Sow Beetroot: How to do it in [12 Steps + Images]
Did you know that the most common use of beets is as a vegetable, but it is also widely used as a source of sugar and to make dyes?
 Or…that beets can cause some people ‘s urine and feces to turn a reddish color?
Or…that beets can cause some people ‘s urine and feces to turn a reddish color?
This is because these people lack the enzyme that metabolizes said pigment in the intestine.
If you are interested inlearn how to plant beets in your gardento be able to cook them in an ecological way and without insecticides, maybe this guide will help you…
are you coming with me?
Important points for Sowing Beetroot:
- When? End of April to mid June.
- Where? The temperate, sunny and humid climates. It needs between 6-8 hours of sunlight.

- Harvest time? Approximately 3 months. From the end of July.
- How do we prepare the land? Neutral, moist and fertile land without much acidity. The proper pH is between 6.5 and 7.0.
- How do we water? It requires moderate irrigation, avoiding waterlogging.
- How do we harvest? 8 weeks after sowing and reach an approximate diameter of 8 cm
- Favorable associations? Garlic, onions, escarole, spinach, cabbage, celery and lettuce.
- Unfavorable associations? Beans, peas and legumes in general.
- Plagues and diseases? The aphid, beet fly, slugs, beet slug, downy mildew and rust.
T he beet or betabel is a plant belonging to the Chenopodiaceae family, which includes some 1,400 plant species.
Other vegetables such as spinach, arugula and chard are also included in this family.
Its botanical name is Beta vulgaris and it is one of the most important crops for obtaining sugar.
When to sow beets? The dates
We want to plant beets from the end of April to the middle of June.
Harvest: At the end of July.
Where to plant beets? The temperature and the light
Mild, sunny, and humid climates contribute to higher beet production.
Is verylight intensity is importantsince it allows the proper exercise of photosynthesis and determines the importance of sugar production.
It is recommended that they be between 4 and 6 hours under intense light and the rest of the day under moderate shade.
They are very sensitive to cold, so beet should not be planted until the frosts are over.
How do we water beets? Moisture and risks
Although it is not very demanding in terms of irrigation, water is a factor that influences the quality of the beet.
It requires moderate watering, avoiding waterlogging.
The volume of water necessary for germination is 20 l/m2, but if it has not received water again within 15-20 days, the sowing may be lost.
The first days, before the first outbreaks, watering should be abundant, trying to keep the soil moist to the touch.
Once the first shoots have emerged, it will only be necessary to water every two weeks when it does not rain.
Overwatering causes beets to produce more leaves and fewer roots, while underwatering causes woody roots.
How do we prepare the land? Substrate and nutrients
To grow, it needs soils that are rich in nutrients, mainly potassium and phosphorous.
They prefer neutral, moist, fertile soil without much acidity.
 The soil should be loose and not have a lot of clay or sand.
The soil should be loose and not have a lot of clay or sand.
Preferably, the soil should be deep, with a high water retention capacity, and good aeration.
Clay, sandy, limestone and dry soils are not suitable for this crop. Since they have a lower water retention capacity or, on the contrary, they easily become waterlogged.
However, they can tolerate clay soil if it is loosened on top and well-decomposed organic matter is added in excess.
The proper pH is between 6.5 and 7.0..
How to plant beets step by step
- Clear the ground.It removes weeds, stones, remains of previous crops and all kinds of residues to ensure that the beets receive the correct amount of nutrients.
- Make sure the substrate has good drainage.Check that puddles do not occur very easily.
- Till the soil to prepare it.The soil needs to be tilled to the depth of a hand shovel. You can use a rake to loosen the soil. If you have heavy soil, it is best to prepare it in late fall. If the soil is light, you can prepare it in early spring.
- Moisten the soil before planting beets.This reduces the risk of expelling the seeds by the force of the water.
- Fertilize the soil.Spread some compost on the soil to improve the overall quality before you start sowing the seeds. Mix it with the soil to a depth between 10 and 15 cm
- Plant the seeds 3 cm deep, in shallow furrows. Place 2 to 3 seeds in each hole, leaving 20 to 25 cm between each hole.
- Try to leave a separation of between 40 and 60 cm between each row. Cover the seeds with soil, pressing down so that it adheres well to the seed.
- Remember that the beet seed must be in complete contact with the soil, so a firm substrate is required for the root to hold firmly to the ground.
- Water abundantly after sowing beets, always keeping the soil moist, but avoiding puddles. When watering, be careful not to wet the leaves, as the roots become more fibrous and the beet loses its sugary taste.
- A drip irrigation is the most recommended, since it also prevents diseases.
- Ten days after sowing, the seeds will germinate.Reduce watering to once a week or every two weeks, depending on the conditions in the region where you live.
- After five weeks, when the plants have 4 or 5 leaves, you should select the healthiest and strongest seedlings, in case more than one seed has germinated in each hole. To do this, do not pull the weak one, as you can damage the leaves.
- A simple pruning at ground level is sufficient. Those that we have withdrawn, we can consume them in salads.
- Fertilize your plants. Add a thin layer of compost rich in phosphorous and potassium. If you consider it necessary, you can hill them. Add soil next to the shoots to prevent the appearance of weeds. The movement of earth must be carried out with the greatest care so as not to damage the beets, since they grow very close to the surface.
- Protect your plants from birds.You can cover them to protect them from birds and other predatory species.
- Check your plants regularly to avoid pests and diseases.
Harvesting and harvesting of beets
We can harvest them from July.
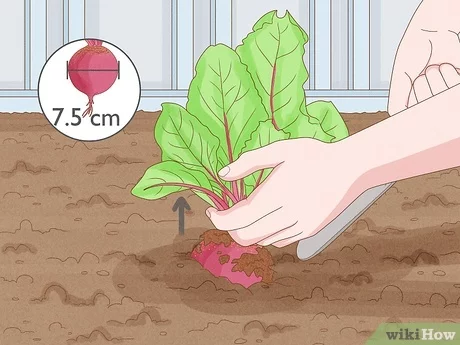
They are ready for harvest when they are 8 weeks old after sowing and reach an approximate diameter of 8 cm, since if they are too large they will not have as much flavor.
To harvest them, hold the top and wiggle the root with a tool.
Cut the roots and leaves half a centimeter above the root.
If the leaves are healthy you can use them to make Compost.
Leave the freshly harvested beets to dry until evening, after removing all the soil.
Beet Favorable Associations
They associate well with garlic and onion, as these, among other things, help repel slugs.
Other good combinations are: escarole, spinach, cabbage, celery and lettuce.
Planting beets with beans and other legumes is not recommended.
Common pests and diseases
aphids
They weaken the plant. The aphid that most attacks beet crops is the black aphid.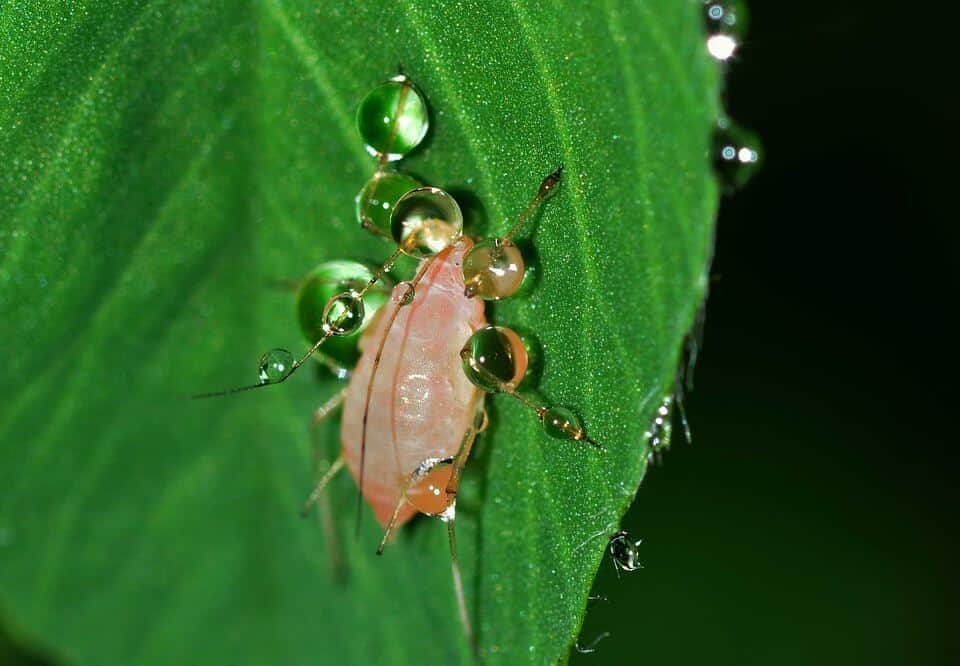
The aphid can endanger the crop in a very short time.
To combat them, potassium soap can be applied to the underside of the plants.
If the plague persists or is very abundant, after cleaning the leaves with soap, we will apply neem extract, which will act as an insecticide.
beet fly
Whose larvae pierce the leaves.
It does not usually cause serious damage, although in favorable weather conditions the larvae reproduce quickly and can endanger the crop. Potassium soap can be applied to the underside of plants and Neem extract.
beet sylph
They are very small beetles.
For its control, the plant can be washed with water and nicotine.
nematodes
The nematodes penetrate the root tissue, suck out the cell juice and lay their eggs in the root cortex.
They are treated with steam sterilization and solarization, which involves raising the temperature of the soil by placing a clear plastic sheet on top of the soil for a minimum of 30 days.
Rust
This disease usually appears in late summer.
Its symptoms are easy to recognize, as pustules appear on the leaves, 1 mm in diameter and brown in color.
For its control, the use of resistant varieties and the excess of nitrogenous fertilizers is recommended.
To prevent its appearance, look for and eliminate the Berberis vulgaris bush in the nearby cultivation areas.
Mildew
To combat it, it is recommended to eliminate weeds and crop residues, as well as to avoid excess humidity by promoting adequate ventilation of the plant.
Affected leaves should be removed. Horsetail extract can also be applied.



![Photo of Quince Tree: [Care, Planting, Irrigation, Substrate and Pests]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/quince-tree-care-planting-irrigation-substrate-and-pests-390x220.jpg)