What is Permaculture?: Objectives, principles, techniques and benefits
Organic farming is the best known of all, but there are other agroecological currents (such as Biodynamic Agriculture, Permaculture – which we will talk about today -, or Natural Agriculture) that have the same basic objectives:
Develop a sustainable agriculture that respects the environment and ensure, in the long term, the fertility of the soil thanks to the maintenance of biodiversity.

What is permaculture?
Biodiversity in agriculture consists of keeping all kinds of living organisms alive: bacteria and fungi in the soil, insects or beneficial plants, so that all their benefits in terms of nutrient conservation and the natural control of pests and diseases are taken advantage of.
It is an agriculture based on the natural philosophy of the Japanese Masanobu Fukuoka (1913-2008), and started in 1972 by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren in Tasmania, Australia.
The word Permaculture derives from the contraction of permanent culture -«permanent agriculture» and/or «permanent culture»-, which allows us to glimpse its main objective: that raw materials and resources (water, soil, organic matter, seeds, food…) endure, remain, in order to cover our future needs. It is about cooperating with nature respecting and taking advantage of natural rhythms without fighting against or changing them.
Permaculture combines various ecological philosophies and practices with the aim of achieving this stability of the environment and living beings. To do this, it uses the imitation of the patterns of nature and the conservation of natural resources, trying to reduce both raw materials and materials as well as waste products from agriculture.
More than a way of doing agriculture, permaculture is a way of life, those who practice it live immersed in nature, collaborating in its balance and benefiting from its resources.
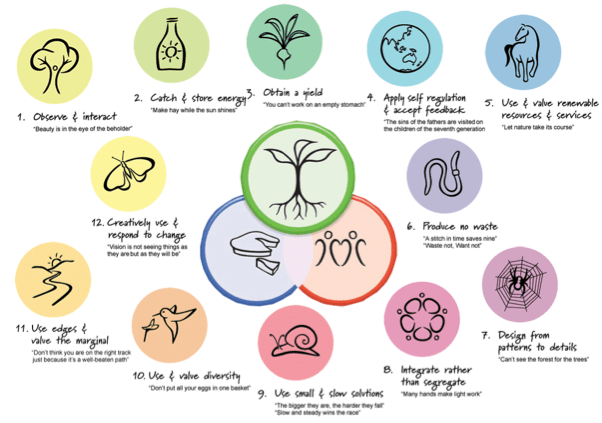
Principles and techniques of permaculture
Basic principles of Permaculture
- The bases of the Natural Agriculture of Fukoka: no use of chemical fertilizers or compost, no tillage, no elimination of weeds, no use of chemical pesticides.
- Each of the elements that make up the agrarian system must be located in relation to the others and thus fulfill several functions. Likewise, each basic function or need is supported by many elements.
- Reproduction of natural mechanisms that contribute to the increase in organic matter and the stability of the ecosystem: protective plant layers, diversity (rotation and association of species), development of transition zones (ecotones) or recycling of organic matter.
- Energy self-sufficiency thanks to efficient energy planning.
- Achieve a high diversity of plants adapted to each specific ecosystem through the presence of staggered productions or natural rotations.

To achieve this, Permaculture is based on the integration of multiple elements: crops, animals, landscape, buildings, technologies and housing, to form an agrarian system that develops and regulates itself practically and is in symbiosis with human activities. But this is not an easy task, and good planning is essential so that all the components fulfill their functions.
Techniques used in permaculture
- Integration in the same place of agriculture, livestock, aquaculture, forestry and grazing.
- Selection of plant and animal species according to their composition, distribution and organization.
- Spatial and ecological planning.
- Zoning of the agrarian system based on the intensity of use by man and external energies (sun, air, light…).
Training and dissemination of permaculture
Most of these techniques and methods of permaculture are based on experience and patience, and that is precisely what anyone who lives in a developed country and wants to start in this world usually lacks. For decades our culture and our way of life have ceased to be marked by natural rhythms…
We can now eat oranges in summer and cherries in winter, for example, without wondering how and where these fruits have been grown, reaching our table at a time so far removed from their typical «harvest season.»
For all this, it is essential for a new permaculturist that someone transmits the necessary knowledge. Permaculturists are aware and for this reason there are countless public and private associations, groups, cooperatives and centers of permaculturists in Spain and throughout the world that, through courses on permaculture, conferences, publications, initiatives such as «ecovillages», etc., they promote this philosophy of life and instruct in the necessary techniques for a sustainable ecological design.
The influence of this way of doing agriculture has even reached the European Parliament, and in the communiqué «Options for a European vision and objective for biodiversity beyond 2010», the European Commission stated that:
«The promise of permaculture as an effective protector and restorer of biodiversity should be explored and enhanced.»
In 2012, a project was launched, included in the «Action Program in the field of Lifelong Learning», to support the professional development of Permaculture teachers. More than a dozen European Permaculture organizations participate in this project, such as Permakultur Akademie ( Germany), Permaculture Association in Britain (UK) or Cambium (Barcelona, Spain), which have come together with the aim of «increasing the professionalism of permaculture in Europe.
Benefits of permaculture
According to the defenders of this type of agriculture, Permaculture not only provides environmental benefits, it also brings social and economic benefits for those who practice it (because it promotes the social economy and local sales, without intermediaries, among other things).
Permaculture is beneficial for physical and mental health, as it provides healthy food free of chemical compounds and makes us surround ourselves with a natural environment and much less polluted than we are used to. In addition, it collaborates in the family economy and in the education of society, since it contributes to the autonomy of those who practice it while at the same time learning to live in a healthy way and to know nature.
These benefits have been recognized by the United Nations Organization, which awarded last year to the Association for the Development of Permaculture in the Ninth International Contest of Good Practices.


![Photo of Cai xin: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/cai-xin-cultivation-irrigation-care-pests-and-diseases-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of High Mountain Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/high-mountain-climate-characteristics-flora-fauna-and-adaptability-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Plant Radishes in your Garden: [Guide + 12 Steps + Images]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/plant-radishes-in-your-garden-guide-12-steps-images-390x220.png)