Reproduction by Cuttings: What is it? How does it work? [Guide]
Reproducing plants by cuttings is a fairly common method. It basically consists of taking a portion of the plant (a stake, branch or splinter) that can take root to form a new individual.
In this article we tell youthe simplest and most efficient wayso that you achieve a correct reproduction by cuttings.
What are cuttings?
Cuttings are parts of a tree or plant, which are shed for reproductive purposes.
They are introduced into the ground to produce roots. When this happens, the plants begin to grow to form a new tree or plant, genetically identical to its parent.
This is, in a nutshell, a cloning method.
There are different ways to obtain cuttings:
- Cuttings from shoots: they are taken by making a cut at the tips of the shoots of certain plants. It is best to do them in the spring.
- Cuttings of tender branches: the ends of the plants are cut, once they have already grown, but are still green.
- Semi-lignified cuttings: These cuttings are cut in late summer, when the growth of the plants has already slowed down, and their stems are thick and strong.
- Lignified cuttings: they are taken from deciduous trees and shrubs during the dormant period, when the branch is woody. They are also known as stakes or pegs.
No products found.
What do you need to carry out reproduction by cuttings?
- Sharp knife.
- Plastic bags to collect the cuttings.
- homemade organic matter such as potting compost.
- Labels.
- Hormone Roots Powder.
For softwood cuttings, you will also need:
- Pencil
- 9 cm pots.
- Plastic bags to cover the cuttings.
- All purpose compost with 30% sharp sand added.
Points to keep in mind before carrying out planting by cuttings
Provide adequate soil
 Depending on the type of cutting (i.e. tree, shrub, succulent, cactus, …) different potting soil mixes can be used. Many commercial companies sell compost or soil specifically for growing cuttings.
Depending on the type of cutting (i.e. tree, shrub, succulent, cactus, …) different potting soil mixes can be used. Many commercial companies sell compost or soil specifically for growing cuttings.
Provide adequate air and soil moisture
Although several options can be used here, plastic is usually chosen to cover softwood and semi-hardwood cuttings.
The soil under the trays (to increase air humidity) and the soil in the tray itself are kept moist but not saturated with water (=fully saturated). The trays in which the cuttings are placed are best placed on stones to avoid capillary action (as this can keep the soil inside the trays too wet).
The soil in the trays should be kept at 85 to 95% saturation.
Automated (overhead) misting systems, barrier systems or fog systems can be used in greenhouses. A typical fogging frequency during sticking and quenching includes fogging for 5-8 seconds every 5-10 minutes over a 24 hour period.
Provide proper air and soil temperature
 Air temperature for softwood and medium hardwood cuttings is optimal around 21.1° but temperatures as low as 12.7° are acceptable. Heating the air above 23.8° stimulates the growth of pathogens.
Air temperature for softwood and medium hardwood cuttings is optimal around 21.1° but temperatures as low as 12.7° are acceptable. Heating the air above 23.8° stimulates the growth of pathogens.
Ventilating (manually or through or via automatic window openers) the greenhouse or cold frame can lower the air temperature. Automatic thermostat systems can also be used in greenhouses to keep heat at a specific temperature.
Bottom (floor) heating tends to be ideal for root initiation, as the temperature of the growing medium is best kept at 20-22°.
Provide the right amount of sunlight
While the cuttings need to be kept warm and some amount of light provided, they need to be kept out of direct sunlight. Some ways to achieve this include the use of semi-white plastic retractable shade curtains.
Optimum light levels are around 120 to 200 µmol/m²s in the first stage.
Once callus has formed and roots begin to form and absorb water (stage 3: root development phase), light intensity levels can be gradually increased (up to 200 to 800 µmol/m²s)
Most propagators find that 5 to 10 moles per day (ie, observed with a daily integral light sensor) will result in consistent rooting and growth.
Make reproduction by cuttings step by step
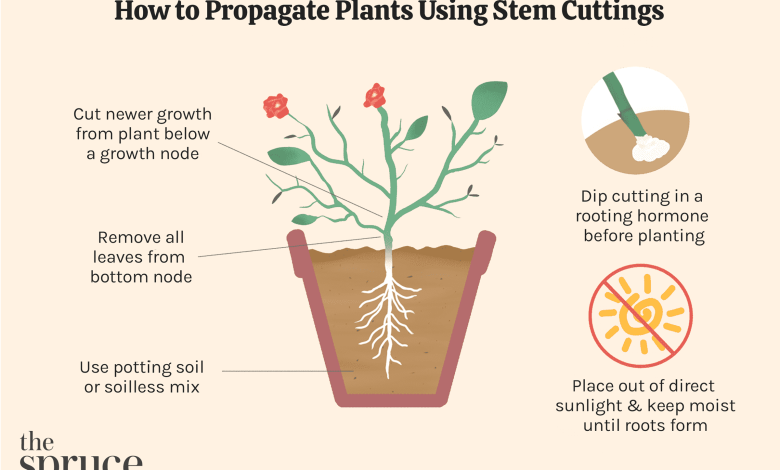
1. Carry out the cutting of a branch
Making sure that said cut is as close as possible to the main trunk.
The ideal is to cut branches that are 1 year old, this ensures that they are strong parts and have what is necessary to develop. Each cutting should be between 10 and 15 cm long.
2. Cut off the leaves and side shoots
They prevent the growth of new roots.
3. Make a diagonal cut
A diagonal cut from 30 to 45 degrees to the part that will be buried. This will facilitate root development.
4. Scrape off the top layer of bark near the tip
In doing so,be very careful not to damage the branch. If you are planting herbaceous cuttings, not woody, you can skip this step
Methods for reproducing cuttings
Now you mustchoose one of the following methodsto get the cutting to start taking root.
method one
- In a container —or black plastic bag— filled with compost, add water until it acquires a muddy consistency.
- When you have achieved this, bury the branch in this mixture to a depth that is equal to or greater than half its length. If your branch is 10 centimeters, bury it 5 centimeters.
- If you chose a bag, tie it perfectly around the stem, trying not to leave space for the branch to move.
- Now, you must keep the humidity level always constant. From this moment on, the substrate containing the branch should no longer look like mud, but it should always be moist .
- Try not to disturb the earth[/su_highlight].
method two
- Place substrate in a pot large enough for the cutting to develop comfortably. Sand and perlite make an excellent substrate due to their porosity.
- Remember that the pot must have good drainage to prevent the soil from flooding.
- Bury the cutting in the substrate, up to half its length.
- Water abundantly, but avoid puddles. The cutting requires plenty of water to form its roots, but if you water it excessively you will prevent this from happening.
- To conserve moisture, so necessary for the cutting to form roots, you can cover the top of the pot with a plastic bag, preventing it from touching the tips of the cutting. Make sure to seal it well with plastic tape.
- Keep the pot in a well-lit area, but out of direct sunlight.
method three
- Place the cutting in a bottle of water for two weeks. After a week you will see how the roots begin to sprout.
- Once the roots have started to develop, remove the plant from the water and place it in a pot with sand or perlite. Do not forget that the pot must have a good drainage system.
- Keep the pot in a dark area for 3 days to prevent the plant from spending energy on photosynthesis.
- Next, place your plant in a well-lit area and water it every 2-3 days. Remember that irrigation should be abundant water, avoiding the formation of puddles.
Some recommendations:
- Protect the cutting from direct sunlight and keep it moist at all times, preventing the soil from waterlogging.
- After 2-3 weeks, roots will have formed at the bottom of the cutting. Carefully run your fingers under the cutting to see if roots have started to develop. If they haven’t already, you’ll need to take another cutting and start the process over.
- The success rate will depend on numerous factors, such as the species of the tree, the climatic conditions, the season, etc.
- In summer, you can try small amounts of organic fertilizer to help the root system develop.
- Remember that while most cuttings can be separated and put into large pots after a year, some species may need a little more time before the cuttings are ready for transplanting.
 The organic family garden (CROPS)
The organic family garden (CROPS)
- Well, Mariano (Author)
€9.49 View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-31 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
What species and plants reproduce by cuttings?
On our page you can learn more about the reproduction by cuttings of some plants and trees:
- Rose cuttings.
- Rosal cuttings in potato.
- Olive cuttings .
- Rosemary cuttings.
- Lavender cuttings.
- Jasmine cuttings.
- Ivy cuttings .
- Geranium cuttings.
- Mandarin cuttings.
- Cypress cuttings.
- Carnation cuttings.
- Dracaena marginata cuttings.
- Carnation cuttings.
- Camellia cuttings .
- Cactus cuttings.
- Bougainvillea cuttings.
- Bamboo cuttings.
- Sweet potato cuttings.
- Boxwood cuttings.
- Artichoke cuttings .
- Begonia cuttings.
- Tree cuttings.
- Almond cuttings.
- Aloe vera cuttings.
- Oleander cuttings .
- Holly cuttings.
There are many types of cuttings.
This is important to know, as certain species respond better to certain planting methods. For example, large plants with thick woody branches develop roots better if you put them in the ground.
Instead, small herbs like basil, mint, and rosemary can be grown in water.
We can distinguish the cuttings as follows:
- Herbaceous stem cuttings: They are obtained from non-woody plants, when they are still growing.
- Softwood cuttings: These are obtained from woody evergreens or deciduous plants. It is best to cut them in early summer, before the stems have begun to harden.
- Semi-hard wood cuttings: Like the previous one, they are obtained from woody evergreens or deciduous plants, except that the cutting is done at the end of summer, after the wood has hardened a bit.
- Hardwood cuttings: Obtained in winter, when the wood is dormant.
Some of the species that are propagated effectively by cuttings are:
Among the fruit trees, we find:
- the almond tree
- pistachio
- the lemon tree
- the apple tree,
- the cacti,
- the cherry tree,
- the handle,
- Papaya and many more.

Among the most common herbaceous plants to grow from cuttings are:
- The rosemary
- The Mint
- basil
- The tomatoes
- the roses
- common ivy
- aglaonema
- The yellow dogwood and the flowering dogwood.
When to reproduce by cuttings?
cuttings in spring
Spring is the time for softwood cuttings of many plants, perennials, shrubs, and vines.
These young cuttings are eager to take root, but are also at high risk of drying out without proper care.
cuttings in summer
Summer is the time for semi-ripe cuttings, where the base of the shoots are hardening (ripening) but the tips are still brittle.
cuttings in autumn
By fall, plant growth is mature. Fall and winter hardwood cuttings can be slow to root but more stable than young, tender cuttings, allowing them to overwinter in a cool greenhouse or under some protection outside.
Cuttings are a very useful method of reproduction for plants that produce few seeds and also for those that are very difficult to grow from seed.
Among its main advantages we can mention:
- They are easy to grow.
- It allows to shorten cultivation time.
- More than one plant can be grown.
One drawback is that mostcuttings are taken only in spring and early summer, which greatly limits cultivation times.
CULIVERS Organic Worm Humus. Plant food. 100% Natural Organic Fertilizer. Soil Restorative (Tomatoes and Vegetables, 20 Kg)
- Worm humus of the highest quality 100% organic.
- Organic matter rich in microorganisms. (1 gram of humus contains about 2 billion microorganisms) The…
- Stimulator of the root development of plants and their absorption of nutrients. It has a neutral pH that makes it ideal for…
- Ecoforce worm humus increases the quality and production of crops. It has a low C/N ratio, allowing…
€19.90 View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-31 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images
 PAPILLON Urban Garden 60x80x80cm, 8093100
PAPILLON Urban Garden 60x80x80cm, 8093100
- Urban garden
- Measurements: 60x80x80cm
- Made of treated wood
- 24 cm deep drawer and tnt fabric
€168.13 View on Amazon Prices with VAT without transport
Last updated on 2022-07-31 / Affiliate Links / Affiliate API Images



![Photo of Lavender Care: [Soil, Humidity, Pruning and Problems]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/lavender-care-soil-humidity-pruning-and-problems-390x220.jpg)
