Thrips: What are they? How to identify them? How to fight them?

T he Thysanoptera (better known as Trips) are small insects between 1 and 3 mm that basically feed on fungi and vegetables. They are so tiny that it is usually necessary to use a magnifying glass to observe them in detail.
What are thrips?
Thrips are insects of various colors, with an elongated shape and whose saliva exerts considerable damage on the structure of plants. They reproduce through eggs that later become larvae. In the adult phase they develop wings with some type of fur.
The main colors in which they can present are yellow, brown and gray.
It is a species that develops in hot environments, so summer provides the ideal conditions for its appearance and multiplication.
How do thrips reproduce?
Thrips reproduce in a simple process that can take a few weeks, from when the egg is generated until the larva hatches .
For this reason, they can spawn a large number of larvae in a short time.
Among the plant species that are most affected by the thrips plague are: onions, tomatoes and cucumbers.
Finally, it is necessary to know that thrips are not a single family but have different types and are attracted to specific types of plants.
The shape of the thrips
They have a cylindrical and elongated shape, and a very small head. Some have folding wings, although they are not great flyers and prefer to move by jumping.
 They have a mouth apparatus that allows them, at the same time, to scrape the surface of the plant and suck the sap to feed.
They have a mouth apparatus that allows them, at the same time, to scrape the surface of the plant and suck the sap to feed.
Their life cycle varies from one month to one year, depending on conditions, and they produce on average up to 12 generations per year, since their biological cycle is relatively short.
They reach maturity 15 days after birth and before that they have to go through six stages of development: egg, first larval stage, second larval stage, pronymph, nymph and adult.
The first three and the last occur on the leaves and it is during these that the greatest damage to crops occurs.
Damage caused by thrips
The damage caused by thrips can be divided into two: direct damage and indirect damage.
direct damage
The direct damages are those that are produced by their feeding. When thrips reach maturity they colonize crops, laying their eggs within the plant tissues of leaves, fruits and flowers.
When larvae and adults feed, they leave whitish spots, especially on the underside of the leaves, which then turn black.
 The symptoms are seen when the deterioration has spread widely over the leaves or when it occurs in the fruits, since the spots are more evident on them.
The symptoms are seen when the deterioration has spread widely over the leaves or when it occurs in the fruits, since the spots are more evident on them.
This occurs due to the toxins contained in the saliva of these insects and that are secreted by the vegetable surface to facilitate their feeding.
This causes the death of the plant or the detriment of the quality of the fruits, since they discolor or present deformities.
Likewise, damaged flowers can become deformed or interrupt their cycle.
indirect damage
As for indirect damage, this is usually even more dangerous, since thrips can act as vectors of more than 20 viruses, among which Tospoviruses stand out, which include some of the most harmful viruses, such as the sun tan virus tomatoes.
How can we identify the thrips that attack our crops?
In order to identify thrips and know that they are affecting our crops, it is necessary to refer to their feeding process.
- The first consumption they make is based on pollen when, in adulthood, they can change from one plant to another.
- But when they are still larvae, their main source of nutrition is in the internal part of the plant ‘s tissues.
- Through their sucking mouth and saliva, they gain access to the internal liquid and consume it. This, not surprisingly, causes a weakening of the blade.
- The problem is that it not only does this function with the leaves, but also with the entire structure of the plant, including the shoots and fruits.
- As the internal vegetable content is sucked out, the leaves begin to lose their characteristic green coloration and this becomes a very visible symptom.
- In the same structure of the discolored leaf, black dots also appear that correspond to the debris of the larva.
- Likewise, yellow or white dots may appear that belong to the damage caused to the surface of the plant material in question.
- If the pest spreads much further, it could transmit diseases to the plants, causing them to shrivel to death.
- Above all, the larvae secrete moderately toxic substances when they notice the presence of other thrips. It’s kind of a defense mechanism.
What crops are affected?
More than nine species of thrips are known to directly affect crops or plants of agronomic importance.
They mainly affect vegetable crops: cucumbers, watermelons, melons, tomatoes, peppers, pumpkins, courgettes and onions.
How do we combat thrips?
Thrips are insects that are attracted to flowers, especially those that are blue and yellow.
One form of preventive control is to place traps or containers of these colors with sticky surfaces so that they adhere.
Another form of prevention is to place meshes around our orchard and clean up weeds and debris.
Biological control can be done through its natural enemies.
Thrips have several natural predators such as certain varieties of mites, especially the Amblyseius barkeri and the Orius bug. To combat them, in addition, ecological alternatives can be used, such as potassium soap and, in extreme cases, natural insecticides such as neem extract.
Thrips represent a group of insects whose main purpose is to attack certain types of crops.
They can become very dangerous as they carry a virus that causes an incurable disease.
The good news is that there are alternatives to prevent their appearance and eradicate them if they occur.
What products do we use to eliminate thrips?
The products to eliminate thrips are varied and will be chosen based on the particular condition of each crop.
glue traps
There are sticky traps, such as those used for flies inside houses, that can be placed around plants to catch them.
These are yellow or blue, colors that are attractive to them and to which they end up approaching and ending up stuck.
potassium soap
Potassium soap also offers very good results, and being ecological, it does not cause damage to the crop.
This also gives security so that we consume what is grown with confidence.
For its application, it will suffice to make a mixture of soap with water and spray it on the entire plant.
It is important to attend to all areas, including the underside of the leaves, to avoid leaving any thrips around.
neem oil
To enhance the effect, in case of a very strong plague, neem oil will help a lot and it is also ecological.
This oil will be placed after the potassium soap and as it is a powerful insecticide, it will cause a very positive effect.
In fact, it is a very valuable agricultural product to have at home when you have plantations because it is effective against many pests.
Finally, it will be necessary to clean the molasses that has remained as remains of the thrips attack.
Prevention of thrips
- For flower thrips on gladioli: Mix one tablespoon of Lysol household cleaner with one gallon of water. Submerge the gladiolus corms in the liquid and plant them while they are moist to prevent thrips.
- You can plant various flowers to attract beneficial insects that are natural predators of thrips. Some good predators are pirate bugs, lacewings, and ladybugs. Learn more about how to attract these predators.
- For onion and western flower thrips, try releasing tiny pirate bugs or the predatory mite Amblyseius cucumeris.
- Reflective mulches can help hide your plants from thrips.
- If there is a very large thrips problem in your area, some plants have resistant varieties.
- Try not to overfertilize the plants, as this can lead to more thrips damage.
What natural predators can we use against thrips?
lady beetles
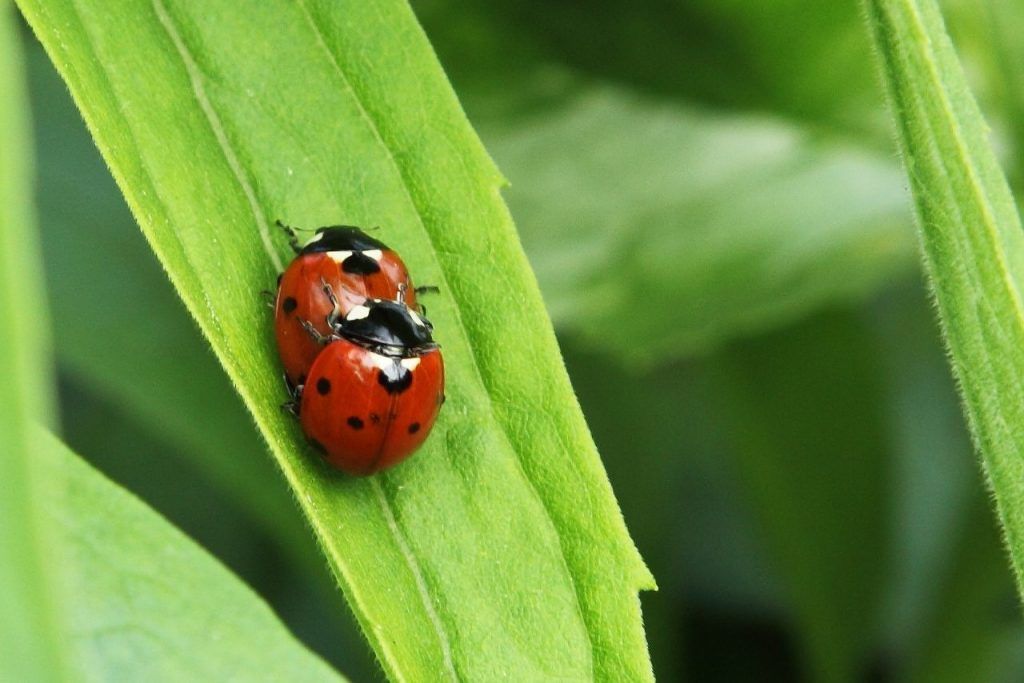

Adult beetles (ladybugs) do not eat as many aphids as in their larval stage, so many people are disappointed by the lack of control they see after releasing purchased live ladybugs into their garden.
There needs to be a large enough aphid population for the ladybugs to feed enough to mate and lay eggs, since it is the larvae that eat the most aphids.
Ladybug larvae look nothing like the adults we know, so their identification is important (see photo). Live ladybugs can be purchased online or at your local nursery.
green lacewings
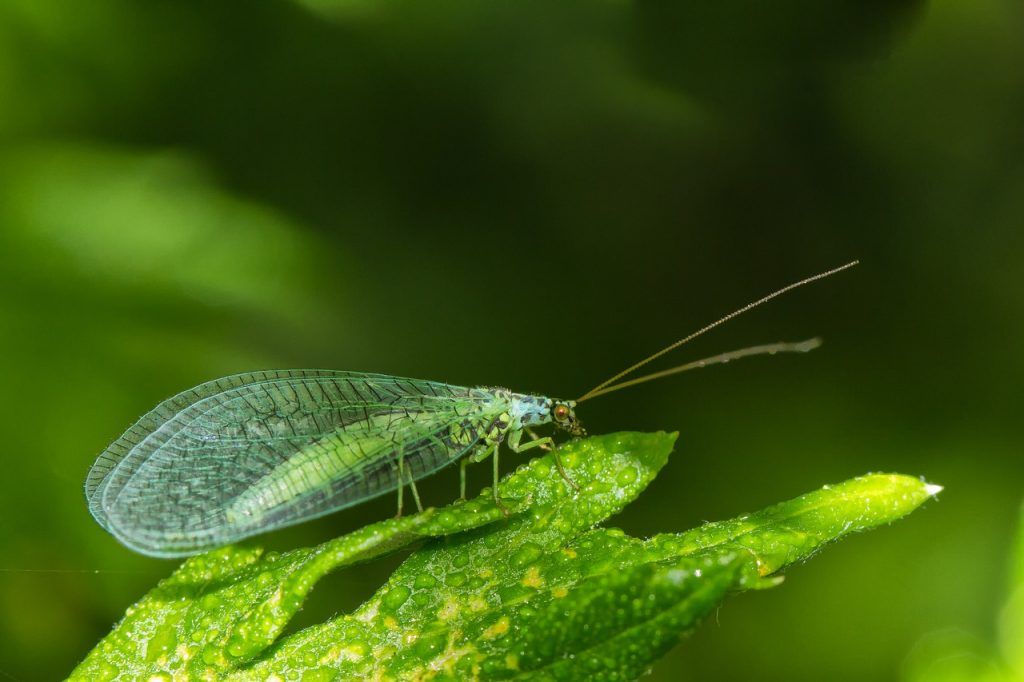

Like ladybugs, green lacewing larvae are responsible for controlling thrips. Green lacewing eggs can also be purchased online and sometimes at a local nursery.
birds
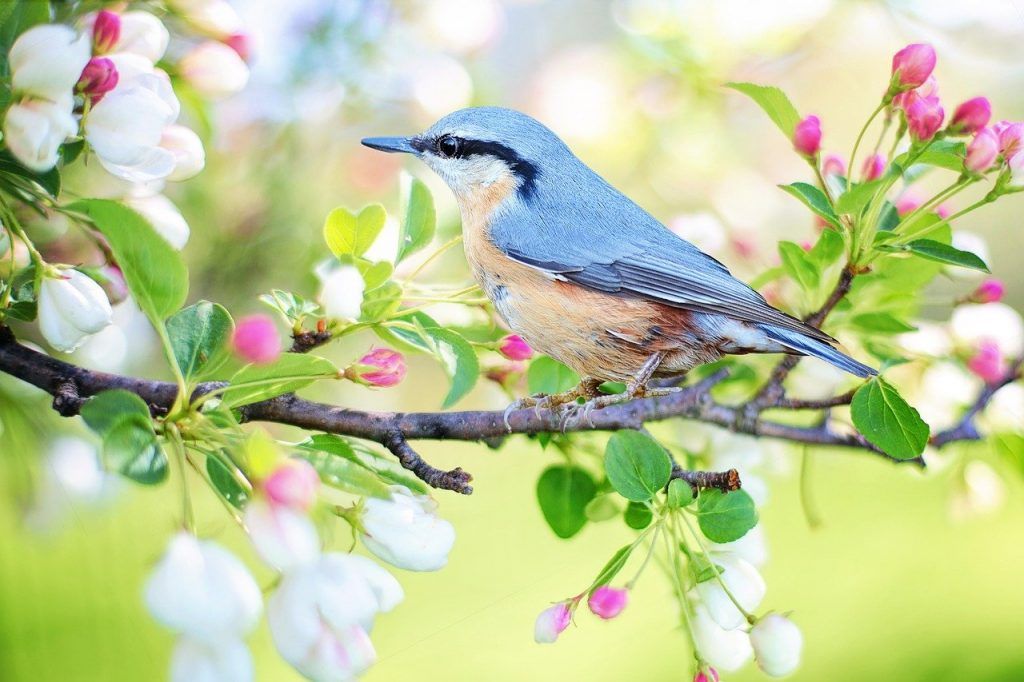

Provide houses for insect-eating birds like wrens and great tits to live in, and they will reward you by helping to keep the insect population under control. Grow small trees and bushes where they can take shelter and build their own nests.

![Photo of Oleander Cuttings: [Concept, Season, Rooting and Planting]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/oleander-cuttings-concept-season-rooting-and-planting-390x220.png)
![Photo of Wormwood: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/wormwood-cultivation-irrigation-care-pests-and-diseases-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Bond of Love or Spider Plant: [Care, Planting, Irrigation and Substrate]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/bond-of-love-or-spider-plant-care-planting-irrigation-and-substrate-390x220.jpg)