Plants That Reproduce Without Seeds: 10 Examples

Can plants reproduce without seeds? Are there plants that can grow without planting a seed? The answer is yes: there are plants that sprout and can give rise to another plant from stems, fruits or other parts.

After the article on How to re-grow potatoes, it occurred to me to write this post about other plants that reproduce without seeds. Below we will see several examples of seedless plants: species of the garden that can be reproduced from parts of the plant such as cuttings, cuttings, runners or a portion of the vegetable itself.
Since we are in Agrohuerto, we will focus on fruits and vegetables that reproduce without seeds. It is true that there are also many other plants that reproduce without seeds such as aloe vera, brazil trunk, sansevieria, ivy and many others, but today I will tell you curiosities about some of the plants that we use in the kitchen, such as vegetables leaf, bulb, small fruits such as strawberries, aromatic herbs, etc.
Below we will see some examples of plants that reproduce without seeds and how to plant garlic, carrots or aromatics without using seeds.
1. Basil
I put it first on the list because the truth is that it is one of my favorite aromatics. It is delicious in salads, to flavor dishes and to make sauces such as the famous pesto sauce.
In addition to the fact that it can be grown in containers inside the house, as we saw in How to grow basil in pots, it is one of the edible plants that reproduces without seeds.
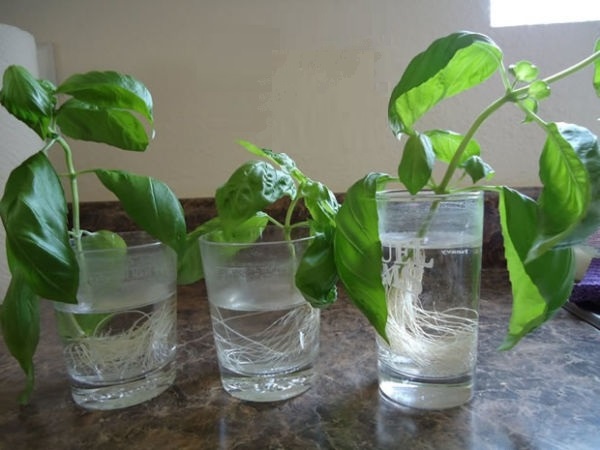

To reproduce basil without using seeds, you just have to cut some leaves and put them in water until they grow roots. When they grow, the new plant is ready to be planted in a new pot, where it will grow and give more shoots.
2. Garlic
The easiest thing if you want to grow garlic is to use your own garlic cloves that you have at home to make new plants come out.
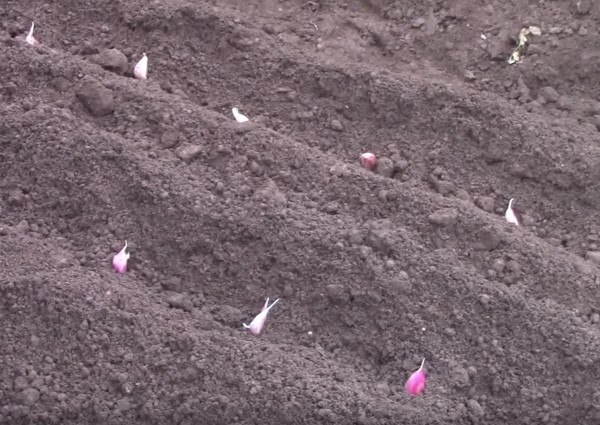

To plant garlic without using seeds, we must use one clove per pot or, if we plant garlic in the ground, put the cloves at a sufficient distance from each other. Each clove of garlic will give rise to a plant that will produce a new head of garlic with dozens of cloves just like the one you planted. We saw it in this post about Garlic: how to grow it in the garden.
3. strawberries
Strawberries have the tiny seeds on the skin or surface of the fruit itself. They are so small that it can be easier to reproduce strawberries asexually (without seeds) by letting new «daughter plants» come out thanks to the runners.
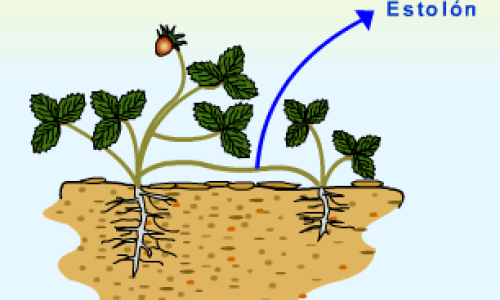
To produce strawberries without using seeds, we just have to leave enough space around the plant for it to continue developing and giving rise to other new shoots.
4. Potatoes
To plant seedless potatoes, we must bury the potato portions where the buds appear (eyebrows and eyes) that will give rise to new shoots.
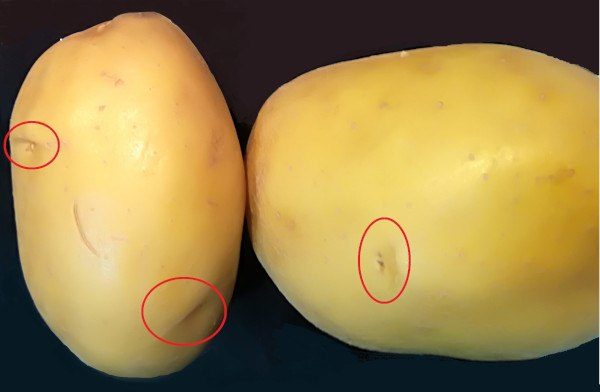
As each potato has several buds, from each one we can obtain several plants that will give rise to new tubers. We saw it in How to Regrow Potatoes in 5 Easy Steps.
5. Carrot s
There is a part of the carrot that we always cut off and usually throw away. I am referring to the upper part, a kind of “button” from which the leaves come out (the apical meristem).

Well, from that small part we can get another carrot to grow as good as the first.
6. Onion, spring onions, leeks…
All these plants, although we buy them in the supermarket, usually come with the roots. If they are not too dry, you can cut off that part of the stem base with the roots and plant again to grow a new plant.
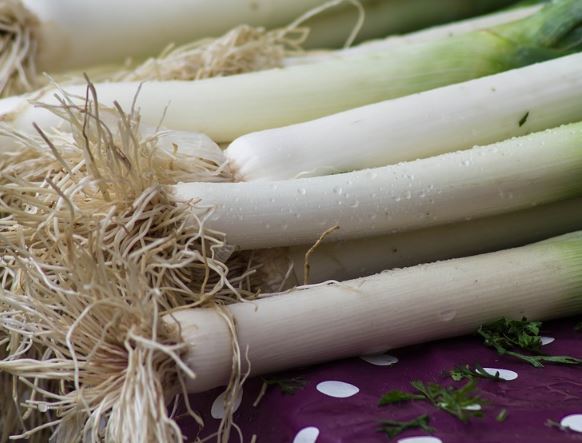

In addition, if we have any of these lilies in the garden, we can cut (not uproot) the harvest and the plant will be able to grow back and produce another new specimen from the base of the stem of the plant that we have already harvested.
7. Lettuce
It is possible that you did not know that from the base of a lettuce that you have already eaten you can grow a new lettuce. As in the case of carrots and other vegetables that grow, we can obtain a new lettuce plant by watering and burying the base of the stem of a lettuce that we have consumed.

In the post that Elena wrote about How to re-grow vegetables you can see the steps to re-grow lettuce at home and also how to reproduce aromatic seeds without seeds.
8. Rosemary
In the post Growing rosemary at home throughout the year, we saw that rosemary is a resistant aromatic plant that is easy to grow, even in pots or anywhere.
If you want to share your plant, or take some more to have more rosemary, you can reproduce it by planting a twig in another pot full of soil or substrate as they tell us in the link that I have put above.
9. Ginger
This tasty root is widely used as a condiment, and the truth is that its peculiar flavor gives a very special touch to most of them. In addition, it has a lot of health properties. If you buy some ginger root from time to time, you can use some of it to get more at home.
10. Kiwi and Banana
If we bury a piece of banana and a piece of kiwi together… do we get a «Baniwi»? Let’s see it!
Well, they could try to sneak it in with the video… (in fact, it was a prank that KinCommunity uploaded to its YouTube channel), but this is not the case… Neither bananas nor kiwis are plants that grow without seeds like potatoes, garlic and others that we have seen in the post.
Although number 10 in the list of examples of plants that reproduce without seeds is just a joke, the rest is true Whenever you want you can try to grow these plants that reproduce without seeds in your own home and you will not have to do seedlings and wait for them to germinate…
As always, we invite you to share with us in the comments thread below any type of comment, experience, suggestion or question that may arise . Do you know of other plants that reproduce without seeds? Have you grown plants at home?
If you liked it, please rate it with the stars below and, if you can, share it on social networks. Thanks for following us!
References
- Giraldo, LD et al., 1986. Let’s propagate vegetables by seeds and vegetative parts. Home Garden, Module 1, Booklet 8. National Learning Service (SENA), Colombia.
- García González de Lena, G., 2014. Guide to fresh potato cultivation in Asturias . Regional Service for Agri-Food Research and Development (SERIDA), Ministry of Livestock Farming and Native Resources of the Principality of Asturias (Spain).
- Morales A., CG (Ed.), 2017. Strawberry agronomic management manual. INIA Bulletin No. 17. Agricultural Research Institute of Chile.
- Sepúlveda, PN, 2018. How to multiply aromatic and medicinal. Fruit Growing and Diversification Magazine No. 81, p. 26-31. National Institute of Agricultural Technology, Argentine Republic




