Conifers: [Characteristics, Growth, Cultivation and Examples]
 Conifers are the plants that we typically find in the coldest areas of the planet. They have the condition of developing a cone-shaped fruit (which is usually called, in some cases, pineapple).
Conifers are the plants that we typically find in the coldest areas of the planet. They have the condition of developing a cone-shaped fruit (which is usually called, in some cases, pineapple).
Its trajectory in the world is older than that of broadleaf plants because they have greater resistance capacity.
There are many types that you have surely heard mentioned at some time (such as pines or sequoias) and here we will study them today, are you coming?
What are conifers?
Conifers are evergreen trees that are pointed in shape and deep dark green in color.Within its family there are more than 600 species and most of them are distributed in the coldest areas of the world.

The seeds are generated inside its fruit, which is shaped like a hard cone that protects them from the environment. This crust in some cases can be really strong, preventing the most extreme environmental conditions from affecting the interior.
Conifers are a group of cone-seeded plants, a subset of gymnosperms.
Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta, also known as the Coniferophyta or Coniferae.
The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The vast majority are trees, although some are shrubs.

Some examples are cedars, Douglas firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, firs, and yews.
In 1998 the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera and 629 living species.
Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants on large tracts of land, especially in the taiga of the northern hemisphere, but also in similar cold climates in mountains further south.
Boreal conifers have many winter adaptations. The narrow conical shape of boreal conifers and their downward-sloping branches help them shed snow. Many of them seasonally alter their biochemistry to make them more resistant to freezing.
Although tropical forests have more biodiversity and turnover, the world’s vast coniferous forests represent the largest terrestrial carbon sink. Conifers have great economic value for the production of wood and paper.
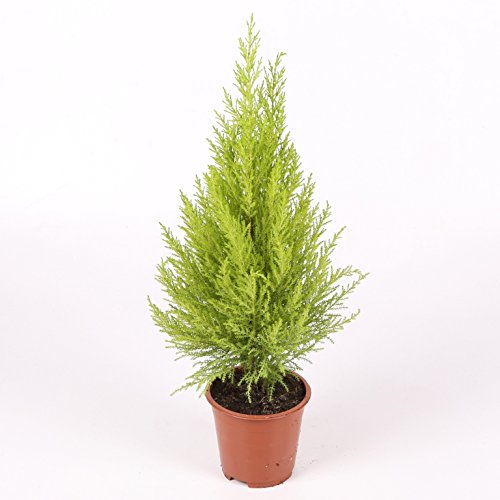
What are the characteristics of conifers?
Conifers are plants that are far from the normal characteristics of other species. Here are things like:
- The general structure of the plant: they are only trees and shrubs, not as in the case of broad-leaved plants that can be climbers, low, etc.
- Trunk: it is the main structure around which the leaves develop, since conifers have a pyramid-like shape. The trunk is straight and its wood is useful on many occasions.
- Habitat: they usually live in cold areas, in spaces known as taigas where they develop as forests. The vast majority of conifers are in the northern hemisphere.
- Adaptation: life in temperate climates does not exempt them from being affected by the action of frost. Given this reality, conifers establish an internal hardening process that allows them to stay healthy in low temperatures. In addition, they have developed a shape of the leaves that helps them to get rid of the snow when they are submerged under it.
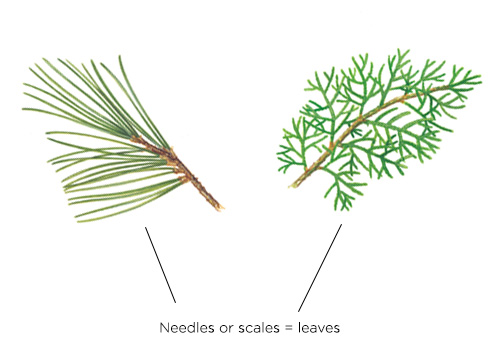
How is the leaf of these trees?
Most conifer species are evergreen, meaning that they keep most of their leaves throughout the year.
However, some species of conifers, such as the larch, are deciduous, meaning they lose all their leaves each fall.
Most evergreens shed leaves (or branches, in the case of cedars) that grew two or more years earlier, so that newer branches are never bare.
Most conifers have needle-shaped leaves, such as spruce, pine, spruce, and larch. Some, such as cedar, cypress, and juniper, have scale-like leaves and do not shed individual leaves, but rather shed short branches that have been growing for a year or more.

How many varieties of conifers are there?
There is a family made up of about 630 species, approximately.
How do conifers grow?
 The vast majority of conifers grow slowly, taking years to reach the adult version.
The vast majority of conifers grow slowly, taking years to reach the adult version.
By having such varied species in your family, this will have a direct influence on how long they will take to grow.
About 10 years is the average time it takes for a coniferous tree to reach its full height.
Keep in mind that many of them take only the first year to develop their strong root system. This is one of the aspects that must be taken into account when planting, since it needs to have enough space for the movements that occur underground.
How do they reproduce?
All conifers have separate seed cones and pollen cones.
These can be born in the same tree (monoecious, one hearth) or in different trees (dioecious, two hearths).
The pollen cones produce abundant yellow pollen, which is dispersed by the wind each spring and enters the seed cones (pollination) where fertilization, embryo and seed development occurs.
In most conifers, pollination, fertilization, and embryo and seed development occur in a single growing season, from spring to fall.
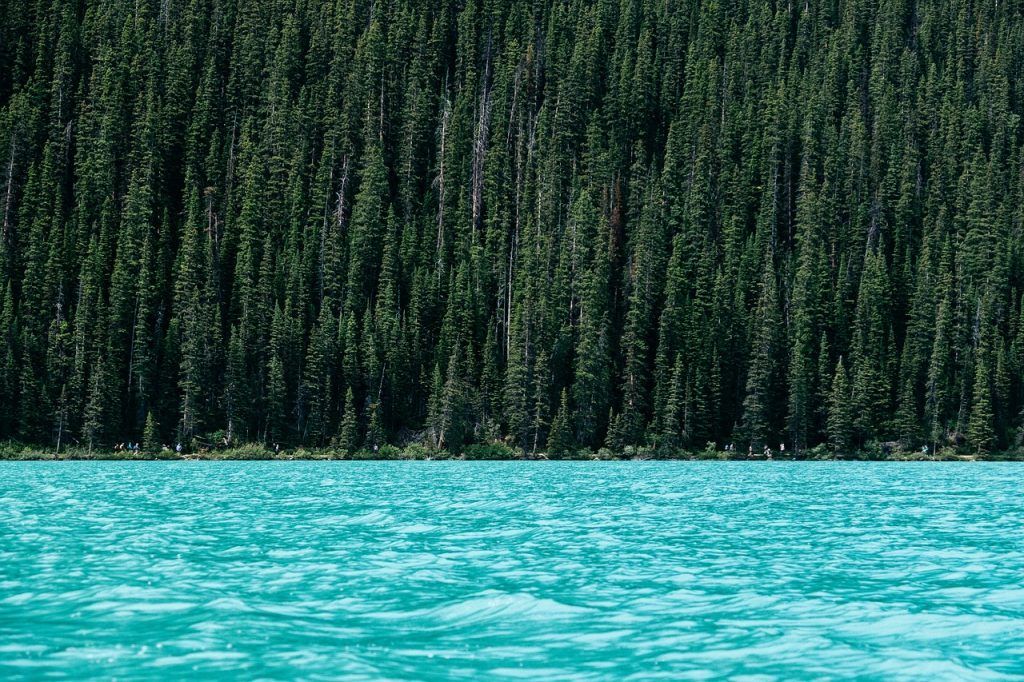

However, in pines and some other genera, there is a one-year delay between pollination and fertilization, or fertilization and seed development, and the reproductive cycle spans two growing seasons.
In both types of reproductive cycles, the seed cones mature in the fall and the seeds are shed when the dry cone splits open or disintegrates.
Most species have seeds with one or two wings that stop their fall, which helps seed dispersal. The seeds are usually wind dispersed, but squirrels and other rodents can also disperse them.
In yew and some species of pine, birds disperse the seeds. In several conifers, entire cones are shed rather than individual seeds.
Why are they called conifers?
They receive this name because the seed is stored in cone-shaped fruits. These fruits are not edible. Its structure is formed by three main parts: the central axis, the bracts and the scales. It is in the scales that the seeds are associated.
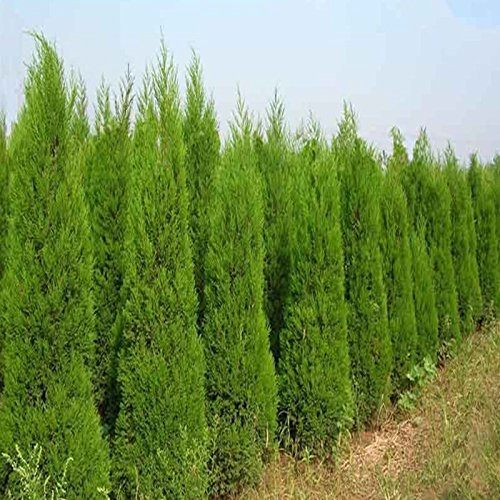

Thanks to the cones, the seeds remain protected. They also play a leading role in pollination, since they can be male or female.
Where are conifers grown?
Conifers are usually grown in areas with temperate climates, although in general they grow by their own reproductive activity. In this, the pollen of the male conifers is transferred to the female conifers with the help of the wind, giving rise to fertilization for the formation of the fruits.
Examples of known conifers
Although conifers are a fairly large family, there are some species that are usually better known than others. Here they are counted:
Fir tree
They are of different types but the most characteristic is the one that has been used to beautify the interior of homes at Christmas. It grows with brush-like leaf areas that spread out in all directions. The leaves are pointed and, depending on the type of fir, can be more or less tall.

Cypress
It is a conifer that is used very frequently to create hedges because its vegetative part reaches a good density. It has an elongated structure that makes it look very imposing, especially when it reaches more than 20 meters in height. Also, it is beneficial in the medicinal world.

Pine tree
Pines are one of the best known conifers for their striking structure and the number of pineapples they are capable of producing in their time. Although in most cases pine trees are trees, there are also some types that develop as shrubs.

It has been very useful in the industrial world for its wood and aroma, from which cleaning and cosmetic products have been made.
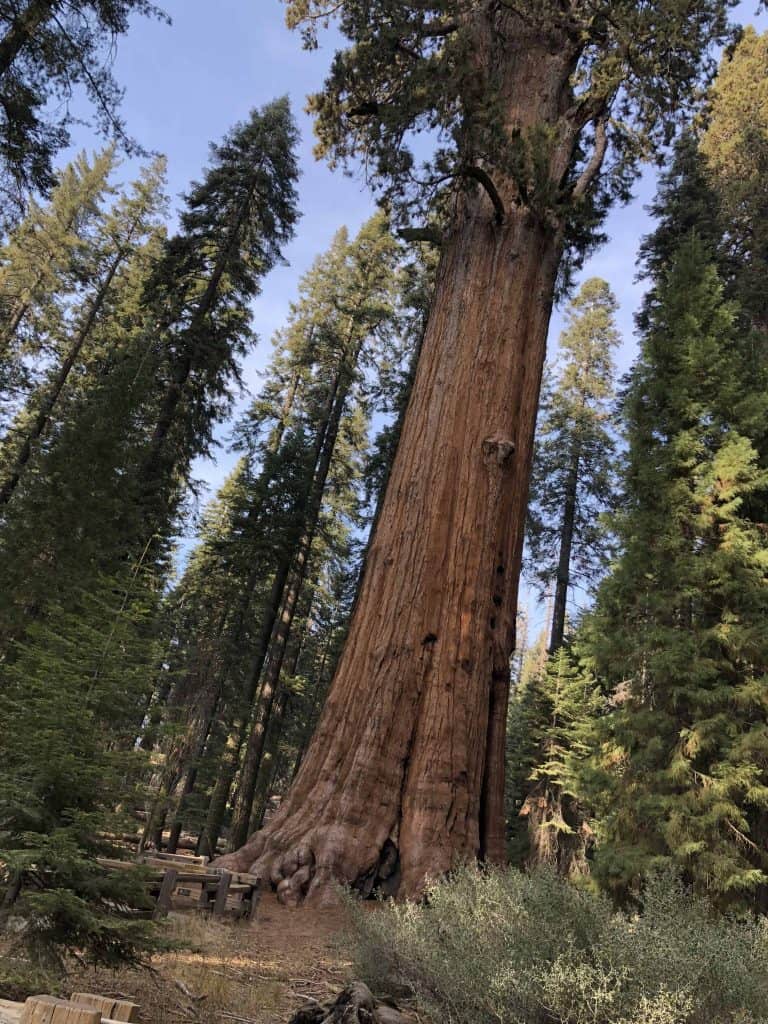
redwoods
Sequoias are the tallest conifers and, not only in that family, but of all plant species in the world. They are especially long-lived, being able to add several tens of years to their lives.

In the state of California, in the United States, there is the largest sequoia forest in the world and it is a true natural spectacle.
Cedar
They grow to a great height and a striking shape that has given them a high ornamental value. Their wood is one of the best in the world and to this is added that they also have an exquisite aroma. Undoubtedly, it is one of the best valued conifers.
Conifers are a large family, striking, popular and of great importance for the ecological balance of the world. Within the coniferous forests the largest carbon reserves in the world are stored, adding about 50% of the total of the entire planet.

In addition, the woods that come from coniferous trees are among the most valuable for carpentry work, which adds commercial importance to them.
Coniferous forests do not have as much biodiversity as occurs within tropical forests, but there is no doubt that they are of transcendental importance for the ecological balance of the planet.
Evolution of conifers throughout history
The first conifers appear in the fossil record during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian), more than 300 million years ago.
Conifers have been suggested to be most closely related to the Cordaitales, a group of Carboniferous-Permian trees and climbing plants whose reproductive structures bear some similarities to those of conifers.
The earliest conifers belong to the paraphyletic assemblage of «Walchian conifers», which were small trees and probably originated in dry upland habitats. The range of conifers was extended during the early Permian (Cisuralian) to the lowlands due to increasing aridity.

The Permian conifers were gradually replaced by more advanced or «transitional» Voltzian conifers. Conifers were largely unaffected by the Permian-Triassic extinction event, and were the dominant land plants of the Mesozoic era.
Modern groups of conifers arose from the Voltzials during the Late Permian and Jurassic. Conifers suffered a major decline in the late Cretaceous corresponding to the explosive adaptive radiation of flowering plants.
coniferous morphology
All living conifers are woody plants, and most are trees, most with a monopodial growth form (a single straight trunk with lateral branches) with strong apical dominance. Many conifers have a distinctly scented resin, secreted to protect the tree against insect infestation and fungal infection of wounds.
The fossilized resin hardens into amber.
The size of mature conifers varies from less than a meter to more than 100.
What is the largest conifer in the world?
The tallest, thickest, largest and oldest living trees in the world are all conifers. The tallest is a coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), with a height of 115.55 meters (although a Victorian mountain ash, Eucalyptus regnans, supposedly reached a height of 140 meters, although the exact dimensions were not confirmed).
The thickest, that is, the tree with the largest trunk diameter, is a Moctezuma cypress (Taxodium mucronatum), 11.42 meters in diameter. The largest tree by three-dimensional volume is a Giant Sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum), with a volume of 1,486.9 cubic meters.

Which conifer is the smallest in the world?
The smallest conifer is the pygmy pine (Lepidothamnus laxifolius) of New Zealand, which rarely exceeds 30 cm in height at maturity. The oldest is a
What is the oldest conifer in the world?
Great Basin Bristlecone Pine (Pinus longaeva), 4,700 years old.
What enemies do conifers have?
At least 20 species of roundhead borers in the family Cerambycidae feed on the wood of spruce, fir, and hemlock (Rose and Lindquist 1985).
Borers rarely tunnel into living trees, although when populations are high, adult beetles feed on the bark of young twigs and can damage young live trees.
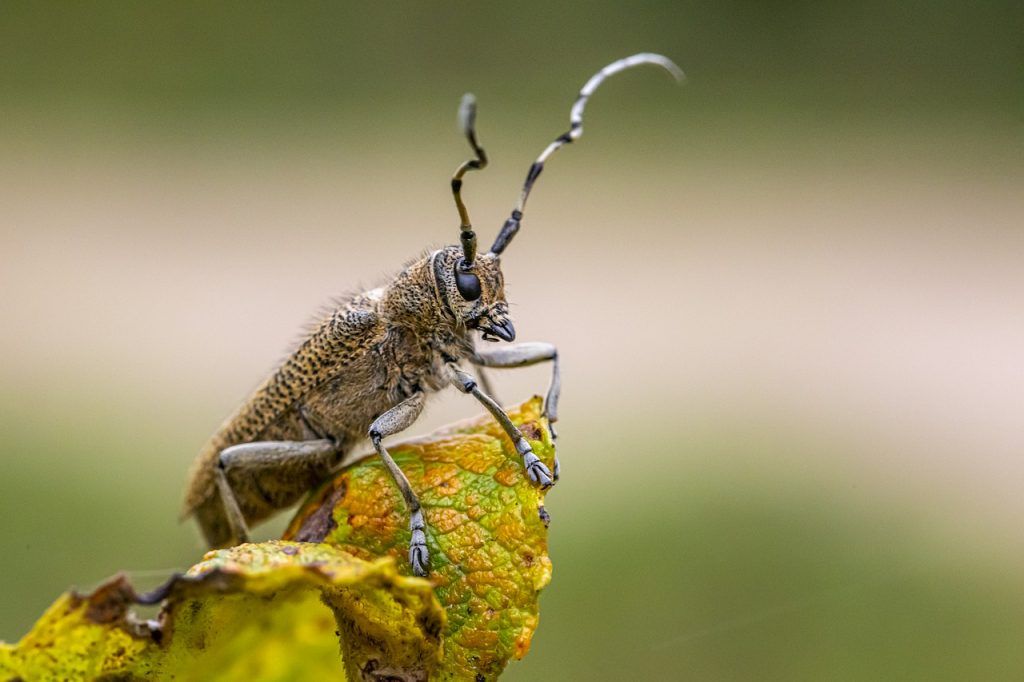

One of the most common borer species is the white -spotted sawyer (Monochamus scutellatus).
Adults are found in summer in freshly felled or recently felled trees, chewing small crevices in the bark in which they lay eggs. The eggs hatch in about two weeks, and the tiny larvae tunnel into the wood and mark its surface with their feeding channels.
With the arrival of the cold, they pierce the wood making oval entrance holes and make deep tunnels. Feeding continues the following summer, when the larvae occasionally return to the surface of the wood and extend the generally U-shaped feeding channels.
During this time, small mounds of fruscus extruded by the larvae accumulate under the trunks. In early spring of the second year after egg-laying, the larvae, about 30 mm long, pupate in the enlarged tunnel just below the surface of the wood.
Adults emerge in early summer, leaving round exit holes, thus completing the usual two-year life cycle.
How do conifers survive harsh winters in some areas?
In late summer and early fall, when days get shorter and temperatures drop, temperate conifers experience several changes to their leaves, stems, and roots.
Cell divisions and cell growth stop.
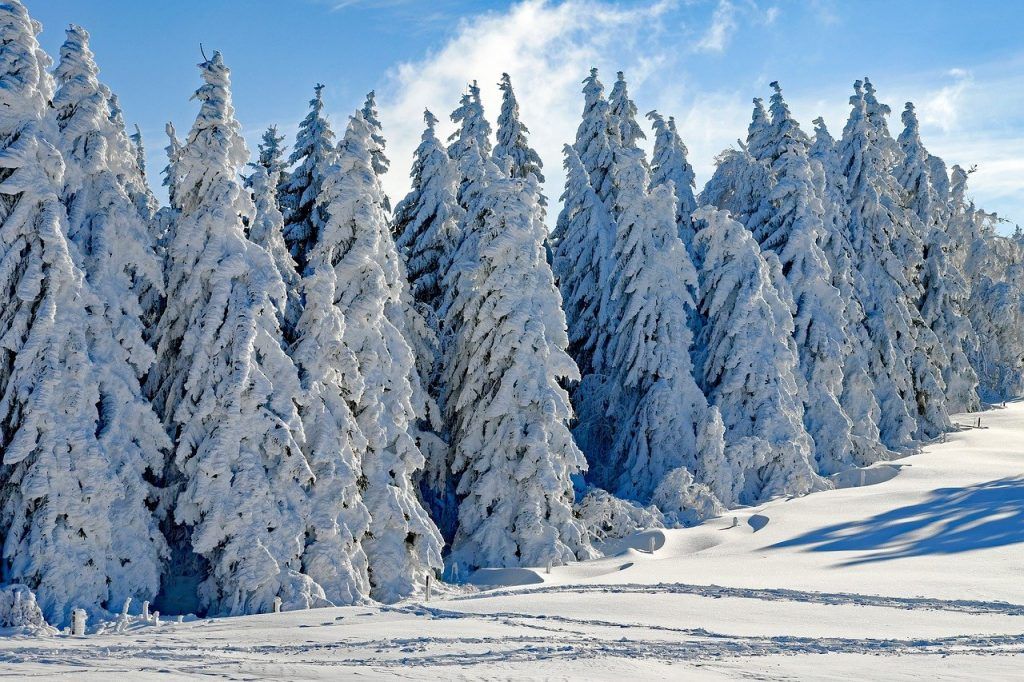

There is no active growth to form new tissues or organs like wood or leaves, respectively.
Many complex chemical changes also occur, ranging from increases in the amount of soluble salts and sugars, and in some, the production of antifreeze compounds, all of which increase the resistance to cold of living tissues.
These complex physiological changes lower the temperature of ice formation by several degrees, allowing living tissue to survive long periods of subzero temperatures.
Bibliographic references
- Anatomical and physical-mechanical characteristics of eight species of conifers from Baja California Norte, C Romero Amaya, C López, P Olvera… – 1982 – sidalc.net
- The coniferous forest of the Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, Baja California, J Delgadillo, JD Rodríguez – 2004 – books.google.com
- Morphological characterization of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae in endemic conifers of southern Chile, R Godoy, R Mayr – Bosque, 1989 – books.google.com
- Technological characterization of some species of conifers from the region of El Salto PN (Durango), A Salazar, R Alemán – Conafor/Inifap, 2002 – conafor.gob.mx
- Permineralized conifers in the Cañadón Asfalto basin, Chubut, Argentina: evolutionary and taxonomic impact, IH Escapa, G Rothwell – X Argentine Congress of Paleontology…, 2010 – sedici.unlp.edu.ar
- Conifers introduced in SNASPE units: a risk for biodiversity, E Peña, A Pauchard – Bosque Nativo, 2001 – udec.cl
Maybe you are also interested in:

![Photo of The Diamond Yam: How, Where and When to Plant it? [Steps + Images]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/the-diamond-yam-how-where-and-when-to-plant-it-steps-images-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Terraces: [Concept and Types] + How to Prepare One](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/terraces-concept-and-types-how-to-prepare-one-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Carambolo: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Carambolo-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Plant Snapdragon in your Garden: [Guide + Steps to Follow]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/plant-snapdragon-in-your-garden-guide-steps-to-follow-390x220.png)