How to Plant Lilies in Your Garden or Orchard: [Complete Guide]
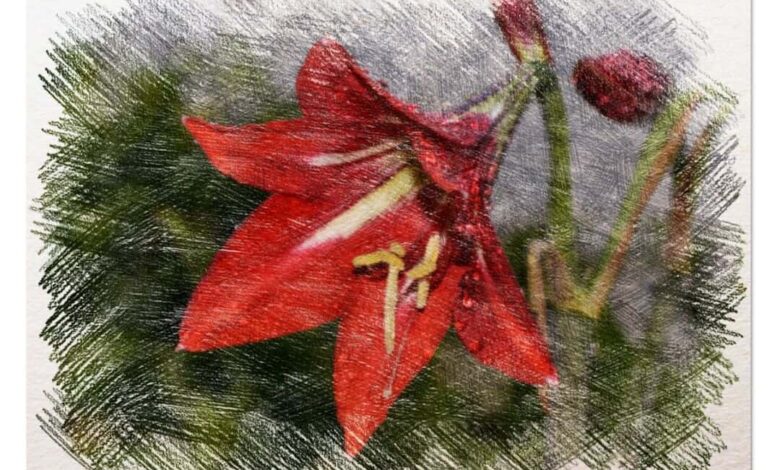

The Lilies ( lillium ) , also called lilies , are flowering plants that have two main types: those with white florets forming a tube and the hybrids in the shape of a calyx.
They are used as ornamental plants in pots or bouquets. They come from Asia and Turkey. The largest producer of bulbs is the Netherlands, as with tulips .
- When? It depends on when you want to harvest the lily bulbs. They are sown 5 months before harvest. Northern Hemisphere (months of August and October) and Southern Hemisphere (months of March and May).

- Where? A semi-shady place. Although it needs some light. Ideally, you should receive 4-6 hours a day. It does not withstand frost and temperatures that are too high.
- Growing time? About 5 months from sowing.
- Optical temperature? Between 14ºC and 19ºC.
- Type of soil? It supports most soils well, although it avoids clayey ones. Try that the pH is 6 and 7 or even 5.5.
- How do we water? We recommend drip irrigation .
- How often do we water? You have to be generous, especially in summer . Water daily in high temperatures. Rest of the year, in case there is no rain, every 3 days.
- What favorable associations do they have? Other ornamental plants, although none in particular.
- Plagues and diseases? Aphids, mites, thrips, ants, snails and nematodes.
Types of lilies
The main species of lilies are: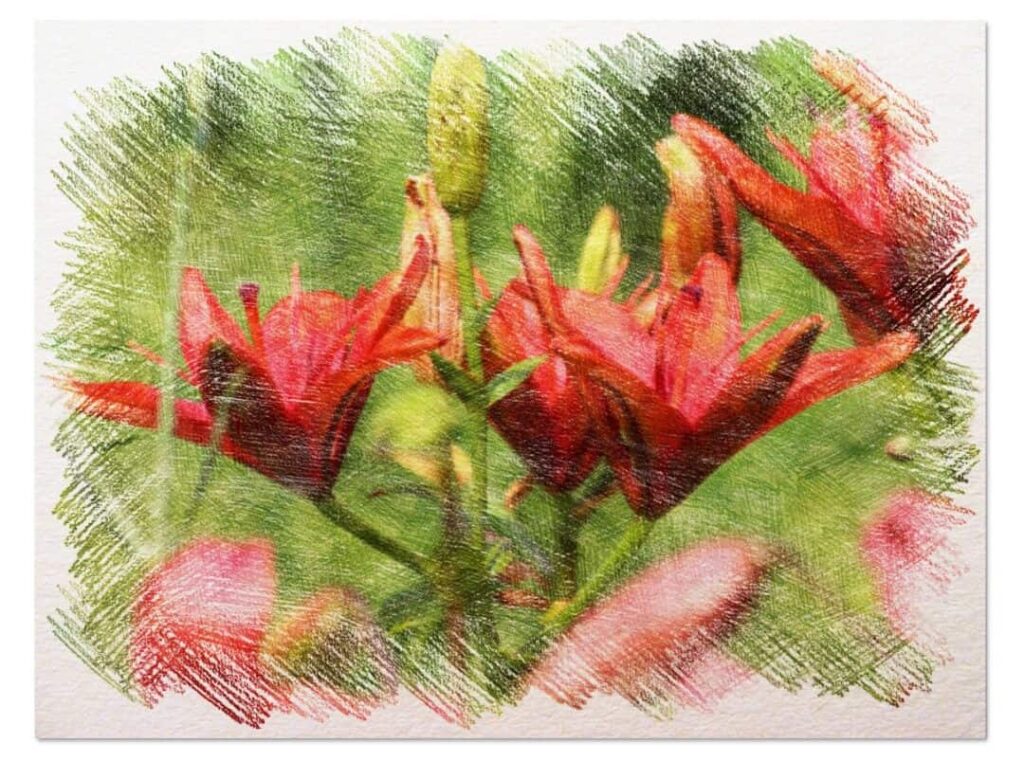
- Longiflorum Group : Or also known as the classic lilies, they have three to five flowers facing outwards, forming a kind of tube.
- Oriental Group : These flowers have a bit more fragrance apart from being star-shaped. It can be of different colors and the leaves are also oriented upwards.
- Asian Group : This spice has a little more flowers (5-9). They have no odor and are shaped like a chalice.
The lilies have a vertical stem , usually short, although it can reach a meter in height and covered by leaves that can be separated and planted in a propagation medium for possible reproduction .
Its roots contain a very important hormonal function so they must be preserved when the plant bulb is stored .
On the other hand, the fruit is a container of seeds with a very complex germination pattern , which is why they are not usually used for this purpose . For the multiplication of lilies its bulb is usually used.
When to sow lily? The dates
 You can plant your lily bulbs about five months before harvest.
You can plant your lily bulbs about five months before harvest.
This varies depending on the hemisphere ; in the north are harvested between the months of August and October Meanwhile in the south are harvested between the months of March and May.
If you want to preserve the bulbs you have to mix them with peat so that they are completely dry and pack them in completely hermetic and permeable bags.
Afterwards, keep them in a dry place without light. You can also choose to freeze them at temperatures between 1 and -2 ° C.
You can store them for a period a little longer than twelve months , although try to consider that the longer the storage period , the shorter the subsequent growth cycle.
Where to plant lily? Light and temperature
If you are going to sow it outdoors, make sure that it always has a good substrate and that it is compact so that the stems of the plant are strong and in general there is good drainage, especially in hot seasons.
As to the light the lilies prefer the semi-shade.
However, very little presence of light causes pale leaves to appear , weak stems and cut flowers have a shorter life in the vase. On the other hand, excess light, especially in summer, can produce short poles.
How to prepare the land? PH and soil type
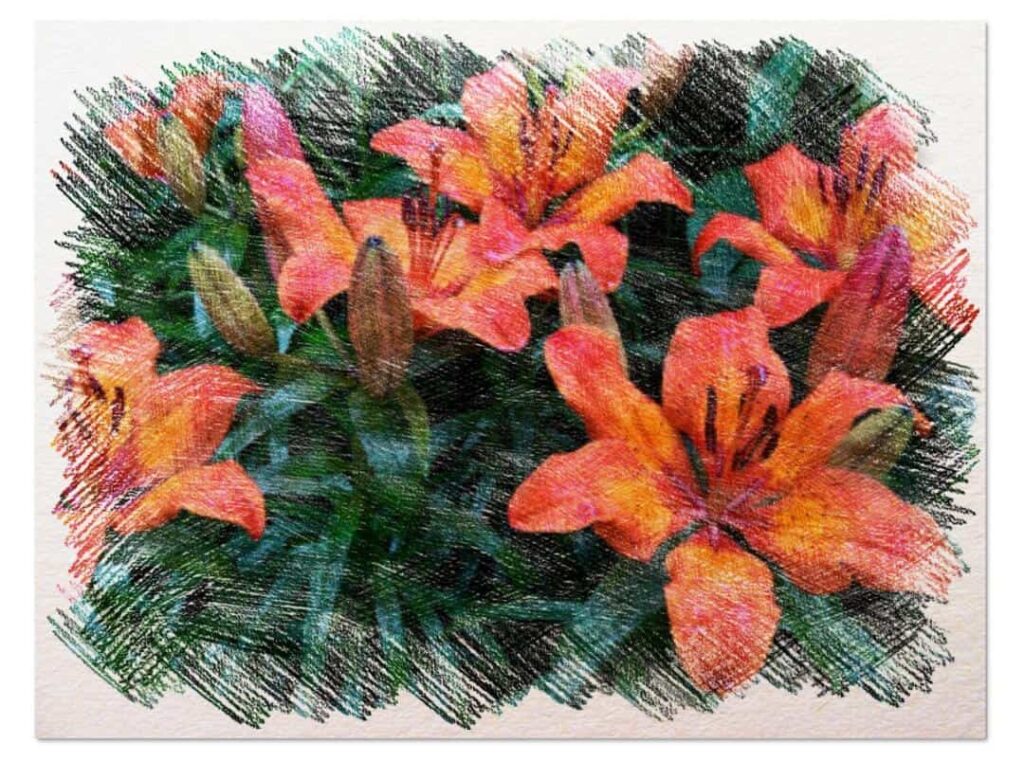 You can sow the lilies in all types of soils, provided they possess a good structure and correct permeability during the entire culture period , especially for the top layer, where are the bulbs , which is where the roots develop.
You can sow the lilies in all types of soils, provided they possess a good structure and correct permeability during the entire culture period , especially for the top layer, where are the bulbs , which is where the roots develop.
If you can, avoid clay soils.
In case you have no other alternative, you can mix them with substrate such as humus so that moisture can be retained and the entry of oxygen can be assimilated.
This is an essential element in the soil to achieve a healthy and abundant root system of the bulbs.
It is very important to maintain an adequate pH . As for the pH levels, try to keep it between 6 and 7 or even 5.5 . Remember that an excess or deficiency of pH can make the plant more susceptible to contracting pests or diseases .
How do we water?
It is important to continuously water daylilies, especially in the early stages of life . If you have doubts about how much you have watered your plant, remember that it is better that the soil is a little dry than that it becomes flooded.
Excess water causes less perspiration of the crop , which means a reduction in the transport of minerals causing the plant to have deficiencies including flower development.
If your plant is too flooded, give it more ventilation and drier substrates such as peat or coconut fiber.
Sowing lily step by step
- Once you have acquired the bulbs, try to plant them as soon as possible on moist soil.
- Then make a hole in the ground the width of your bulb and bury it so that it is a little less than half above the surface. That is, it has to look like an iceberg.
- Make sure the roots are well buried and the apex is completely vertical.
- Then put some substrate around it to level it out and don’t crush the soil.
- If you have bought the frozen bulbs it is very important that you do not defrost them in the sun , but rather that you leave them in temperatures of approximately 10 ° C.
- If you thaw it at higher temperatures, you will cause a loss of quality.
- The bulbs that you have thawed can never be frozen again .
- Let them thaw for approximately two to three weeks and then sow the same as the process already described.
What favorable associations does it have?
Daylilies are typically potted individually , but you can place them alongside other ornamental plants to give your garden or orchard a beautiful look .
What pests and diseases affect you?
The main pests of the crop are aphids, thrips, mites and nematodes:
Aphids
Aphids suck the sap from the plant reducing its strength. They are located in the apical part of the plant, in tender shoots and flower buds. We recommend spraying with neem extract or potassium soap .
Trips
Thrips develop on the scales of planted and stored bulbs, producing a brown coloration and wrinkling of the scales.
Preventive measures against aphids and thrips include : use of insect screens in greenhouses and the elimination of weeds.
Mites
Mites attack the scales on stored bulbs that turn reddish-brown in color . These wounds can lead to bulb rot.
Nematodes
Nematodes cause brown streaks on leaves, bulging and cleft stems , and on bulbs, brown- spotted scales that look wrinkled and hard. They can be controlled by disinfecting the bulb with steam, as well as pruning the plants.
What secondary pests but that cause serious damage if they are present are the snails, slugs , pruning ants , soil drills and rodents.



![Photo of Nigella Sativa: [Sowing, Care, Watering, Pests and Characteristics]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/nigella_sativa_1591303434-390x220.jpg)