thuringiensis “. Depending on the bacterial strain, it will be more or less effective against insects. Therefore, we must find the one that best suits our problem.
Bacillus thuringiensis insecticides are generally used to control butterfly and moth caterpillars (Lepidoptera), fly and mosquito larvae (Diptera), and beetle larvae (Coleoptera).
Below, we present the main pests that can be treated with this bacterium.
Tuta absolute or tomato moth
It is one of the main tomato pests that affects the aerial parts of the plant. Its most characteristic symptoms are the presence of white mines on the leaves or fruits that later turn brown and necrotic. This pest can also affect the aubergine or potato crop.

Ostrinia nubilalis or corn borer
It could be said that the corn borer is one of the most important pests of this crop. The caterpillars of this lepidoptera damage ears and stems by tunneling into them to feed.
pine processionary
The main damages are defoliations produced by the feeding of the larvae.
Other insects such as: Pandemis heparana or fruit tortricid and Eupoecilia ambiguella or vine moth
As in the previous cases, the use of Bacillus thuringiensis can be very effective against the caterpillars of tortricids and the grapevine moth.
When and how to apply the insecticide based on Bacillus thuringiensis
Its effectiveness is highly dependent on several factors such as the insect’s way of life, weather conditions or the concentration of product used.
In any case, we must take into account the following considerations when applying it:
- When our plants are dry.
- Since we see the presence of caterpillars on our plants or preventively before the eggs hatch.
- If it rains after applying the treatment, wait about 12 hours and apply again.
- It is recommended to apply in the evening-night since the caterpillars usually feed during the night.
- Young caterpillars or larvae are more susceptible to treatment.
The rest of the application requirements will be specified in the product at the time of purchase.
If you have other types of problems with caterpillars, here is the link to the article I have caterpillars on my plants, how can I eliminate them.
References
- G. Keshavareddy, ARV Kumar. (2016). Chapter 14 – Bacillus thuringiensis, Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security, Academic Press, 2016, 443-473.
- Alejandra Bravo, Sarjeet S. Gill, Mario Soberón. Bacillus Thuringiensis: Mechanisms and Use, Reference Module in Life Sciences, Elsevier.
Do not hesitate to ask us all the questions you want in the comments about Bacillus thuringiensis and see you in the next article!

![Photo of Prune Dahlias: [Importance, Time, Tools, Considerations and Steps]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/prune-dahlias-importance-time-tools-considerations-and-steps-390x220.jpg)


