Tomato Pests and Diseases: Complete Guide with Photos and Tips

Hello to all Farmers! In today’s article we will talk about tomato pests and diseases. We are going to start with a series of articles that summarize the diseases and pests that can affect the different crops in the garden and later we will talk about each one of them and how to treat them. Let’s start with the tomato!

tomato pests
Absolute tomato tuta
Tuta (Tuta Absoluta): The symptoms caused by this Lepidoptera are wide mines that leave the epidermis intact but remains of excrement can be seen inside. The shoots are moth-eaten and the tomatoes have holes and blackened internal areas.
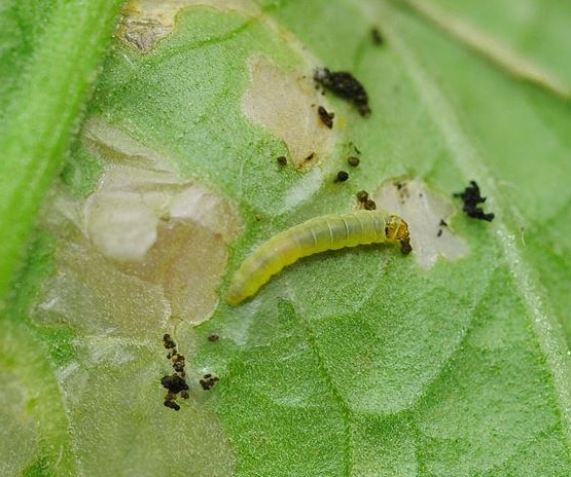

tomato caterpillars
Tomato hornworm (Heliotis sp.) and other caterpillars (Helicoverpa spp., Spodoptera spp., Autographa gamma, etc.): We find some considerable-sized perforations through which, sometimes, we can see the caterpillar gobble up our fruit. You can also see gnawing on leaves, flowers, fruits and tender shoots, usually with droppings and NO SLIME (it gives us the clue that it is not a snail or slug)
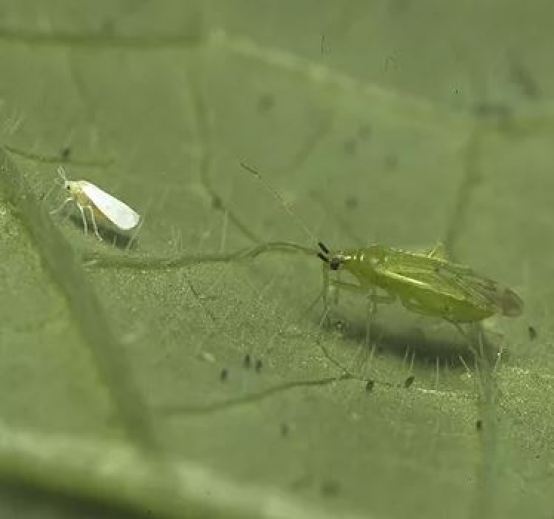
Aphids on tomato leaves
Aphids (Myzus persicae, Macrosiphum euphorbiae, Aulacorthum solani…): Aphids produce downward curling and wrinkling of leaves. In addition, you can see colonies of these small dark or greenish insects, especially in the tender shoots of the developing plant. Another clue is the presence of molasses (sugary and sticky substance) and ants around them defending them.

whitefly on tomato
White fly (Trialeurodes vaporarium, Bermisia tabaci): We can see some white flies (which are not really flies) with a characteristic erratic flight when shaking the plant. Also, like aphids, they release honeydew. They are usually arranged on the underside of the leaves.

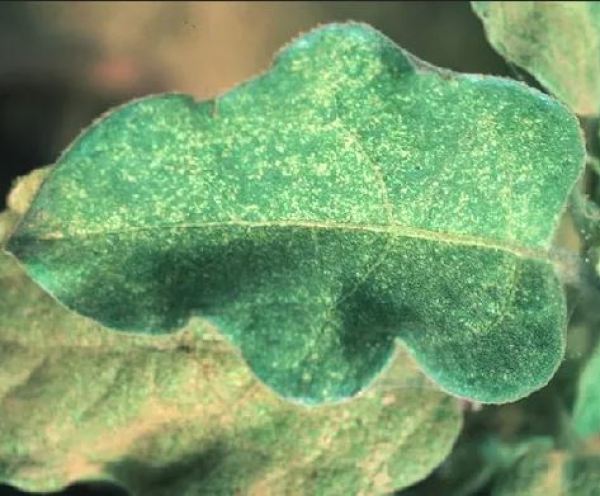
red spider on tomato
Red spider (Tetranychus urticae): The red spider is a mite that leaves discolored leaves with small dots and silks. If it affects significantly, it can cause desiccation and defoliation of the plant.

white spider on tomato
White spider (Polyphagotarsonemus latus): This mite leaves the leaves convex, curved, darker and with an elongated appearance and protruding nerves.
Vasates of the tomato
Vasates (Aculops lycopersici): the leaves of the tomato plant dry out, taking on a pinkish color and the stem turns tan until they are both dry with a reddish-yellow color due to this mite.
Liriomyza or tomato miner fly
Leafminer fly (Liriomiza spp.): Makes clear and sinuous galleries in the leaves.

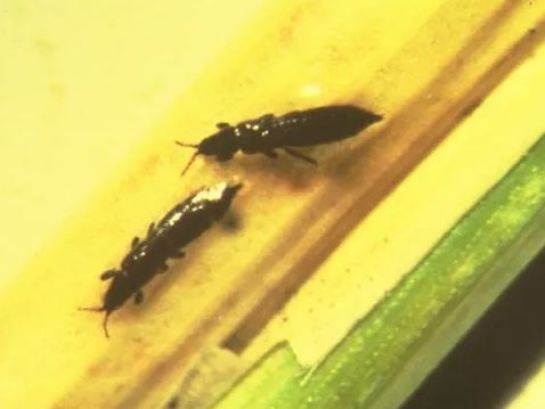
tomato flower thrips
Flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis): Damaged plants have leaves with small, irregular silver spots, which correspond to lesions on the underside.

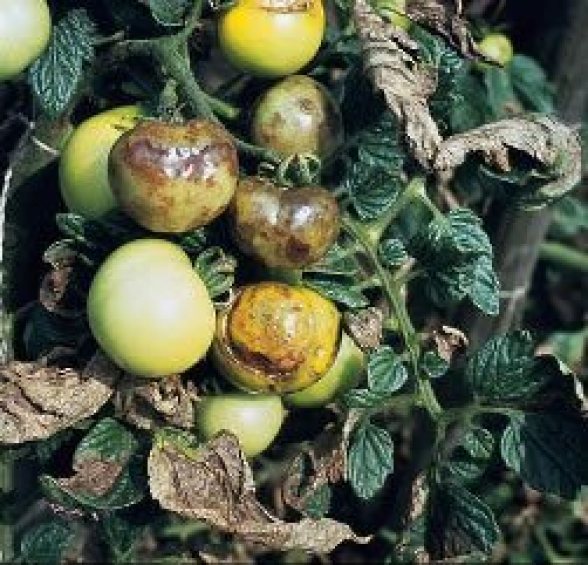
Tomato Diseases
Mildew (Phytophtora infestans): Initially, the leaves of the plant are shown with yellowish spots with an oily appearance that turn brown, with the center becoming necrotic.
On the underside appears a fine white veil that corresponds to the spores. On the stem, we find elongated brown spots that are a symbol of necrosis and wilting in the plant. The crop takes on a burnt appearance. In the developing fruits, soft spots of brown appearance are observed, generally in the upper half.

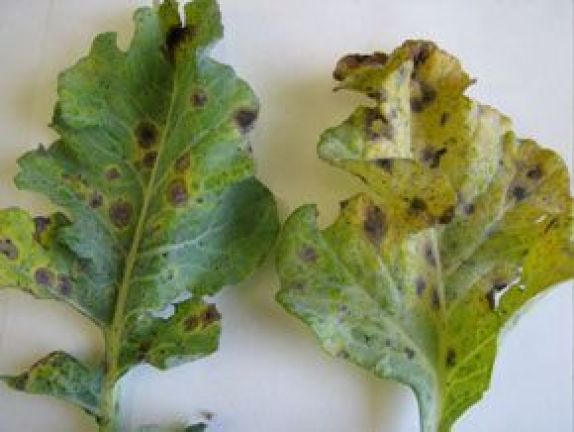
oidiopsis tomato
Oidiopsis (Leveillula taurica, Phytophtora capsici, Alternaria solana): We find yellowish spots on the upper side of the leaf that quickly become necrotic and a kind of whitish powder appears on the underside.

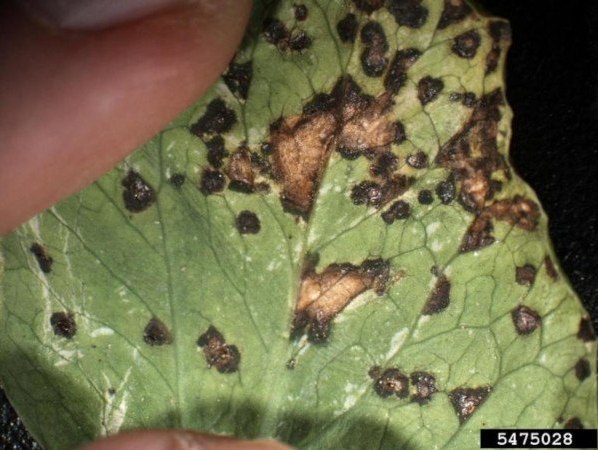
tomato alternariosis
Alternariosis (Alternaria solana): On the lower leaves we find circular brown spots in concentric rings. On stems and petioles the spots are black and well defined. In fruits, a depressed necrosis is produced and covered with a black mold.

Rotten root and stem of tomatoes
Neck and root rot (Phytophtora spp. Pythium sp., Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sp. etc.): Young plants wither, presenting strangulation and rot in the neck (the lowest area of the stem that adjoins the substrate).
Vascular fusarium
Vascular fusarium (Fusarium oxysporum sp. lycopersici): Withering and flaccidity of the upper leaves, pronounced in hot hours. A progressive yellowing and necrosis of the leaves from bottom to top is observed, observing the green veins.
bacterial black spots
Bacterial black spot (Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato): In all the aerial organs of small tomato plants we find black spots with an irregular outline. On the leaves, the spots have a yellow halo and can dry them out. On tomatoes, we find small black pustules often with a lighter «eye» in the center.

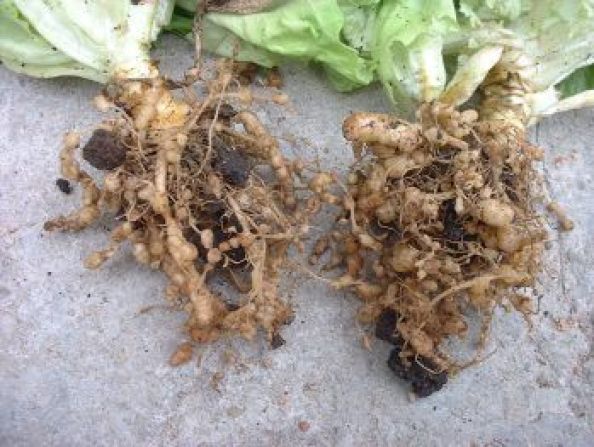
nematodes
Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.): Plants infected by nematodes exhibit weak growth, wilting, chlorosis, and deformed and galled roots (nodules). Distribution in stands (plants forming more or less circular areas) or following irrigation lines.

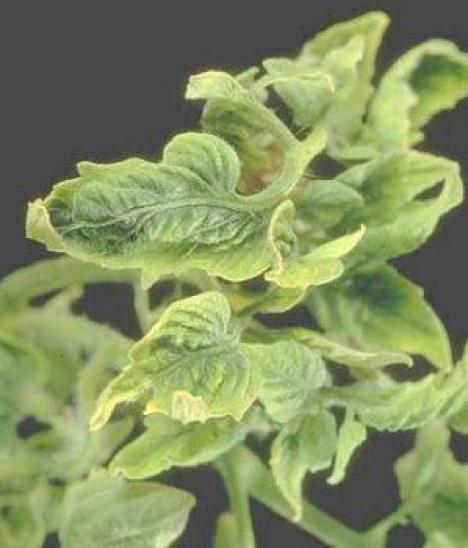
tomato virus
Virus: Mosaics in leaves, dwarfism, chlorotic rings (yellow), curling and curling of leaves, deformation of fruits with wavy spots or rings…

Common physiopathies in Tomato and Pepper
Physiopathies are diseases caused by abiotic factors, that is, there is no causal pathogen but it is caused by poor conditions in the environment such as deficiencies or excesses of nutrients, low or high temperatures, drought or poor management of irrigation or salinity, among others..
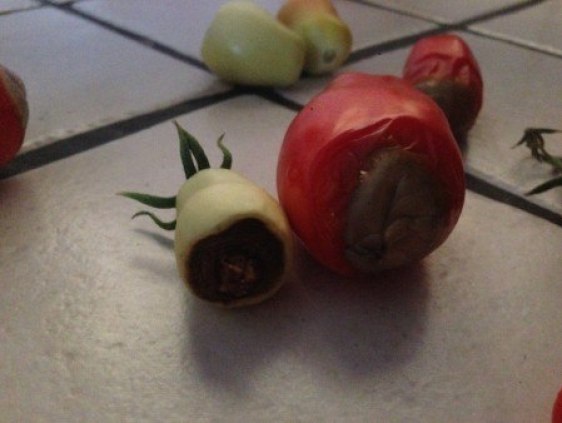
Tomato Rotten Asses
Necrosis or apical rot of fruits («Rotten or shitty asses»): A depressed black spot appears at the base of the tomato, usually round.

Roasted or ironed tomato
Scorched or ironed fruits: On the side of the fruits exposed to the sun a depressed white area appears, leaving the tissue with a papery appearance and, if the fruit is still young, a scar is formed later.
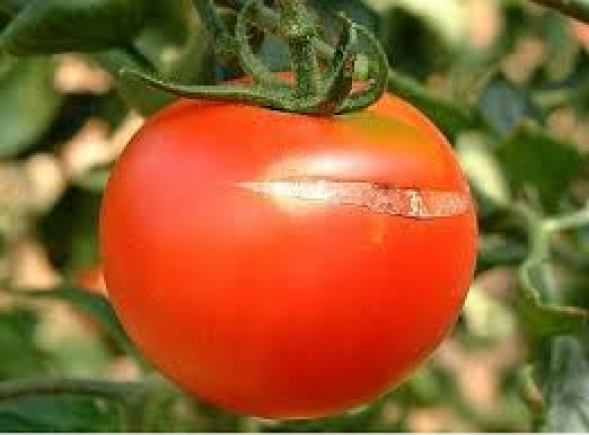

Cracked or cracked tomato
Cracked or cracked fruit: Appearance of longitudinal or concentric cracks around the fruit peduncle area that can take on a cork-like appearance.
tomato leaf curl
Leaf curling: Tomato plants curl upwards the leaflets of their leaves, giving the plant a coiled appearance.
References
- Nalam, V., Louis, J., & Shah, J. (2018).Plant defense against aphids, the pest extraordinaire. Plant Science, (April), 1–12.
- Faria, M., Wraight, S. Biological control of Bemisia tabaci with fungi. Crop Protection. 20(9), 2001, 767-778.
- Bawin, T., Collard, F., Backer, L., Yarou, B., Compère, P., Francis, F., Verheggen, F. (2016). Structure and distribution of the sensilla on the antennae of Tuta Absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), Micron. 96.16-28.
I hope it will help you to have an idea, at least, of the pests or diseases that may be spoiling your tomato crop. I will try to talk about each of them as soon as possible so that you can remedy them. Until next time Agrohuerters!




