White spider on plants: What is it, damage it causes and how to eliminate this pest
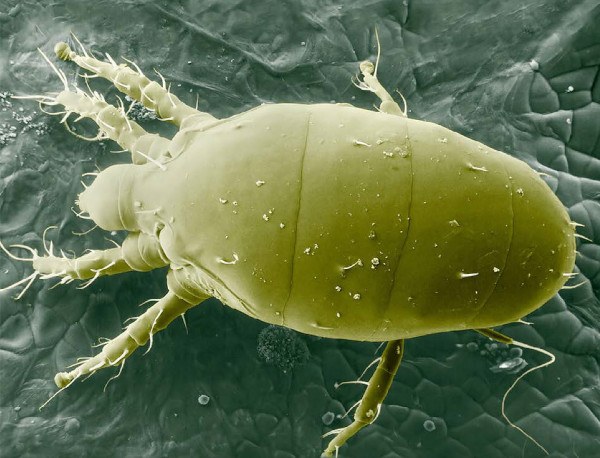
Today I come to tell you a little about a mite that we may find in one of our crops this season. I’m talking about Polyphagotarsonemus latus, better known as the white spider or white spider . Throughout this article I will introduce you to this bug that can damage some of our plants.

What are white spiders like?
In reality, precisely speaking, it is not a spider. We are talking about a species of mite that belongs to the Acarina order and the Tarsonemidae family . That is why it is more correct to use the term «white mite» or white spider mite.
In Latin America it is also known as the chile mite, broad mite, tropical mite or yellow mite .
In the life cycle of this mite four stages are distinguished: egg, larva, pupa and adult .
The females lay the eggs in priceless holes in the surface of the leaf or fruit. The eggs are firmly attached to these surfaces. The white spider prefers for its development to be located on the underside of the leaves , where it finds the optimal climatic conditions of humidity and shade, and necessary food.
The larvae have 6 legs (3 pairs) and the adults 8 legs (4 pairs). In adults, there are important differences between males and females.
How are the females
Female mites are about 0.2mm long and oval in shape. Their bodies are swollen in profile and transparent, light yellow to pale brown or green, and waxy with a faint mid-stripe that forks near the rear end of the body.
The fourth pair of legs of the female is reduced to a thin and long hair that extends from the tip.
How are the males
Males are small (0.11 mm) and have relatively long legs. They are similar in color and lack the median stripe found in
females.
The fourth pair of legs of the males end in strong claws that are used to pick up the female nymph and place it at right angles to that of the male for transport and subsequent mating.
How are the eggs
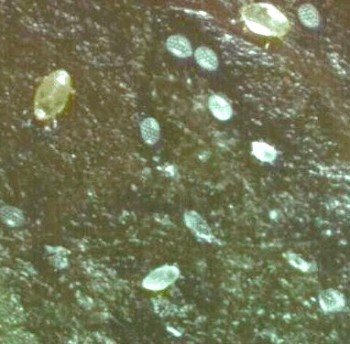
The eggs of the broad mites are elliptical, shiny and colorless, about 0.08 mm long, and are covered by 30-40 white eggs scattered on the upper surface of each egg.
The distinctive egg is a key identifying feature that should be used to confirm that plant damage is being caused by this type of mite. When the eggs hatch, larvae emerge that are approximately 0.05-0.1 mm long and due to the tiny ridges found on their skin appear white, but then turn transparent.
How are the larvae
The larvae have three pairs of legs. After 2-3 days, the larvae develop into a quiescent «pupa» that appears as a clear, immobile swollen body that is pointed at both ends.
How are the pupae
The «pupa» is about 0.08 mm long. Once they molt from this stage they become adults, having four pairs of legs.
Multiplication and longevity
In conditions of high temperatures, humidity and a shady environment, it multiplies very quickly . At 25º C the development of a generation of these mites (from egg to egg) lasts between four and five days.
The longevity of a female is about ten days under normal conditions. During this period it lays about 50 eggs. Unfertilized females produce only male offspring, while females are produced from fertilized eggs.
In winter, the reproduction rate and the activity of the mites decrease. For its survival, this mite depends on living plant material, so it cannot hibernate in parts of the greenhouse structure, as spider mites do.
What are the Symptoms and damages of the white spider infestation?
It is a species that especially affects crops grown in greenhouses, but it can also attack crops outdoors or indoors. This spider or white mite attacks both ornamental and horticultural crops.
The white spider or white spider mite affects different species in our garden in a polyphagous way. Around the world, Polyphagotarsonemus latus grows preferentially in humid areas with warm temperatures.
This mite is an important pest in the tropics throughout the year. In the subtropics it is an important pest during
the summer and fall if the weather conditions are hot and humid.
And in temperate zones it is a pest during the summer months, but under the right environmental conditions of heat and humidity it can cause severe damage.
About 50 plants that it attacks (host plants) are recognized, among others are the pepper, the raspberry, the tea plant, the citrus fruit, the tobacco and the potato. In the greenhouse, they cause damage mainly to peppers, aubergines, tomatoes, cucumbers and ornamental crops such as azalea or begonia .
It also causes very important damage to Cannabis.
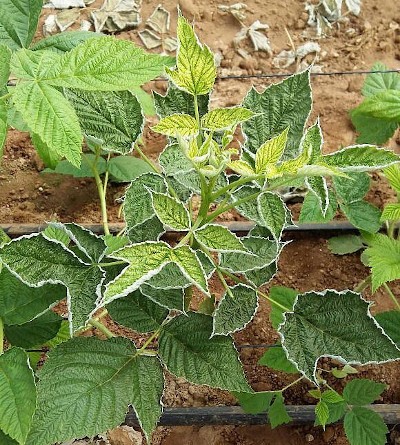

Damages caused by Polyphagotarsonemus latus consists mainly of deformation of leaves and stems.
The mites prefer young tissues in development, such as leaves and young flowers. The white mite sucks the sap and produces deformations and corky scars .
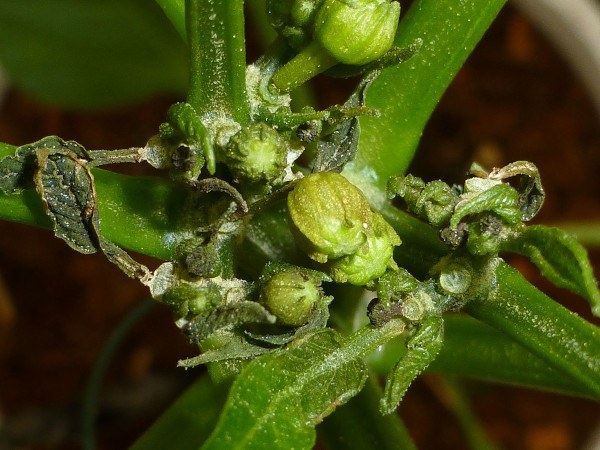

In leaves, suction occurs on the petiole part, which causes the leaf to roll up . The apical part of the plant is deformed, and brown discolorations appear locally . Left unchecked, it can lead to plant death.
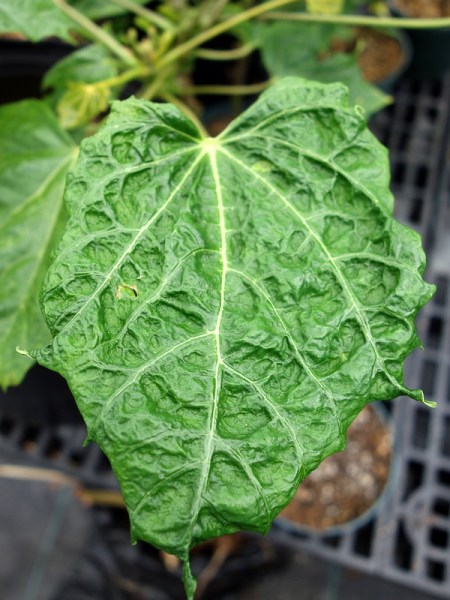

In the case of tomato , a tan discoloration occurs on the stem, terminal shoots and underside of young leaves. The leaves of the shoots dry out, so that the upper parts of the plant appear burned, with the stems wrinkled and discolored. The leaves are bulging and have protruding ribs.
In potatoes , it forms blackish spots with an oily appearance on the underside of the young leaves, acquiring a reddish color, and the leaf bends irregularly at the edges.
The same thing happens in the pepper plant , where it also prevents flowering, or makes the flowers fall.
How to control the white spider?
Preventive cultural measures
To control the white spider infestation, it is important to use cultural measures such as eliminating the remains affected by the mite.
Keeping crops in good health helps control all species of mites. It is recommended to keep the area around the crop free of weeds or wild plants that can act as hosts, which will reduce the sources of infestation.
In seasonal crops, such as tomatoes or peppers, once the harvest is over, crop residues must be destroyed to prevent them from becoming a breeding ground for spider mites.
It is also recommended to prune the affected plants, removing the leaves and stems that are attacked.
Other advice to follow is to avoid depositing dust on the leaves. The fact that there is dust deposited on the leaves facilitates the attack by mites.
In the tomato it has been seen that it is important that the plants are well watered and nourished. It is recommended to use organic fertilizers such as mulch. Water stress (lack of water) favors the appearance of mites.
Nor should go over with the subscriber, because an excess of fertilizer also favors the development of this pest.
Control methods in organic farming
In organic farming, to combat this pest, it is recommended to use sulfur and neem oil. Both work well. Commercial products are available in both cases.
If you want to make a homemade acaricide, you can use hot chili (chilli or pepper), garlic and liquid soap to wash the dishes . There are scientific studies where it has been proven and it has been seen that this mixture gives good results to control this white mite (5).
The chili contains capsaicin, which is an irritating substance for insects and mites, which causes them to flee the place, stop feeding and die (5).
Garlic contains certain sulfur compounds, which affect the nervous system of insects and mites, acting as an irritant and repellent (5).
The soap helps the product adhere better to the stems and leaves of the plants. And also, when it comes into contact with the fatty tissues of the mites, it causes them to die of dehydration (5).
How to make a homemade acaricide
Ingredients
- 100 grams of chili
- 28 grams of dish soap
- a whole head of garlic (10 or 12 cloves)
- 1 liter of water
Preparation
Grind it all together and let it rest for 24 hours. Once it has settled, filter it and dissolve it in a container with 20 liters of water.
If you want to make less quantity, reduce the proportions.
Chemical control
If conventional agriculture is carried out, acaricidal active ingredients such as Abamectin, Tau-Fluvalinate or Cypermethrin can be used.
These active ingredients are usually found in the acaricides that are sold in stores.
Biologic control
Biological control is allowed in both organic and conventional agriculture.
In this case, the white spider have natural predators, that is, there are other animals that eat them. In this case, they are insects and other mites, which can be used to combat this pest.
They are sold in envelopes, which are put on the plants. The effects are greater in closed environments such as greenhouses, although they can also be done freely outdoors.
The main species used are:
- Amblyseius swirskii
- Eretmocerus mundus
- Eretmocerus eremicus
- Encarsia Formosa
Here you have the link to an article about white bugs and white bugs on earth in case it also helps you.

![Photo of Plant Orchids in Your Garden: [8 Steps + Images]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/plant-orchids-in-your-garden-8-steps-images-390x220.jpg)


