Powdery mildew in the Garden: powdery mildew in cucumber, in pumpkin,… How to combat it?

In the last visits we have made to several urban gardens, their members have told us that during this spring they have had to fight with powdery mildew. Therefore, it may be interesting to share with you HOW TO FIGHT OIDIUM.
As you know, under all the articles we have a forum where we would like you to share with us different remedies or experiences that you have had to broaden the knowledge of the agrohuerter community. Let’s start!
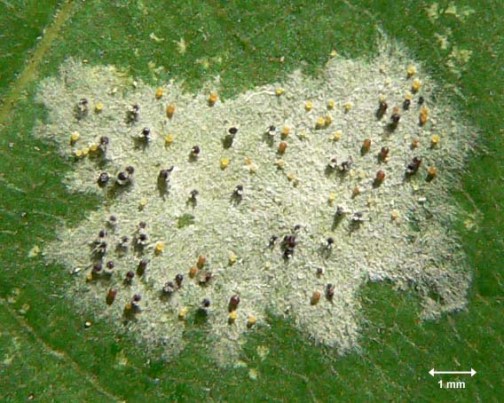

What is Oidium?
Powdery mildew is a disease caused by a parasitic fungus, that is; It settles in the plant to benefit from its mechanism and in turn causes a disease.
With fungi, the problem we have is that most are microscopic, so the identification of the disease they can cause in a plant is done when we observe the symptoms
How is the Oidium?
In the article that Lucía wrote in March, FUNGI IN THE GARDEN: POWDERWOOD, MILDIU, RUST AND BOTRITIS, she already introduced us to powdery mildew:
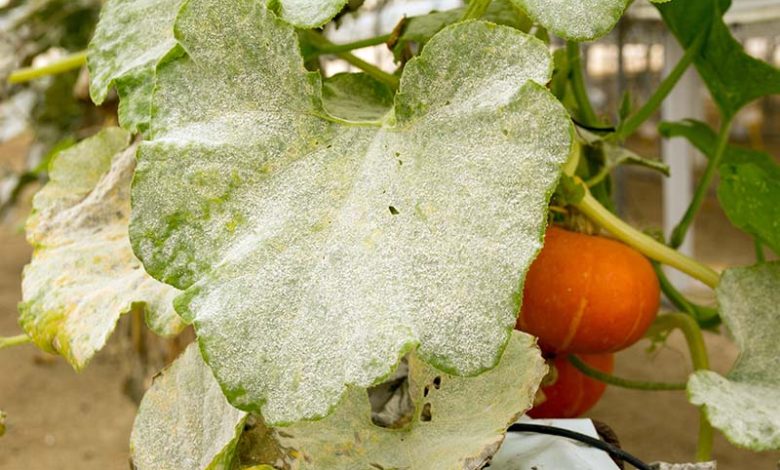
Description and symptoms: most of the time it develops in the upper part of the leaves, although it can also spread through the stem or the fruits if the attack is not controlled. It appears in the form of white spots that turn into a white or gray powder that covers the leaves and that, when removed, leaves yellowish spots. They hinder photosynthesis and if the attack is not controlled, the leaves turn yellow and can become deformed or dry. It is probably the easiest fungus to detect, because of that characteristic white powder.
Due to this shape and color, it is common to call powdery mildew as ash or bad white.
If the disease is already advanced, you can see some balls that contain the spores.
Affected crops: powdery mildew in cucumber, powdery mildew in calbaza…
Powdery mildew is a fairly common disease in cucurbits, such as pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima duchesne), courgette (Cucurbita pepo), melon (Cucumis melo) or cucumber (Cucumis sativus).As you can see in the photos and unfortunately you may have already seen in one of your orchards, powdery mildew has that characteristic way of identifying it.
It can also affect other vegetables, such as beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris), spinach (Spinacea oleracea) or potatoes (Solanum tuberosum).
But without a doubt, the best known powdery mildew is the powdery mildew of the vine.

It is a disease caused by the fungus Uncinula necator.It spreads through all the green parts of the plant:
- White powder appears on the leaves
- In the clusters, the grain is covered by dust giving a rotten appearance, later affecting the quality of the grain.
Why does it appear in our garden?
Powdery mildew usually appears in areas of high humidity with temperatures between 10ºC and 20ºC. So BE CAREFUL with the irrigation that we give to our crop.
With this combination of temperature and precipitation, it is not surprising that powdery mildew can appear in spring or late summer; when temperatures are calm and rain is common.
We also have to be careful when we are going to use our tools (hoes, blades…) because if we cause a cut or wound, with humidity; These areas may be affected.
So we see again that planning our garden can be the first step to combat any disease.Very shaded areas, poor ventilation, poor pruning or excessive irrigation can be agents that benefit the appearance of powdery mildew in the orchard.
Another cause is excess nitrogen, due to excessive fertilization, as this forces the plant to absorb more water than normal.
Oidium: How to remove it?
Prevent the appearance of powdery mildew
The first thing we have to do is remove the areas affected by powdery mildew. In this way we will prevent it from spreading to other parts of the plant.
Therefore, good pruning and adequate aeration of the land can be two activities that help us prevent it from appearing. I also recommend that you keep in mind what you are going to put in your garden. Perhaps your garden, due to the humidity it has, is not suitable for putting chard and it is better that you move it or put another plant that is better adapted to your garden.
The main element that we have to keep in mind to eliminate this problem is sulfur, which can be applied directly in powder form on the plant or in liquid solution.
Prepared to control hate
As for control preparations, I am going to list some that may be interesting:
- Horse tail;It works as a preventative and you can prepare it at home by putting about 20 grams of dried plant per liter of water with 5-10 grams of silicate of soda for a day. It is then boiled for 20 minutes and strained. The solution of one part of the preparation in 9 parts of water is sprayed.
- Garlic;It is another preventative that you can prepare at home by preparing an infusion with 50 grams of garlic cloves per liter of water and spraying the solution of one part of the infusion in 4 parts of water. It should be applied in full sun and for several consecutive days.
- Milk;I hang a video that I have been recommended in which they use milk:
References
- Polak, E., Aebi, M., KÜES, U. (2001). Morphological variations in oidium formation in the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus.MycologicalResearch. 105(5), 603-610.
- Braun, U. (1980). Morphological Studies in the Genus Oidium. Flora. 170(1–2), 77-90.
- U.Braun. (1982). Morphological Studies in the Genus Oidium (II). Zentralblatt für Mikrobiologie. 137(2),138-152.
I hope these tips have helped you and I look forward to your opinions/experiences in order to expand our knowledge.
See you in the orchard!



![Photo of Kumquat cuttings: [Grafts, Time, Rooting and Planting]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/kumquat-cuttings-grafts-time-rooting-and-planting-390x220.jpg)
