Hydroponics or Hydroponic Cultivation: [Concept, Characteristics and Use]
hydroponic cultivationit dates back many centuries to ancient Babylon. The hanging gardens were a great example.
Today, this method has regained popularity and there are several tools to ensure a successful grow.
This type of cultivation can be carried out both on an industrial scale and in home gardens.
Did you know…Hydroponic farming was used in World War II to provide food for soldiers.
What is hydroponics?
Hydroponic cultivation is known as that method that can dispense with the land for its maintenance.
Instead, water with substrate and mineral solutions are used that provide the same nutrients to the plant. In other words, as long as the plant is in a culture medium with the same nutrients provided by the soil, it will be able to grow.
Characteristics of Hydroponics
- Plant nutrition.
- Spacing.
- Weed control.
- Diseases and pathogens in the soil.
- Water.
Hydroponics was born out of a need that most agricultural areas are no longer as productive as they once were, either due to lack of water, poor soil fertility, space, climate change, among others.
For this reason, technological methods have been sought that allow any human being to be cultivated.
What are the benefits of hydroponic cultivation?
Among the main benefits of growing using hydroponic methodsis saving water.
When plants are grown in soil it is very difficult to know exactly how much water they need. For example, if we give them more water, they rot and drown and if we don’t, they dry up.
 On the other hand, depending on the type of soil (and its pH), it can block the passage of oxygen to the roots. If instead the roots are suspended, it will be easier for them to capture the oxygen they need.
On the other hand, depending on the type of soil (and its pH), it can block the passage of oxygen to the roots. If instead the roots are suspended, it will be easier for them to capture the oxygen they need.
Hydroponic cultivation isparticularly advantageous in arid areassince the water will not be absorbed by the soil, but can be conserved for future uses.
Likewise, the control of pests and diseases is simpler since the pests that inhabit the soil, such as cochineals, are eliminated in the first instance.
In addition, hydroponic cultivation allows us to regulate the amount and number of nutrients, which makes it a more economically viable method.
Another advantage is that the harvest normally remains stable throughout the year. Normally, plants are less exposed to sudden changes in temperature and exposure to pesticides that can harm health.
What are the disadvantages of hydroponic cultivation?
 One of the disadvantages of this type of cultivation is fungus and mold. They are somewhat dangerous as they usually affect the entire crop and ruin the entire crop. When grown in soil it is sometimes easier to deal with pests as the soil has a buffer effect.
One of the disadvantages of this type of cultivation is fungus and mold. They are somewhat dangerous as they usually affect the entire crop and ruin the entire crop. When grown in soil it is sometimes easier to deal with pests as the soil has a buffer effect.
However, with the lack of water, difficult to predict temperatures and little space, hydroponic cultivation brings more advantages than growing in soil.
Another disadvantage is the quality of the fruits we collect.
Inevitably the fruits and vegetables that we harvest will not have the same taste as those grown on land.
How do we install a hydroponic crop?
There are various ways ofCreate a hydroponic garden.Everything will depend on the conditions such as space and budget.
There are people who choose to use inorganic substrates such as foam or organic substrates such as moss or bark. It also doesn’t take much space to place it. You can even put it in the window vertically or on a wall.
To install a hydroponic crop, it is advisable to have opaque containers so that the light does not act on the roots, with a medium to small depth (no more than 30 centimeters) and with an open nozzle. That is, a rectangular container is better than a vase.
You can use decorated pots or tetrapack, plastic or wood packaging.

The designs of a hydroponic garden can take many forms, but in general they all have: The container for the plants, an aerator and a pump with a hose to connect it to the containers (like the one used in fish tanks).
The general steps to install a not very complex system like the one above are:
- First you need to have a solution for the plants, that is, what will provide them with the nutrients that are normally in the soil. These solutions can be purchased on the market as ready-made compounds for hydroponic solutions. If you like to do it yourself, you can dissolve 118 grams of calcium nitrate, 49 grams of magnesium sulfate and 29 grams of mono-potassium phosphate in 100 liters of water .
- The second thing you have to take into account is the PH of the water. Normally the water has a pH of 8, but for cultivation a pH of 6-6.5 is recommended. To regulate it you can mix an aspirin tablet for every two liters, stir completely and then measure it with the PH strips that you can find at the pharmacy.
- Once you have completed the previous steps, you need to fill half of the first container with some substrate. The most common and easy to get are rice husks, sand, gravel, vermiculite, etc. Make sure you have washed the substrate beforehand to prevent it from altering the composition of the crop. You can also grow only in water, but you must provide the plant with a support such as plumavit or wide Styrofoam.
- The container with the substrate is the one that will remain in suspension and where the seeds will be sown. Remember that it must have a hole below with a mesh that prevents the substrate from falling into the larger container.
- In the largest container is where you will place the water with the nutrient solution. To facilitate its emptying, you can perforate it and place a plug on it.
- If there is a lack of space or you want to grow vertically, you can use PVC tubes and plastic cups.

What can we plant in a hydroponic crop?
- Sow the seeds about 10-12 inches apart by making a small hole in the gravel and covering without crushing.
- Turn on the pump and allow the solution to be in contact for 3 to 4 hours two to three times a day.
- If the water becomes cloudy you can increase the operating time of the pump. Every 30 days proceeds to the total emptying of the solution for a new one. The waste can be used to water the plants in the garden.
Where can I buy a hydroponic kit or package?
Here we give you a series of options




Can you grow hydroponics with plastic bottles?
Yes, the method is practically the same and it is ideal if you do not have much space.
You can do without the water pump and do the emptying of the solution yourself. For the water to reach the plant you can place a mesh of cloth or cotton.

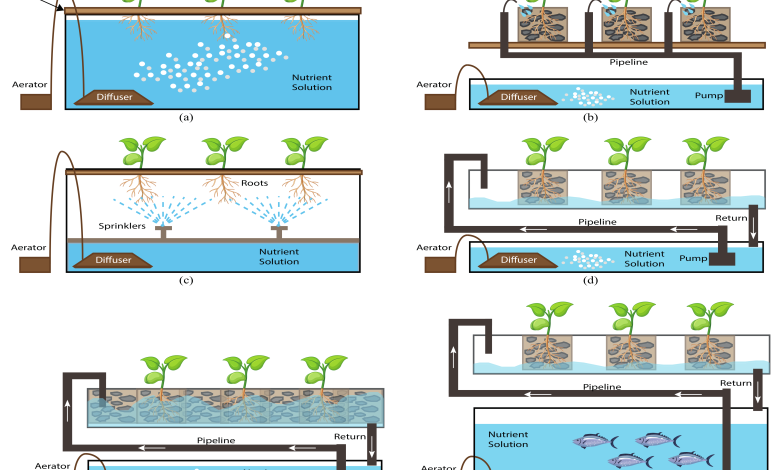
Hydroponic growing techniques
Static Solution Culture
In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass Mason jars (typically in home applications), pots, buckets, tubs, or tanks.
The solution is usually gently aerated, but can be unaerated. If not aerated, the solution level is kept low enough that there are enough roots above the solution to get adequate oxygen.
- A hole is cut (or drilled) in the top of the tank for each plant; if it is a jar or a tub, it can be its lid, but otherwise, you can put cardboard, paper, wood or metal on top.
- A single repository can be dedicated to a single plant, or to multiple plants. The size of the reservoir can increase as the size of the plant increases.
- A home system can be built from food containers or glass jars with aeration provided by an aquarium pump, aquarium aeration tubes, and aquarium valves.
- Clear containers are covered with aluminum foil, butcher paper, black plastic, or other material to exclude light, thus helping to eliminate algae growth. The nutrient solution is changed on a schedule, for example once a week, or when the concentration falls below a certain level, as determined by an electrical conductivity meter.
- Whenever the solution is depleted below a certain level, water or fresh nutrient solution is added. A Mariotte bottle, or float valve, can be used to automatically maintain the solution level.
In raft solution culture, plants are placed on a floating plastic sheet that floats on the surface of the nutrient solution. In this way, the level of solution never drops below the roots.
Continuous Flow Solution Culture
In continuous flow solution cultivation, the nutrient solution is constantly passing through the roots.
It is much easier to automate than static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to temperature, pH, and nutrient concentrations can be done in a large storage tank that has the potential to serve thousands of plants.
A popular variation is the nutrient film technique, or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients necessary for plant growth is recirculated over bare plant roots in a thick mat. of hermetic roots, which develops at the bottom of the channel and has an upper surface that, although moist, is in the air.
Subsequently, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of plants.
A well-designed NFT system relies on using the correct channel slope, correct flow rate, and correct channel length. The main advantage of the NFT system over other forms of hydroponics is that the plant roots are exposed to an adequate supply of water, oxygen and nutrients.
In all other forms of production, there is a conflict between the supply of these requirements, since excessive or deficient amounts of one result in an imbalance of one or both of the others.
TNF, by design, provides a system in which all three requirements for healthy plant growth can be satisfied at the same time, provided the simple concept of TNF is always remembered and practiced.
The result of these advantages is that higher yields of high-quality products are obtained over a long growing period.
One disadvantage of NFT is that it has very little buffering capacity against interruptions in flow (for example, power outages). But, in general, it is probably one of the most productive techniques.
The same design features apply to all conventional NFT systems.
aeroponics
Aeroponics is a system in which roots are kept continuously or intermittently in an environment saturated with fine droplets (a mist or spray) of nutrient solution.
The method does not require any substrate and part of the plants grow with their roots suspended in an air or deep growth chamber. These are periodically moistened with a fine mist of pulverized nutrients.
The main advantage of aeroponics is its excellent way of aerating.
Aeroponic techniques have proven commercially successful in propagation, seed germination, production of seed potatoes, production of tomatoes, and other leafy vegetables.
Since inventor Richard Stoner commercialized aeroponic technology in 1983, aeroponics has taken hold around the world as an alternative to water-intensive hydroponic systems.
The limitation of hydroponics is the fact that 1 kilogram of water can only contain 8 milligrams (0.12 g) of air, regardless of whether or not aerators are used.
Another distinct advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics is that any plant species can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be precisely controlled. The limitation of hydroponics is that certain plant species can only survive for a limited time in water before being drowned.
The advantage of aeroponics is that suspended aeroponic plants receive 100% of the available oxygen and carbon dioxide in the root zone, stems and leaves thus accelerating biomass growth and reducing rooting time.
NASA research has shown that aeroponically grown plants have 80% more dry weight biomass (essential minerals) compared to hydroponically grown plants.
Aeroponics use 65% less water than hydroponics. NASA also concluded that aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics.
Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted into soil, offering growers the ability to reduce the spread of disease and pathogens.
Did you know…?Aeroponics is also widely used in laboratory studies of plant physiology and pathology. NASA has paid special attention to aeroponic techniques, since a mist is easier to handle than a liquid in a zero – gravity environment.
Bibliography and references
-
[BOOK] Hydroponic cultivation, J Beltrano, DO Gimenez – 2015 – sedici.unlp.edu.ar
-
[PDF] Hydroponics, J Barbado – Your company in water crops. Editorial Albatross…, 2005 – academia.edu
-
[PDF] Nutrient solution management in hydroponic tomato production, AL Herrera – Latin American Terra, 1999 – redalyc.org
-
Practical manual of hydroponics, A Rodríguez Delfín, M Chang la Rosa, M Hoyos Rojas… – 2004 – sidalc.net
-
Quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) produced in hydroponics with different granulometries of tezontle, S Martín-Hernández, VM Ordaz-Chaparro… – Agrociencia, 2012 – scielo.org.mx
-
Hydroponics – Growing plants without soil. GO Huterwal – 1979 – sidalc.net
-
[BOOK] Practical manual of soilless cultivation and hydroponics, M Urrestarazu Gavilán – 2015 – books.google.com
-
[PDF] Selection of a substrate for growing strawberries in hydroponics, L López-Pérez, R Cárdenas-Navarro, P Lobit… – Revista Fitotecnia…, 2005 – redalyc.org
-
[BOOK] Basic course of Hydroponics, JHB Vargas – 2010 – books.google.com
-
[BOOK] Manual for quality seed potato production using aeroponics, V Otazú – 2010 – books.google.com
-
[PDF] Aeroponics and Potatoes, MA Nichols, New Zealand – 2015 – researchgate.net
-
Aeroponics. Development of designs for prototypes of urban agriculture, SM Salgado Ornelas, ASG Rosario Sandoval – 2017 – repository.iberopuebla.mx
-
Mechatronic design of a controlled environment for the growth of vegetables using aeroponics, HH Oscanoa Fernández – 2018 – repository.pucp.edu.pe

![Photo of Peace Lilies: [Care, Sowing, Irrigation and Substrate]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/peace-lilies-care-sowing-irrigation-and-substrate-390x220.jpg)


